Abstract
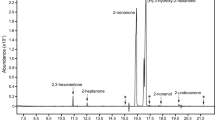
Observations of wasp behavior indicate that male beewolves,Philanthus basilaris andP. bicinctus apply a “marking pheromone” to the leaves and stems of plants within their territories. We now provide direct evidence for the presence of volatile chemicals in the paired mandibular glands of the males, provide preliminary identification of these volatiles, and show that all of the volatile chemicals in the mandibular glands are present on freshly marked plant surfaces but are absent from unmarked plants. Pyrazines, which have been reported in other species of aculeate wasps including the EuropeanPhilanthus triangulum, were not found inP. basilaris orP. bicinctus.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abley, P., McQuillan, F.J., Minnikin, D.E., Kusamran, K., Maskens, K., andPolgar, N. 1970. Location of olefinic links in long-chain esters by methoxymercuration-demercuration followed by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry.Chem. Commun. 1970:348–349.
Alcock, J. 1975. Territorial behavior by males ofPhilanthus multimaculatus (Hymenoptera: Sphecidae) with a review of territoriality in male sphecids.Anim. Behav. 23:889–895.
Bergström, G., andLöfqvist, J. 1971.Camponotus ligniperda Latr.—a model for the composite volatile secretions of the Dufour's gland in formicine ants, pp. 195–223,in A.S. Tahori (ed.).Chemical Releasers in Insects. Gordon and Breach, New York.
Blum, M.S. 1981. Chemical Defenses of Arthropods. Academic Press, New York. 562 pp.
Blum, M.S., Jones, T.H., Overal, W.L., Fales, H.M., Schmidt, J.O. andBlum, N.A. 1983. Exocrine chemistry of the monotypic ant genus Gigantiops.Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 74B:15–16.
Borg-Karlson, A.-K., andTengö, J. 1980. Pyrazines as marking volatiles in philanthine and nyssonine wasps (Hymenoptera: Sphecidae).J. Chem. Ecol. 6:827–835.
Budzikiewicz, H., Djerassi, C., andWilliams, D.H. 1967. Interpretation of Mass Spectra of Organic Compounds. Holden-Day, San Francisco. 690 pp.
Duffield, R.S., Shamim, M., Wheeler, J.W., andMenke, A.S. 1981. Alkylpyrazines in the mandibular gland secretions ofAmmophila wasps (Hymenoptera: Sphecidae).Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 70B:317–318.
Evans, H.E. 1983. Nesting and territorial behavior ofPhilanthus barbatus Smith (Hymenoptera: Sphecidae).J. Kans. Entomol. Soc. 55:571–576.
Gwynne, D.T. 1978. Male territoriality in the bumblebee wolf,Philanthus bicinctus (Mickel) (Hymenoptera: Sphecidae): Observations on the behavior of individual males.Z. Tierpsychol. 47:89–103.
Gwynne, D.T. 1980. Female defense polygyny in the bumblebee wolf,Philanthus bicinctus (Hymenoptera: Sphecidae).Behav. Ecol. Sociobiol. 7:213–225.
Heffetz, A., andBatra, S.W.T. 1980. Chemistry of the cephalic secretions of eumenid wasps.Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 65B:455–456.
McDaniel, C.A., andHoward, R.W. 1985. Mass spectral determination of aldehydes, ketones, and carboxylic acids using 1,1-dimethylhydrazine.J. Chem. Ecol. 11:303–310.
O'Neill, K.M. 1979. Territorial behavior in males ofPhilanthus psyche (Hymenoptera: Sphecidae).Psyche 86:19–43.
O'Neill, K.M. 1981. Male mating strategies and body size in three species of beewolves (Hymenoptera: Sphecidae,Philanthus). Dissertation, Colorado State University.
O'Neill, K.M. 1983. The significance of body size in territorial interactions of male beewolves (Hymenoptera: Sphecidae,Philanthus).Anim. Behav. 31:404–411.
O'Neill, K.M. 1984. Territoriality, body size, and spacing in males of the beewolfPhilanthus basilaris (Hymenoptera: Sphecidae).Behaviour 86:295–321.
Quennedey, A., Brule, G., Rigaud, J., Dubois, P., andBrossut, R. 1973. La glande frontale des soldats deSchedorhinotermes putorius (Isoptera): Analyse chimique et fonctionment.Insect Biochem. 3:67–74.
Raw, A. 1975. Territoriality and scent marking byCentris males (Hymenoptera, Anthophoridae) in Jamaica.Behaviour 54:311–321.
Wilson, E.O., andRegnier, F.E. 1971. The evolution of the alarm-defense system in the formicine ants.Am. Nat. 105:279–289.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schmidt, J.O., O'Neill, K.M., Fales, H.M. et al. Volatiles from mandibular glands of male beewolves (Hymenoptera: Sphecidae,Philanthus) and their possible roles. J Chem Ecol 11, 895–901 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01012076
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01012076