Abstract
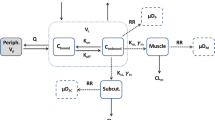
The nonlinear tissue distribution of quinidine in rats was investigated by a physiologically based pharmacokinetic model. Serum protein binding of quinidine showed a nonlinearity over thein vivo plasma concentration range. The blood-to-plasma concentration ratio (C b/C p) of quinidine also showed a concentration dependence. The steady-state volume of distribution (V ss) determined over the plasma concentration range from 0.5 to 10 μg/ml was 6.0 ±0.45 L/kg. The tissue-to-plasma partition coefficient (Kp) of muscle, skin, liver, lung, and gastrointestinal tract (GI) showed a nonlinearity over thein vivo plasma concentration range of quinidine, suggesting saturable tissue binding. The concentration of quinidine in several tissues and plasma was predicted by a physiologically based pharmacokinetic model usingin vitro plasma protein binding and theC b/C p of quinidine. The tissue binding parameters were estimated fromin vivo Kp values. The predicted concentration curves of quinidine in each tissue and in plasma showed good agreement with the observed values.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
H. R. Ochs, D. J. Greenblatt, and E. Woo. Clinical pharmacokinetics of quinidine.Clin. Pharmacokin. 5:150–168 (1980).
G. Bianchetti, J. L. Elghozi, R. Gomeni, P. Meyer, and P. L. Morselli. Kinetics of distribution of dl-propranolol in various organs and discrete brain areas of the rat.J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 214:682–687 (1980).
M. H. Bickel, R. Stegmann, and C. di Francesco. On the roles of uptake, binding, and metabolism in the liver cells of drugs displaying first-pass effects. InLiver, Proceedings International Gstaad Symposium 2nd, 1975, pp. 130–134.
M. Mintun, K. J. Himmelstein, R. L. Schroder, M. Gibaldi, and D. D. Shen. Tissue distribution kinetics of tetraethylammonium ion in the rat.J. Pharmacokin. Biopharm. 8:373–409 (1980).
H. Iven. The pharmacokinetics and organ distribution of ajmaline and quinidine in the mouse.Naunyn-Schmiderberg's Arch. Pharmacol. 298:43–50 (1977).
D. Fremstad, S. Jacobsen, and P. K. M. Lunde. Influence of serum protein binding on the pharmacokinetics of quinidine in normal and anuric rats.Acta Pharmacol. Toxicol. 41:161–176 (1977).
T. W. Guentert and S. Øie. Effect of plasma protein binding on quinidine kinetics in the rabbit.J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 215:165–171 (1980).
T. W. Guentert, J. D. Huang, and S. Øie. Disposition of quinidine in the rabbit.J. Pharm. Sci. 71:812–815 (1982).
C. T. Ueda, B. Ballard, and M. Rowland. Concentration-time effects on quinidine disposition kinetics in rhesus monkeys.J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 200:459–468 (1977).
D. J. Greenblatt, H. J. Pfeifer, H. R. Ochs, K. Franke, D. S. MacLaughlin, T. W. Smith, and J. Koch-Weser. Pharmacokinetics of quinidine in humans after intravenous, intramuscular and oral administration.J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 202:365–378 (1977).
H. R. Ochs, D. J. Greenblatt, E. Woo, K. Franke, and T. W. Smith. Effect of propranolol on pharmacokinetics and acute electrocardiographic changes following intravenous quinidine in humans.Pharmacology 17:301–306 (1978).
D. Fremstad, O. G. Nilsen, L. Storstein, J. Amlie, and S. Jacobsen. Pharmacokinetics of quinidine related to plasma protein binding in man.Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 15:187–192 (1979).
H. R. Ochs, E. Grube, D. J. Greenblatt, E. Woo, and G. Bodem. Intravenous quinidine: Pharmacokinetic properties and effects on left ventricular performance in humans.Am. Heart J. 99:468–475 (1980).
N. H. G. Holford, P. E. Coates, T. W. Guentert, S. Riegelman, and L. B. Sheiner. The effect of quinidine and its metabolites on the electrocardiogram and systolic time intervals: Concentration-effect relationships.Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 11:187–195 (1981).
R. L. Dedrick and K. B. Bischoff. Pharmacokinetics in application of the artificial kidney.Chem. Eng. Prog. Symp. Ser. 64:32–44 (1968).
K. J. Himmelstein and R. J. Lutz. A review of the applications of physiologically based pharmacokinetic modeling.J. Pharmacokin. Biopharm. 7:127–145 (1979).
H. S. G. Chen and J. F. Gross. Physiologically based pharmacokinetic models for anticancer drugs (general review).Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2:85–94 (1979).
N. Benowitz, R. P. Forsyth, K. L. Melmon, and M. Rowland. Lidocaine disposition kinetics in monkey and man I. Prediction by a perfusion model.Clin. Pharm. Ther. 16:87–98 (1974).
N. Benowitz, R. P. Forsyth, K. L. Melmon, and M. Rowland. Lidocaine disposition kinetics in monkey and man II. Effects of hemorrhage and sympathomimetic drug administration.Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 16:99–109 (1974).
L. I. Harrison and M. Gibaldi. Physiologically based pharmacokinetic model for digoxin disposition in dogs and its preliminary application to humans.J. Pharm. Sci. 66:1679–1683 (1977).
Library Program (D2/TC/RKM) of the University of Tokyo Computer Center, Tokyo, Japan, 1980.
R. L. Dedrick. Animal scale-up.J. Pharmacokin. Biopharm. 1:435–461 (1973).
K. B. Bischoff, R. L. Dedrick, D. S. Zaharko, and J. A. Longstreth. Methotrexate pharmacokinetics.J. Pharm. Sci. 60:1128–1133 (1971).
Y. Sasaki and H. N. Wagner. Measurement of the distribution of cardiac output in unanesthetized rats.J. Appl. Physiol. 30:879–884 (1971).
R. L. Dedrick, D. S. Zaharko, and R. J. Lutz. Transport and binding of methotrexatein vivo.J. Pharm. Sci. 62:882–890 (1973).
R. J. Lutz, R. L. Dedrick, H. B. Matthews, T. E. Eling, and M. W. Anderson. A preliminary pharmacokinetic model for several chlorinated biphenyls in the rat.Drug Metab. Dispos. 5:386–396 (1977).
T. Nakagawa, Y. Koyanagi, and H. Togawa. SALS, A Computer Program for Statistical Analysis with Least Squares Fitting, Library Program of the University of Tokyo Computer Center, Tokyo, Japan, 1978.
O. G. Nilsen, L. Storstein, and S. Jacobsen. Effect of heparin and fatty acids on the binding of quinidine and warfarin in plasma.Biochem. Pharmacol. 26:229–235 (1977).
H. S. G. Chen and J. F. Gross. Estimation of tissue-to-plasma partition coefficients used in physiological pharmacokinetic models.J. Pharmacokin. Biopharm. 7:117–125 (1979).
Y. Igari, Y. Sugiyama, S. Awazu, and M. Hanano. Comparative physiologically based pharmacokinetics of hexobarbital, phenobarbital, and thiopental in the rat.J. Pharmacokin. Biopharm. 10:53–75 (1982).
O. Sugita, Y. Sawada, Y. Sugiyama, T. Iga, and M. Hanano. Prediction of drug-drug interaction fromin vitro plasma protein binding and metabolism. A study of tolbutamidesulfonamides interactions in rats.Biochem. Pharmacol. 30:3347–3354 (1981).
O. Sugita, Y. Sawada, Y. Sugiyama, T. Iga, and M. Hanano. Physiologically based pharmacokinetics of drug-drug interaction: A study of tolbutamide-sulfonamide interaction in rats.J. Pharmacokin. Biopharm. 10:297–316 (1982).
J. H. Lin, Y. Sugiyama, S. Awazu, and M. Hanano. Physiological pharmacokinetics of ethoxybenzamide based on biochemical data obtainedin vitro as well as on physiological data.J. Pharmacokin. Biopharm. 10:649–661 (1982).
J. H. Lin, Y. Sugiyama, S. Awazu, and M. Hanano. Effect of product inhibition on elimination kinetics of ethoxybenzamide in rabbits: Analysis by physiological pharmacokinetic model.Drug Metab. Dispos. 12:253–256 (1984).
Y. Igari, Y. Sugiyama, Y. Sawada, T. Iga, and M. Hanano. Prediction of diazepam disposition in the rat and man by a physiologically based pharmacokinetic model.J. Pharmacokin. Biopharm. 11:577–593 (1983).
I. E. Hughes and K. F. Ilett. The distribution of quinidine in human blood.Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2:521–525 (1975).
R. L. Dedrick, D. S. Zaharko, and R. J. Lutz. Transport and binding of methotrexatein vivo.J. Pharm. Sci. 62:882–890 (1973).
H. Harashima, Y. Sugiyama, Y. Sawada, T. Iga, and M. Hanano. Comparison betweenin-vivo andin-vitro tissue-to-plasma unbound concentration ratios (K p,f) of quinidine in rats.J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 36:340–342 (1984).
T. Yoshikawa, Y. Sugiyama, Y. Sawada, T. Iga, and M. Hanano. Effect of pregnancy on tissue distribution of salicylate in rats.Drug Metab. Dispos. 12:500–505 (1984).
B. Fichtl, B. Bondy, and H. Kurz. Binding of drugs to muscle tissue: Dependence on drug concentration and lipid content of tissue.J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 215:248–253 (1980).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This study was supported by a grant-in-aid for Scientific Research provided by the Ministry of Education, Science and Culture of Japan.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Harashima, H., Sawada, Y., Sugiyama, Y. et al. Analysis of nonlinear tissue distribution of quinidine in rats by physiologically based pharmacokinetics. Journal of Pharmacokinetics and Biopharmaceutics 13, 425–440 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01061478
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01061478