Abstract
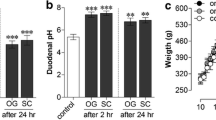
The influence of dietary protein deficiency on pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of furosemide was investigated after iv bolus (1 mg/100 g) and oral (2 mg/100 g) administration of furosemide to male Sprague-Dawley rats fed on a 23% (control) or a 5% (protein-calorie malnutrition: PCM) protein diet ad lib.for 4 weeks. After iv administration, the mean values of CL R , V ss, and the percentages of dose excreted in 8-hr urine as furosemide were increased 81, 31, and 61%, respectively, in PCM rats when compared with those in control rats, however, CL NR was 54% decreased in PCM rats. The decreased CLNR in PCM rats suggested the significantly decreased nonrenal metabolism of furosemide. The urine volume per g kidney after iv administration was not significantly different between the two groups of rats although the amount of furosemide excreted in 8-hr urine per g kidney increased significantly in PCM rats. The diuretic, natriuretic, kaluretic, and chloruretic efficiencies reduced significantly in PCM rats after iv administration. After oral administration, the extent of bioavailability increased considerably from 27.6% in control rats to 47.0% in PCM rats, probably as a result of decreased gastrointestinal and hepatic first-pass metabolism. This was supported by a tissue homogenate study; the amount of furosemide remaining per g tissue after 30-min incubation of 50 μg of furosemide with the 9000 × gsupernatant fraction of stomach (42.4 vs. 47.9 μg) and liver (41.4 vs. 45.9 μg) homogenates increased significantly in PCM rats. No significant differences in CLR and t1/2 were found between the control and the PCM rats after oral administration. The 24-hr urine volume and the amount of sodium excreted in 24-hr urine per g kidney increased significantly in PCM rats, and this might be due to a significantly increased amount of furosemide reaching the kidney excreted in urine per g kidney.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
K. Krishnaswamy. Drug metabolism and pharmacokinetics in malnutrition.Clin. Pharm-acokin. 3:216–240(1978).
N. Buchanan. Drug kinetics in protein energy malnutrition.S. Afr. Med. J. 53:327–330 (1978).
D. Jung. Pharmacokinetics of theophylline in protein-calorie malnutrition.Biopharm. Drug Dispos. 6:291–299 (1985).
D. Jung. Disposition of acetaminophen in protein-calorie malnutrition.J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 232:178–182 (1985).
M. G. Lee and W. L. Chiou. Evaluation of potential causes for the incomplete bioavailability of furosemide: Gastric first-pass metabolism.J. Pharmacokin. Biopharm. 11:623–640 (1983).
D. E. Smith, E. T. Lin, and L. Z. Benet. Absorption and disposition of furosemide in healthy volunteers, measured with a metabolite-specific assay.Drug Metab. Dispos. 8:337–342 (1980).
D. C. Brater, R. Seiwell, S. Andreasen, A. Burdette, G. J. Dekmer, and P. Chennavasin. Absorption and disposition of furosemide in congestive heart failure.Kidney Int. 22:171–176 (1982).
T. P. Green and B. L. Mirkin. Furosemide disposition in normal and proteinuric rats: Urinary drug-protein binding as a determinant of drug effect.J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 218:122–127 (1981).
B. Beermann, E. Dalén, B. Lindström, and A. Rosén. On the fate of furosemide in man.Em. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 9:57–61 (1975).
L. Z. Benet. Pharmacokinetics/pharmacodynamics of furosemide in man: A review.J. Pharmacokin. Biopharm. 7:1–27 (1979).
M. Hammarlund-Udenaes and L. Z. Benet. Furosemide pharmacokinetics and pharmaco-dynamics in health and disease—An update.J. Pharmacokin. Biopharm. 17:1–46 (1989).
J. Patrick. Death during recovery from severe malnutrition and its possible relationship to sodium pump activity in the leucocyte.Br. Med. J. 23:1051–1054 (1977).
A. Young and R. J. Levin. Diarrhoea of famine and malnutrition-investigations using a rat model, 2-ileal hypersecretion induced by starvation.Gut 31:162–169 (1990).
M. G. Lee, M. L. Chen, and W. L. Chiou. Pharmacokinetics of drugs in blood II: Unusual distribution and storage effect of furosemide.Res. Commun. Chem. Pathol. Pharmacol. 34:17–23 (1981).
W. G. Shin, M. G. Lee, M. H. Lee, and N. D. Kim. Factors influencing the protein binding of vancomycin.Biopharm. Drug Dispos. 12:637–646 (1991).
S. Øie and T. W. Guentert. Comparison of equilibrium times in dialysis experiments using spiked plasma or spiked buffer.J. Pharm. Sci. 71:127–128 (1982).
C. L. Litterst, E. G. Mimnaugh, R. I. Reagan, and T. E. Gram. Comparison of in vitro drug metabolism by lung, liver and kidney of several common laboratory species.Drug Metab. Dispos. 3:259–265 (1975).
O. H. Lowry, N. J. Rosebrough, A. L. Farr, and R. J. Randall. Protein measurement with the folin phenol reagent.J. Biol. Chem. 173:265–275 (1951).
T. Omura and R. Sato. The carbon monoxide-binding pigment of liver microsomes I. Evidence for its hemoprotein nature.J. Biol. Chem. 239:2370–2378 (1964).
M. L. Chen, G. Lam, M. G. Lee, and W. L. Chiou. Arterial and venous blood sampling in pharmacokinetic study: Griseofulvin.J. Pharm. Sci. 71:1386–1389 (1982).
W. L. Chiou. Critical evaluation of potential error in pharmacokinetic studies using the linear trapezoidal rule method for the calculation of the area under the plasma level-time curve.J. Pharmacokin. Biopharm. 6:539–546 (1978).
M. Gibaldi and D. Perrier.Pharmacokinetics, 2nd ed., Marcel Dekker, New York, 1982.
W. L. Chiou, C. Y. Lui, and G. Lam. Plasma area method in relative bioavailability evaluation of drugs with changing biological half-lives.J. Pharm. Sci. 70:109–112 (1981).
S. Øie and D. Jung. Bioavailability under variable renal clearance conditions.J. Pharm. Sci. 68:127–128 (1979).
W. L. Chiou. New calculation method for mean apparent drug volume of distribution and application to rationale dosage regimens.J. Pharm. Sci. 68:1067–1069 (1979).
D. Varma. Influence of dietary protein on the anti-inflammatory and ulcerogenic effects and on the pharmacokinetics of phenylbutazone in rats.J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 211:338–344 (1979).
J. C. Merrill and T. M. Bray. The effect of dietary protein quantity on the activity of UDP-glucuronyltransferase and its physiological significance in drug metabolism.Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 60:1556–1561 (1982).
M. M. Hammarlund and L. K. Paalzow. Dose-dependent pharmacokinetics of furose-mide in the rat.Biopharm. Drug Dispos. 3:345–359 (1982).
D. E. Smith and L. Z. Benet. Relationship between urinary excretion rate, steady-state plasma levels and diuretic response of furosemide in the rat.Pharmacology 19:301–306 (1979).
W. L. Chiou. A new simple approach to study the effect of changes in urine flow and/ or urine pH on renal clearance and its applications.Int. J. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. Toxicol. 24:519–527 (1986).
M. G. Lee. Absorption and disposition of furosemide. Ph.D. thesis, University of Illinois at Chicago, 1982.
D. E. Smith and L. Z. Benet. Plasma protein binding of furosemide in kidney transplant patients.J. Pharmacokin. Biopharm. 10:663–674 (1982).
L. L. Boles Ponto and R. D. Schoenwald. Furosemide (Frusemide). A pharmacokinetic/ pharmacodynamic review (Part I and II).Clin. Pharmacokin. 18:381–408, 460–471 (1990).
Y. M. Choi, S. H. Kim, and M. G. Lee. Effects of phenobarbital and 3-methylchol-anthrene pretreatment on the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of furosemide in rats.J. Pharm. Sci. 80:638–642 (1991).
S. Inui, M. Yamamoto, H. Nakae, and S. Asada. Dose dependency of loop diuretics, furosemide and piretanide in the rat.Yakugaku Zasshi 102:1053–1060 (1982).
S. Seno, S. M. Shaw, and J. E. Christian. Distribution and urinary excretion of furosemide in rat.J. Pharm. Sci. 58:935–938 (1969).
V. S. Chungi, L. W. Dittert, and R. B. Smith. Gastrointestinal sites of furosemide absorption in rats.Int. J. Pharm. 4:27–38 (1979).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This work was supported in part by a research grant from the Korea Science and Engineering Foundation, 1990–1992.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, S.H., Choi, Y.M. & Lee, M.G. Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of furosemide in protein-calorie malnutrition. Journal of Pharmacokinetics and Biopharmaceutics 21, 1–17 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01061772
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01061772