Abstract
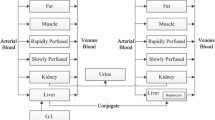
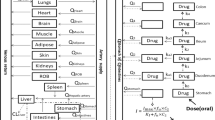
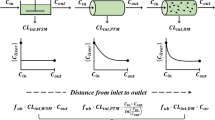
Based on the concept of physiological pharmacokinetics, the hepatic first-pass metabolism and plasma levels following intravenous and oral administration of barbiturates in the rabbit was predicted based on the relationships between principle kinetic parameters and lipophilicity (chloroform-water partition coefficient). Good log-log linear relationships between kinetic parameters and lipophilicity were obtained for the seven barbiturates examined. The values of correlation coefficient were improved slightly by using the corrected values for partition coefficients of nonionic molecules in the cases of principle parameters such as drug-protein and drug-blood cell affinity, intrinsic hepatic clearance, and unbound volume of distribution. There was also a good linear relationship between absorption rate constant (mean absorption time) and lipophilicity. The mean hepatic transit time was negligible for the most lipophilic drug (hexobarbital) examined; this suggests that the mean absorption time for these barbiturates does reflect the absorption process. The available fraction in relation to hepatic first-pass metabolism was well predicted from the lipophilicity by both well-stirred and parallel-tube models, and the difference in the values predicted by both models was minimal. There were good relationships between predicted and observed values for plasma levels after intravenous and oral administration, except for two (cyclobarbital and phenobarbital) of the seven drugs used. The great difference between predicted and observed values for these two drugs was considered due to substituent effects in liver metabolism.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. K. Seydel, D. Trettin, and H. P. Cordes. Quantitative structure-pharmacokinetic relationships derived on antibacterial sulfonamides in rats and its comparison to quantitative structure-activity relationships.J. Med. Chem. 23:607–613 (1980).
C. Hansch. A quantitative approach to biochemical structure-activity relationships.Accounts Chem. Res. 2:232–239 (1969).
C. Hansch and T. Fujita.ρ-σ-χ analysis. A method for the correlation of biological activity and chemical structure.J. Am. Chem. Soc. 86:1616–1626 (1964).
G. Levy. Kinetics of pharmacologic efiects.Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 7:362–372 (1966).
S. Toon and M. Rowland. Quantitative structure pharmacokinetic activity relationship with some tetracyclines.J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 31:(suppl.):43P (1979).
S. Toon and M. Rowland. Structure-pharmacokinetic relationships among the barbiturates in the rat.J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 225:752–763 (1983).
A. E. Bird and A. C. Marshall. Correlation of serum binding of penicillins with partition coefficients.Biochem. Pharmacol. 16:2275–2290 (1967).
J. B. Houston, D. G. Upshall, and J. W. Bridges. Further studies using carbamate esters as model compounds to investigate the role of lipophilicity in the gastrointestinal absorption of foreign compounds.J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 195:67–72 (1975).
Y.-J. Lin, S. Awazu, M. Hanano, and H. Nogami. Pharmacokinetic aspects of elimination from plasma and distribution to brain and liver of barbiturates in rats.Chem. Pharm. Bull. 21:2749–2756 (1973).
T. Morishita, M. Yamazaki, N. Yata, and A. Kamada. Studies on absorption of drugs. VIII. Physicochemical factors affecting the absorption of sulfonamides from rat small intestine.Chem. Pharm. Bull. 21:2309–2322 (1973).
J. K. Seydel and K.-J. Schaper. Quantitative structure-pharmacokinetic relationships and drug design.Pharmacol. Ther. 15:131–182 (1982).
W. A. Ritschel and G. V. Hammer. Prediction of the volume of distribution fromin vitro data and use for estimating the absolute extent of absorption.Int. J. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. Toxicol. 18:298–316 (1980).
J. K. Seydel. Quantitative structure-pharmacokinetic relationships and their importance in drug design, possibilities and limitations.Meth. Findings Exptl. Clin. Pharmacol. 6:571–581 (1984).
N. Kaneniwa, M. Hiura, and S. Nakagawa. Effect of lipid solubility and dose on the elimination of barbiturates in rabbits.Chem. Pharm. Bull. 27:1501–1509 (1979).
K. Kakemi, T. Arita, R. Hori, and R. Konishi. Absorption and excretion of drugs. XXX. Absorption of barbituric acid derivatives from rat stomach.Chem. Pharm. Bull. 15:1534–1539 (1967).
M. Hiura, S. Nakagawa, H. Kawashima, and N. Kaneniwa. Effect of lipid solubility on hepatic first-pass metabolism of barbiturates in rabbits.Int. J. Pharmaceut. 20:73–85 (1984).
R. Kuntzman. Drugs and enzyme induction.Ann. Rev. Pharmacol. 9:21–36 (1969).
N. Kaneniwa, M. Hiura, and T. Funaki. Effect of fasting on the elimination of barbital and phenobarbital in rabbits.Chem. Pharm. Bull. 27:2157–2162 (1979).
M. Rowland, L. Z. Benet, and G. G. Graham. Clearance concepts in pharmacokinetics.J. Pharmacokin. Biopharm. 1:123–136 (1973).
G. R. Wilkinson and D. G. Shand. A physiological approach to hepatic drug clearance.Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 18:377–390 (1975).
K. S. Pang and M. Rowland. Hepatic clearance of drugs. I. Theoretical considerations of a “well-stirred” model and a “parallel-tube” model. Influence of hepatic blood flow, plasma and blood cell binding, and the hepatocellular enzymatic activity on hepatic drug clearance.J. Pharmacokin. Biopharm. 5:625–653 (1977).
L. Bass, S. Keiding, K. Winkler, and N. Tygstrup. Enzymatic elimination of substrates flowing through the intact liver.J. Theor. Biol. 61:393–409 (1976).
L. Bass and K. Winkler. A method of determining intrinsic hepatic clearance from the first-pass effect.Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 7:339–343 (1980).
J. G. Wagner, G. J. Szpunar, and J.J. Ferry. Exact mathematical equivalence of the venous equilibration (“well-stirred”) model, the sinusoidal perfusion (“parallel-tube”) model, and a specific two-compartment open model.Drug Metab. Dispos. 12:385–388 (1984).
M. Rowland. Influence of route of administration on drug availability.J. Pharm. Sci. 61:70–74 (1972).
M. Gibaldi, R. N. Boyes, and S. Feldman. Influence of first-pass effect on availability of drugs on oral administration.J. Pharm. Sci. 60:1338–1340 (1971).
J. G. Wagner. Comparison of nonlinear pharmacokinetic parameters estimated from sinusoidal perfusion and venous equilibrium models.Biopharm. Drug Dispos. 6:23–31 (1985).
W. L. Chiou. Mean hepatic transit time in the determination of mean absorption time.J. Pharm. Sci. 72:1365–1368 (1983).
L. S. Schanker. Absorption of drugs from the rat colon.J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 126:283–290 (1959).
K. Kakemi, T. Arita, R. Hori, R. Konishi, and K. Nishimura. Absorption and excretion of drugs. XXXIII. The correlation between the absorption of barbituric acid derviatives from the rat small intestine and their binding to the mucosa.Chem. Pharm. Bull. 17:248–254 (1969).
K. Yamaoka, T. Nakagawa, and T. Uno. Statistical moments in pharmacokinetics.J. Pharmacokin. Biopharm. 6:547–558 (1978).
S. Riegelman and P. Collier. The application of statistical moment theory to the evaluation ofin vivo dissolution time and absorption time.J. Pharmacokin. Biopharm. 8:509–534 (1980).
E. W. Maynert and H. B. Van Dyke. The metabolism of barbiturates.Pharmacol. Rev. 1:217–242 (1949).
E. L. Dobson and H. B. Jones. The behavior of intravenously injected particulate matter; its rate of disappearance from the flow stream as a measure of liver blood flow.Acta Med. Scand. 144 (Suppl. 273):1–71 (1952).
J. M. Neutze, F. Wyler, and A. M. Rudolph. Use of radioactive microspheres to assess distribution of cardiac output in rabbits.Am. J. Physiol 215:486–495 (1968).
L. E. Gaudette and B. B. Brodie. Relationship between the lipid solubility of drugs and their oxidation by liver microsomes.Biochem. Pharmacol. 2:89–96 (1959).
C. Hansch, A. R. Steward, S. M. Anderson, and D. Bentley. The parabolic dependence of drug action upon lipophilic character as revealed by a study of hypnotics.J. Med. Chem. 11:1–11 (1967).
C. Hansch. Quantitative relationships between lipophilic character and drug metabolism.Drug. Metab. Rev. 1:1–14 (1972).
T. D. Yih and J. M. van Rossum.Ks values of some homologous series of barbiturates and the relationship with the lipophilicity and metabolic clearance.Biochem. Pharmacol. 26:2117–2120 (1977).
I. Jansson, S. Orrenius, L. Ernster, and J. B. Schenkman. A study of the interaction of a series of substituted barbituric acids with the hepatic microsomal monooxygenase.Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 151:391–400 (1972).
J. C. Topham. Relationship between difference spectra and metabolism. Barbiturates, drug interaction, and species difference.Biochem. Pharmacol. 19:1695–1701 (1970).
M. Yamazaki, M. Aoki, and A. Kamada. Biological activity of drugs. IV. Physicochemical factors affecting the excretion of sulfonamides in rats.Chem. Pharm. Bull. 16:721–727 (1968).
T. Koizumi, T. Arita, and K. Kakemi. Absorption and excretion of drugs. XXI. Some pharmacokinetic aspects of absorption and excretion of sulfonamides (3). Excretion from the kidney.Chem. Pharm. Bull. 12:428–432 (1964).
Y. Sugiyama and M. Hanano. Pharmacokinetics. In Ito, Ohta, Nakashima, Nakamura, and Fukawa (eds.),Shin'yakuhinyoran-Rinshohen, R & D Planning, Tokyo, 1986, pp. 136–180.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Watari, N., Sugiyama, Y., Kaneniwa, N. et al. Prediction of hepatic first-pass metabolism and plasma levels following intravenous and oral administration of barbiturates in the rabbit based on quantitative structure—Pharmacokinetic relationships. Journal of Pharmacokinetics and Biopharmaceutics 16, 279–301 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01062138
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01062138