Abstract
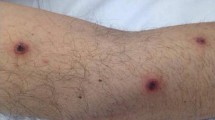
A 35 year old female patient with acute lymphocytic leukemia developed fusariosis in which dissemination appeared to be limited to cutaneous and vascular invasion. The first evidence of fungemia occurred nearly seven months after initial hospitalization. The fungus was identified asFusarium sp. and was considered a contaminant. Two weeks later blood cultures were again positive forFusarium sp. and the patient was placed on amphotericin B and 5-fluorocytosine therapy. The following day developing lesions were noted on her forearms and face; lesions ultimately spread to her trunk, abdomen, and lower extremities. Skin lesion biopsy sections revealed abundant septate and branching hyphae throughout the dermis and within capillaries. Twenty-six days after the initial isolation the patient died. Post-mortem blood cultures gave rise to the same fungus, which was identified asFusarium monoliforme. Postmortem cultures and stains of spleen, liver, lung, and brain specimens were all negative for fungi. The primary source and portal of entry of the organism remained undetermined.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Booth C. The GenusFusarium. Bucks (UK): Commonwealth Agricultural Bureau.
Cole RJ, Kirksey JW, Cutter HG, Doupnik BL, Peckham JC. Toxin fromFusarium moniliforme: Effects on plants and animals. Science 1973; 30: 1324–26.
Mirocha CJ, Pathre SV, Schauerhamer B, Christensen CM. Natural occurrences ofFusarium toxins in feedstuff. App Environ Microbiol 1976; 32: 553–56.
Wilson BJ, Maran RR. Causative fungus agent of leucoencephalomalacia in equine animals. Vet Rec 1971; 8: 484–86.
Austwick PKC.Fusarium infections in man and animals. In: MD Moss and JE Smith, eds. The Applied Mycology of Fusarium. New York: Cambridge University Press, 1986: 129–40.
Frelier PF, Sigler L, Nelson PE. Mycotic pneumonia caused byFusarium moniliforme in an alligator. J Med Vet Myc 1985; 23: 399–402.
Rebell G.Fusarium infections in human and veterinary medicine. In: Nelson PE, Touson TA, Cook, RJ, eds.Fusarium: disease, biology and taxonomy. University Park: The Pennsylvania State University, 1981: 210–20.
Smith AG, Muhvich AG, Muhvich KH, Wood C. FatalFusarium solani infections in baby sharks. J Med Vet Myc 1989; 27: 83–91.
Anaissie E, Kantarjian R, Hepfer R, Fainstein V, Bodey G. The emerging role ofFusarium infections in patients with cancer. Medicine 1988; 67: 77–83.
Merz WG, Karp JE, Hoagland M, Jett-Foheen M, Junkins JM, Hood AF. Diagnosis and successful treatment of fusariosis in the compromised host. J Inf Dis 1988; 158: 1046–55.
Richardson SE, Banntyne RM, Summerbell RC, Milliken J, Gold R, Weitzman SS. Disseminated fusarial infection in the immunocompromised host. Rev Infect Dis 1988; 10: 1171–81.
Rippon JW, Larson RA, Rosenthal DM, Clayman J. Disseminated cutaneous and peritoneal hyalohyphomycosis caused byFusarium species: three cases and a review of the literature. Mycopathologia 1988; 101: 105–11.
Venditti M, Micozzi A, Gentile G, Polonelli L, Morace G, Bianco P, Avvisati S, Papa G, Martino P. InvasiveFusarium solani infections in patients with acute leukemia. Rev Inf Dis 1988; 10: 653–60.
Young NA, Kwon-Chung KJ, Kubota IT, Jennings AE, Fisher RI. Disseminated infection byFusarium moniliforme during treatment for malignant lymphoma. J Clin Microbiol 1978; 7: 589–94.
Chaulk CP, Smith PW, Feagler JR, Verdirame J, Commers JR. Fungemia due toFusarium solani in an immunocompromised child. Ped Inf Dis 1986; 5: 363–66.
June CH, Beatty PG, Shulman HM, Rinaldi MG. DisseminatedFusarium monoliforme infection after allogenic marrow transplantation. South Med J 1986; 79: 513–15.
Kiehn TE, Nelson PE, Bernard EM, Edwards FF, Koziner B, Armstrong D. Catheter-associated fungemia caused byFusarium chlamydosporum in a patient with lymphocytic lymphoma. J Clin Microbio 1985; 21: 501–4.
Veglia KS, Marks VJ.Fusarium as a pathogen: A case report ofFusarium sepsis and review of the literature. J Am Acad Dermatol 1987; 16: 260–63.
Blazar BR, Hurd DD, Shover DC, Alexander JW, McGlane PB. InvasiveFusarium infections in bone marrow transplant recipients. Am J Med 1984; 77: 645–51.
Wheeler MS, McGinnis MR, Schell WA, Walker DH.Fusarium infection in burned patients. Am J Clin Path 1981; 75: 304–11.
Gradon JD, Lerman A, Lutwock LI. Septic arthritis due toFusarium moniliforme. Rev Inf Dis 1990; 12: 716–17.
Attapattu MC, Anandakrishnan C. Extensive subcutaneous hyphomycosis caused byFusarium oxysporum. J Med Vet Myc 1986; 24: 105–111.
Collins MS, Rinaldi MG. Cutaneous infection in man caused byFusarium moniliforme. Sabouraudia 1977; 15: 151–160.
Riddell RW. Permanent stained mycological preparations obtained by slide culture. Mycology 1950; 42: 265.
Fisher NL, Marasas WFO, Toussoun TA. Taxonomic importance of microconidial chains inFusarium Section Liseola and effects of water potential on their formation. Mycologia 1983; 75: 693–98.
Joffe AZ. A modern system ofFusarium taxonomy. Mycopath et Mycol Appl 1974; 53: 201–28.
Hsieh WH, Snyder WC, Smith SN. Influence of carbon sources, amino acids and water potential on growth and sporulation ofFusarium moniliforme. Phytopathology 1979; 69: 602–4.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Smith, A.G., Bustamante, C.I. & Wood, C. Disseminated cutaneous and vascular invasion byFusarium moniliforme in a fatal case of acute lymphocytic leukemia. Mycopathologia 122, 15–20 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01103704
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01103704