Abstract
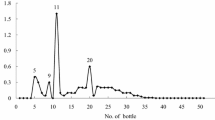
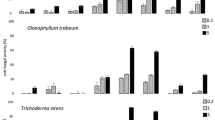
The fungal toxin ‘orellanine’, isolated by Grzymala (10) from Cortinarius orellanus, seems to be a heterogeneous mixture of several toxic and nontoxic substances. We succeeded in isolating a lethal toxin which is sensitive to light and which is striking because of its long latency period. We consider this the main toxin of C. orellanus. Even in extremely high doses often times LD 100 mice do not die earlier than 48 hours after application. The paper gives details about the isolation and several properties of this slow acting toxin.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Antkowiak, W. Z. & Gessner, W. P., 1975. Isolation and characteristics of toxic components of Cortinarius orellanus Fr. Bul. de l'Academie Polonaise des sciences 23(9): 729–733.
Antkowiak, W. Z. & Gessner, W. P., 1979. The structure of orellanine and orelline. Tetrahedron Letters 21, 1931–1934.
Benedict, R. C., 1972. Mushroom toxins other than Amanita. In: Microbial Toxins, Vol VIII, 281–320.
Csordas, A., Kürnsteiner, H. & Moser, M. (In preparation)
Ebneter, K., 1976. Vergiftungen durch Knollenblätterpilze. Dissertation, Zurich.
Faulstich, H. & Georgopoulos, D. et al. 1974. Analysis of the toxins of amanitin-containing mushrooms. Zeitschr. f. Naturforsch. 29c: 86–88.
Faulstich, H., 1977. Biochemistry of toxicity in Amanita phalloides and other amanitin containing species. Abstracts, Second Intern. Mycol. Congr. I, 190.
Gamper, R., 1977. Untersuchungen über die Giftstoffe der Pilze Cortinarius orellanus Fr. und C. speciosissimus Kühn. Dissertation Innsbruck.
Grzymala, S., 1957. Massenvergiftungen durch den Orangefuchsigen Hautkopf. Zeitschr. f. Pilzk. 23: 139–142.
Grzymala, S., 1962. L'isolement de l'orellanine poison du Cortinarius orellanus Fr. et l'etude de ses effect anatomopathologique. Bull. Soc. Myc. de France 78: 394–404.
Hörhammer, L. et al. 1963. Pharm. Ztg. 108: 259.
Johnston, K. M. et al. 1968. Separation of flavonoid compounds on Sephadex LH-20. Journ. Chromatogr. 33: 539–541.
Kürnsteiner, H., 1978. Untersuchungen über die Giftstoffe von Cortinarius orellanus Fr. Dissertation, Innsbruck.
Kürnsteiner, H. Einfluß von UV-Bestrahlung auf die Toxizität des langsam wirkenden Giftes von Cortinarius orellanus Fr. (in preparation).
List, P. H. (in litt.)
Möttönen, M., Nieminen, L. & Heikkilä, H., 1975. Damage caused by two finnish mushrooms, Cortinarius speciosissimus and Cortinarius gentilis on the rat kidney. Zeitschr. f. Naturforsch. 30c: 668–671.
Moser, M., 1969. Cortinarius Fr., Untergattung Leprocybe subgen. nov., die Rauhköpfe. Zeitschr. f. Pilzk. 35: 213–248.
Nieminen, L. & Pyy, K., 1976. Individual variation in mushruum poisoning caused by Cortinarius speciosissimus in the rat. Med. Biol., Helsinki, 54(2): 156–158.
Repas, A. & Nikolin, B., 1968. The separation of phenolic glucosides and carbohydrates from the bark of Populus tremula by gel filtration. J. Chromatogr. 35: 99–100.
Saito, M., et al. 1979. In Proc. 28th Ann. Meeting Japan. Cancer Assoc. Kanazawa, 225.
Steyn P. S., 1971. Ochratoxin and other dihydroisocoumarins. In: Kadis, S., A. Ciegler, S. J., Ajl, Microbial Toxins, Vol. VI, 179–205. Academic Press New York and London.
Testa, E., 1970. Indagini sulle tosicita dei funghi del genere Cortinarius. Nota 1. Cortinarius orellanus. Rassegna Micol. ticinese nr. 2.
Wieland, Th. 1967. The toxic peptides of Amanita phalloides. Fortschr. Chem. org. Naturstoffe 25: 214.
Wieland, Th. & Wieland, O., 1972. The toxic peptides of Amanita species. In: Microbial Toxins Vol. VIII, 249–280.
Wieland, Th., 1972. Struktur und Wirkung der Amatoxine. Naturwissenschaften 59: 225–231.
Wieland, Th., 1973. Über die Giftstoffe der Gattung Amanita. Zeitschr. f. Pilzk. 39: 103–112.
Woof, J. B. & Pierce, J. S., 1967. Separation of complex mixtures of polyhydroph enoles on columns of Sephadex. J. Chromatogr. 28: 94–103.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kürnsteiner, H., Moser, M. Isolation of a lethal toxin from Cortinarius orellanus Fr. Mycopathologia 74, 65–72 (1981). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01259460
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01259460