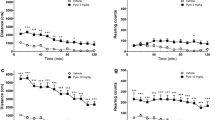
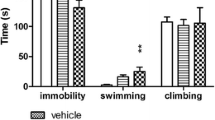
Summary
SDZ PSD 958, a novel benzo[g]quinoxaline derivative exhibits the properties of a potent orally active selective D1 receptor antagonist. It has high affinity for D1-like receptors (D1, D5; pKi=9.7–9.8) labelled by [3H]SCH23390 and is at least 400 fold less active at D2-like receptors (i.e. D2, D4) labelled by [3H]spiperone. Effects in functional tests are consistent with d1 receptor antagonist properties. SDZ PSD 958 inhibited apomorphine-induced rearing in mice and prevented prolongation of novelty-induced locomotion in rats elicited by the selective D1 receptor agonist CY 208-243. By contrast, SDZ PSD 958 did not induce catalepsy and only weakly inhibited apomorphine-induced stereotyped gnawing in rats. This suggests that SDZ PSD 958 preferentially inhibits responses mediated by dopamine systems innervating the limbic system.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andersen PH, Nielsen EB, Gronvald FC, Braestrup C (1986) Some atypical neuroleptics inhibit [3H]SCH23390 binding in vivo. Eur J Pharmacol 120: 143–144
Andersen PH, Gronvald FC, Hohlweg R, Hansen LB, Guddal E, Braestrup C, Nielsen EB (1992) NNC-112, NNC-687 and NNC-756, new selective and highly potent dopamine D1 receptor antagonists. Eur J Pharmacol 219: 45–52
Billard W, Ruperto G, Crosby L, Iorio LC, Barnett A (1984) Characterization of the binding of [3H]SCH23390, a selective D1 receptor antagonist ligand, in rat striatum. Life Sci 35: 1885–1893
Bruinvels AT, Lery H, Nozulak J, Palacios JM, Hoyer D (1992) 5-HT1D binding sites in various species: similar pharmacological profile in dog, monkey, calf, guineapig and human brain membranes. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 346: 243–248
Cheng YC, Prusoff WH (1973) Relationship between the inhibition contast (Ki) and the concentration which caused 50% inhibition (IC50) of an enzymatic reaction. Biochem Pharmacol 22: 3099–3108
Chipkin RE, Iorio LC, Coffin VL, McQuade RD, Berger JG, Barnett A (1988) Pharmacological profile of SCH39166: a dopamine D1 selective benzonaphthazepine with potential antipsychotic activity. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 247: 1093–1102
Christensen AV, Arnt J, Hyttel, J, Larsen JJ, Svendsen O (1984) Pharmacological effects of a specific dopamine d1 antagonist SCH23390 in comparison with neuroleptics. Life Sci 34: 1529–1540
Closse A, Bittiger H, Langenegger D, Wanner A (1987) Binding studies with [3H]cis-methyldioxolane in different tissue. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 355: 372–377
Ellenbroek BA, Artz MT, Cools AR (1991) The involvement of dopamine D1 and D2 receptors in the effects of the classical neuroleptic haloperidol and the atypical neuroleptic clozapine. Eur J Pharmacol 196: 103–108
Engel G, Hoyer D, Berthold R, Wagner H (1981) (±)[125Iodo]cyanopindolol, a new ligand for β-adrenoceptors: identification and quantitation of subclasses of β-adrenoceptors in guinea pig. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 317: 277–285
Ernst AM, Smelik PG (1966) Site of action of dopamine and apomorphine on compulsive gnawing behavior in the rat. Experientia 22: 837–838
Fink JS, Smith GP (1980) Mesolimbic and mesocortical dopaminergic neurons are necessary for normal exploratory behavior in rats. Neurosci Lett 17: 61–65
Frandsen EK, Krishna G (1976) A simple ultrasensitive method for the assay of cyclic AMP and cyclic GMP in tissues. Life Sci 18: 529–542
Gerhardt S, Gerber R, Liebman JM (1985) SCH23390 dissociated from conventional neuroleptics in apomorphine climbing and acute dyskinesia models. Life Sci 37: 2355–2363
Gerlach J, Andersen J, Clemmesen L, Haffner F, Lublin H (1994) Antipsychotic efficacy of D1 receptor antagonists evaluated in primates (NNC 01-0756) and in a phase II clinical study (NNC 01-0687). Neuropsychopharmacol 10 (no 3S, part I): 237S
Gessa GL, Canu A, Del Zompo M, Burrai C, Serra G (1991) Lack of acute antipsychotic effect of SCH23390, a selective dopamine D1 receptor antagonist. Lancet 337: 854–855
Hoffman DC, Donovan H (1995) Catalepsy as a rodent model for detecting antipsychotic drugs with extrapyramidal side effect liability. Psychopharmacol 120: 128–133
Hoyer D, Engel G, Kalkman HO (1985) Molecular pharmacology of 5-HT1 and 5-HT2 recognition sites in rat and pig brain membranes: radioligand binding studies with [3H]5-HT, [3H]8-OH-DPAT, (−)[125I]iodocyanopindolol, [3H]mesulergine and [3H]ketanserin. Eur J Pharmacol 118: 13–23
Hoyer D, Neijt HC (1988) Identification of serotonin 5-HT3 recognition sites in membranes of N1E-115 neuroblastoma cells by radioligand binding. Mol Pharmacol 33: 303–309
Hietala J, Lappalainen J, Koulu M, Syvälahti E (1990) Dopamine D1 receptor antagonism in schizophrenia: is there reduced risk of extrapyramidal side effects. Trends Pharmacol Sci 11: 406–410
Imperato A, Angelucci L (1989) The effects of clozapine and fluperlapine on the in vivo release and metabolism of dopamine in the striatum and in the prefrontal cortex of freely moving rats. Psychopharmacol Bull 25: 383–389
Iorio LC, Barnett A, Leitz FH, Houser VP, Korduba CA (1983) SCH23390, a potential benzazepine antipsychotic with unique interactions on dopaminergic systems. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 226: 462–854
Janssen PAJ, Niemegeers CJE, Schellekens KHL, Lenaerts FM (1967) Is it possible to predict the clinical effects of neuroleptic drugs (major tranquillizers) from animal data? Drug Res 17: 841–854
Karlsson P, Smith L, Farde L, Harnryd C, Wiesel FA, Sedvall GC (1994) Lack of apparent antipsychotic effect of the dopamine D1-receptor antagonist SCH39166 in schizophrenia. Neuropschopharmacol 10, 3 [Suppl], Pt 2: 32S
Kebabian JW, Calne DB (1979) Multiple receptors for dopamine. Nature 277: 93–96
Kelly PH (1977) Drug-induced motor behavior. In: Iversen LL, Iversen SD, Snyder SH (eds) Handbook of psychopharmacology, vol 8. Drugs, neurotransmitters, and behavior. Plenum Press, New York, pp 295–331
Kerkman DJ, Ackerman M, Artman LD, MacKenzie RG, Johnson MC, Bednarz L, Montana W, Asin KE, Stampfli H, Kebabian JW (1989) A-69024: a non-benzazepine antagonist with selectivity for the dopamine D1 receptor. Eur J Pharmacol 166: 481–491
Lublin H, Gerlach J, Morkeberg F (1994) The potential antipsychotic effects of selective d1 antagonists evaluated in monkeys and in an open study. Psychopharmacol 114: B5
Markstein R (1986) Pharmacological characterisation of central dopamine receptors using functional criteria. In: Winlow W, Markstein R (eds) The neurobiology of dopamine. Manchester University Press, Manchester UK, pp 41–52
Markstein R, Enz A, Vigouret JM, Jaton AL, Closse A, Briner U, Gull P (1987) Biochemical, behavioural, and endocrine effects of CK 204-933, a novel beta-ergolene. J Neural Transm 69: 179–199
Markstein R, Seiler MP, Vigouret JM, Urwyler S, Enz A, Dixon K (1988) Pharmacological properties of CY 208-243 a novel D1 agonist. In: Sandler M, Dahlstroem A, Belmaker RH (eds) Progress in catecholamine research, part B: central aspects. A Liss, New York, pp 59–64
Meller E, Kuga S, Friedhoff AJ, Goldstein M (1985) Selective D2 dopamine receptor agonist prevent catalepsy induced by SCH23390, a selective D1 antagonist. Life Sci 36: 1857–1864
Murray AM, Waddington JL (1990) The interaction of clozapine with dopamine D1 versus dopamine D2 receptor mediated function: behavioral indices. Eur J Pharmacol 186: 79–86
Rüdeberg C, Urwyler S, Schulthess C, Herrling PL (1986) Biochemical and pharmacological effects of fluperlapine on noradrenaline and acetylcholine systems in some rodent, bovine and crustacean preparations. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 332: 357–363
Sanberg PR (1980) Haloperidol-induced catalepsy is mediated by postsynaptic dopamine receptors. Nature 284: 472–473
Scatton B (1982) Further evidence for the involvement of D2 but not D1 dopamine receptors in dopaminergic control of striatal cholinergic transmission. Life Sci 31: 2883–2890
Sibley DR, Monsma FJ (1992) Molecular biology of dopamine receptors. Trends Pharmacol Sci 13: 61–69
Somogyi GT, Szerb JC (1972) Demonstration of acetylcholine release by measuring efflux of labelled choline from cerebral cortical slices. J Neurochem 19: 2667–2677
Starke K, Späth JD, Adelung C (1983) Further functional in vitro comparison of pre- and postsynaptic dopamine receptors in the rabbit caudate nucleus. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 323: 298–306
Stille G (1969) Die Neuroleptikatherapie der Schizophrenie in pharmakologischer Sicht. Schweiz Med Wochenschr 99: 1645–1652
Stoof JC, Thieme RE, Vrijmoed-de Vries MC, Mulder AH (1979) In vitro acetylcholine release from rat caudate nucleus as a new model for testing drugs with dopamine receptor activity. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 309: 119–124
Sunahara RK, Guan HC, O'Dowd BF, Seeman P, Laurier LG, Ng G, George SR, Torchia J, Van Tol HHM, Niznik HB (1991) Cloning the gene for a human dopamine D5 receptor with higher affinity for dopamine than D1. Nature 350: 614–619
Urwyler S, Coward D (1987) Binding of [3H]spiperone and [3H]sulpiride to dopamine D2 receptors in rat striatal membranes: methodological considerations and demonstration of the identical nature of the binding sites for the two ligands. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 335: 115–122
Van Tol HHM, Bunzow JR, Guan HC, Sunahara RK, Seeman P, Niznik HB, Civelli O (1991) Cloning of the gene for a human dopamine D4 receptor with high affinity for the antipsychotic clozapine. Nature: 350: 610–614
Vigouret JM, Buerki HR, Jaton AL, Zueger PE, Loew DM (1978) Neurochemical and neuropharmacological investigations with four ergot derivatives: bromocriptine, dihydroergotoxine, CF 25-397 and CM 29-712. Pharmacology 16 [Suppl 1]: 156–173
Waeber C, Schoeffter P, Palacios JM, Hoyer D (1988) Molecular pharmacology of 5-HT1D recognition sites: radioligand binding studies in human, pig and calf brain membranes. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 337: 595–601
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Markstein, R., Gull, P., Rüdeberg, C. et al. SDZ PSD 958, a novel D1 receptor antagonist with potential limbic selectivity. J. Neural Transmission 103, 261–276 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01271238
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01271238