Summary
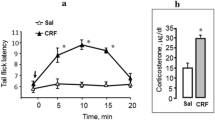
This study examined whether corticotropin releasing factor (CRF), given prior to test, would produce an improved retrieval of aversive memory in the same way as pre-exposure to inescapable footshocks and the CRF antagonist, alpha-helical CRF 9-41 (a-h CRF), blocks this effect in rats. For this purpose animals conditioned in a T-maze with appetitive (10% sucrose) and aversive (2.0mA footshock) events were given intracerebroventricularly (i.c.v.) 20 min before testing, a single dose of 0.05, 0.1, 0.2 or 0.4 μg/rat of CRF, or 5μg/rat of a-h CRF, or both at 10min interval. In the retention test conducted with the same training apparatus 72-hr after conditioning, CRF (0.05, 0.1 and 0.2 μg) treated rats showed a dose-dependent increase in latencies to enter the previously shocked goalarm, with the absence of such a difference in responding to the nonshocked goalarm. The highest dose of CRF (0.4 μg), however, increased the latencies to enter both the goalboxes. Alpha-helical CRF, administered 10 min before, antagonized the memory-enhancing effect of CRF. Further, CRF (0.1, 0.2 and 0.4 μg) significantly decreased the total number of center entries in the open field, consistent with the view that i.c.v. administered CRF produces “anxiogenic-like” effect. Alpha-helical CRF reversed this effect. The effect of CRF on memory retrieval was similar to that seen following inescapable footshock in rats. The results thus suggest the possible involvement of central CRF mechanisms in the differential enhancement of memory of helplessness condition.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berridge CW, Dunn AJ (1986) Corticotropin-releasing factor elicits naloxone-sensitive stress-like alteration in exploratory behavior in mice. Regul Pept 16: 83–93
Berridge CW, Dunn AJ (1987) A corticotropin-releasing factor antagonist reverses the stress-induced changes of exploratory behavior in mice. Horm Behav 21: 393–401
Britton KT, Morgan J, Rivier J, Vale W, Koob GF (1985) Chlordiazepoxide attenuates response suppression induced by corticotropin releasing factor in the conflict test. Psychopharmacology 86: 170–174
Britton KT, Lee G, Koob GB (1988) Corticotropin-releasing factor and amphetamine exaggerate partial agonist properties of benzodiazepine antagonist RO 15-1788 in the conflict test. Psychopharmacology 94: 306–311
Brown MR, Fisher LA, Spiess J, Rivier C, Rivier J, Vale W (1982) Corticotropin-releasing factor: activities on the sympathetic nervous system and metabolism. Endocrinology 111: 928–931
Brown MR, Fisher LA, Webb V, Vale WW, Rivier JE (1986) Corticotropin-releasing factor: a physiologic regulator of adrenal epinephrine secretion. Brain Res 328: 355–357
Bures J, Buresova O, Huston JP (1983) Techniques and basic experiments for the study of brain and behavior. Elsevier, New York, pp 77–103
Butler PD, Weiss JM, Stout JC, Lilts CD, Cook LL, Nemeroff CB (1988) Corticotropin-releasing factor produces anxiogenic and behavioral activating effects following microinfusion into the locus coeruleus. Neurosci Abstr 14: 288
Cole BJ, Koob GF (1989) Propranolol antagonises the enhanced conditioned fear produced by corticotropin-releasing factor. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 247: 902–910
Dunn AJ, Berridge CW (1987) Corticotropin-releasing factor administration elicits a stress-like activation of cerebral catecholaminergic systems. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 27: 685–691
Endroczi E, Hraschek A, Nyakas C, Szabo G (1975) Brain catecholamines and pituitary-adrenal function. In: Endroczi E (ed) Cellular and molecular bases of neuroendocrine processes. Akademiai Kiado, Budapest, pp 607–618
Foa E, Zinbarg R, Rothbaum B (1992) Uncontrollability and unpredictability in post traumatic disorder: an animal model. Psychol Bull 112: 218–237
Foot SL, Bloom FE, Aston-Jones G (1983) Nucleus locus coeruleus: new evidence of anatomical and physiological specificity. Physiol Rev 63: 844–914
Gold PW (1988) Stress-responsive neuromodulators. Biol Psychiatry 24: 371–374
Gold PW, Frederick K, Goodwin MD, Geprge P, Chrousos MD (1988) Clinical and biochemical manifestations of depression: relation to the neurobiology of stress (part II). N Engl J Med 7: 413–420
Kalin NH, Shelton SE, Kraemer GW, McKinney WT (1983) Corticotropin-releasing factor administered intraventricularly to rhesus monkeys. Peptides 4: 217–220
Koob GF, Bloom FE (1985) Corticotropin-releasing factor and behavior. Fed Proc 44: 259–263
Kovacs GL, De Wied D (1994) Peptidergic modulation of learning and memory processes. Pharmacol Rev 46: 269–291
Krahn DD, Gosnell BA, Grace M, Levine AS (1986) CRF antagonist partially reverses CRF and stress-induced effects on feeding. Brain Res Bull 17: 285–289
Krystal JH, Kosten TR, Perry BD, et al (1989) Neurobiological aspects of PTSD: review of clinical and preclinical studies. Behav Ther 20: 177–198
Kumar KB, Karanth KS (1991) Enhanced retrieval of unpleasant memory in helpless rats. Biol Psychiatry 30: 493–501
Kumar KB, Karanth KS (1993) Enhanced processing of an aversive memory following inescapable shock in rats. Biol Psychiatry 33: 169–172
Kumar KB, Karanth KS (1995) Effects of ACTH and ACTH 4-10 on aversive memory retrieval in rats. J Neural Transm [Gen Sect] 101: 223–229
Lee EH, Sung YJ (1989) Differential influences of corticotropin-releasing factor on memory retention of aversive learning and appetitive learning in rats. Behav Neural Biol 52: 285–294
Lee EH, Lin WR (1991) Nifedipine and verapamil block the memory-facilitating effect of corticotropin-releasing factor in rats. Life Sci 48: 1333–1340
Lee EH, Hung HC, Lu KT, Chen WH, Chen HY (1992) Protein synthesis in the hippocampus associated with memory facilitation by corticotropin-releasing factor in rats. Peptides 13: 927–937
Leonard BE (1974) The effect of two synthetic ACTH analogues on the metabolism of biogenic amines of the rat brain. Arch Int Pharmacol Ther 207: 242–253
Liang KC, Lee EH (1988) Intra-amygdala injections of corticotropin-releasing factor facilitate inhibitory avoidance learning and reduce exploratory behavior in rats. Psychopharmacology 96: 232–236
McNaughton N, Mason ST (1979) The neuropsychology and neuropharmacology of the dorsal ascending noradrenergic bundle — a review. Prog Neurobiol 14: 157–219
Overmier JB, Murison R, Taklo T, Espelid R (1994) Effects of traumatic stress on defensive burying: an alternative test of the learned helplessness animal model of depression and enhanced retrieval of unpleasant memories. Biol Psychiatry 36: 703–704
Owens MJ, Nemeroff CB (1991) Physiology and pharmacology of corticotropin releasing factor. Pharmacol Rev 43: 425–464
Pitman RK (1989) Post traumatic stress disorder, hormones and memory. Biol Psychiatry 26: 221–223
Rivier C, Rivier J, Vale W (1986) Stress-induced inhibition of reproductive functions. Role of endogenous corticotropin-releasing factor. Science 231: 607–609
Seligman MEP, Maier SF, Geer J (1968) The alleviation of learned helplessness in the dog. J Abnorm Psychol 73: 256–262
Smith MA, Jonathan D, Ritchie JC, Kudler H, Lipper S, Chappell P, Nemeroff CB (1989) The corticotropin-releasing hormone test in patients with post traumatic stress disorder. Biol Psychiatry 26: 349–355
Southwick SM, Krystal J, Johnson D, Charney DS (1992) Neurobiology of PTSD. Annual review of psychiatry. APA Press, Washington
Sutton RE, Koob GF, Moal ML, Rivier J, Vale W (1982) Corticotropin-releasing factor produces behavioral activation in rats. Nature 297: 331–333
Tazi A, Dantzer R, Le Moal N, Rivier J, Vale W, Koob GF (1987) Corticotropin-releasing factor antagonist blocks stress-induced fighting in rats. Regul Pept 18: 37–42
Valentino RJ, Foote SL, Aston-Jones G (1983) Corticotropin-releasing factor activates noradrenergic neurons of the locus coeruleus. Brain Res 270: 363–367
Van Der Kolk B, Greenberg M, Boyd H, Krystal J (1985) Inescapable shock, neurotransmitters, and addiction to trauma: toward a psychobiology of post traumatic stress disorder. Biol Psychiatry 20: 314–325
Versteeg DHG (1973) The effect of two ACTH analogues on noradrenaline metabolism in rat brain. Brain Res 49: 483–485
Willner P (1985) Depression: a psychobiological synthesis. Wiley, New York, pp 101–143
Willner P (1986) Validation criteria for animal models of human mental disorders: learned helplessness as a paradigm case. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 10: 677–690
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kumar, K.B., Karanth, K.S. Alpha-helical CRF blocks differential influence of corticotropin releasing factor (CRF) on appetitive and aversive memory retrieval in rats. J. Neural Transmission 103, 1117–1126 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01291796
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01291796