Summary
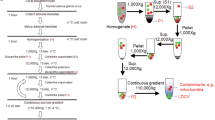
Large dense core vesicles (LDV) were purified from bovine splenic nerve homogenates by the sucrose-D2O density gradient method. Vesicles were subjected to a 50% increase and decrease in osmolarity from the control 330 mosmol 1−1 by adjusting sucrose or potassium phosphate buffer during pre- and/or postfixation. Control vesicles with a mean diameter of 717 Å readily swelled to ∼ 1050 Å and shrunk to ∼ 600 Å in the hypotonic and hypertonic media, respectively, with either sucrose or phosphate buffer. The dense core responded similarly but to a lesser degree. Prefixation in glutaraldehyde had little effect on vesicle sensitivity to subsequent tonicity change, nor did the fixativeper se exert an obvious osmotic effect. Thus, final vesicle size was largely determined by the OsO4 postfixation medium and principally by the vehicle rather than the fixative. In controls there was a mixture of spherical to oblate vesicles mostly filled with an electron-dense matrix. Upon swelling, more vesicles became spherical and nearly all had a prominent translucent halo between core and membrane. Upon shrinking, more vesicles became oblate, the halo was obliterated and the electron-density of the matrix increased. Frequency distributions of vesicle diameters at different tonicity clearly indicated that the diameter of LDV could overlap the 400–500 Å range characteristic of small dense core vesicles; however, there was no suggestion of a population of the latter in the purified LDV fraction. Implications are discussed concerning the biochemical and morphological identification of ‘light’ and ‘heavy’ density peaks of noradrenaline and dopamine β-hydroxylase from mixed vesicle populations and the possible relevance of changes in vesicle shape to a functional statein situ.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Belmar, J., De Potter, W. P. andDe Schaepdryver, A. F. (1974) Subcellular distribution of noradrenaline and dopamine β-hydroxylase in the hypothalamus of the rat. Evidence for the presence of two populations of noradrenaline storage particles.Journal of Neurochemistry 23, 607–9.
Birks, R. I. (1971) Effects of stimulation on synaptic vesicles in sympathetic ganglia, as shown by fixation in the presence of Mg++.Journal of Physiology (London) 216, 26–28P.
Birks, R. I. (1974) The relationship of transmitter release and storage to fine structure in a sympathetic ganglion.Journal of Neurocytology 3, 133–60.
Bisby, M. A. andFillenz, M. (1971) The storage of endogenous noradrenaline in sympathetic nerve terminals.Journal of Physiology (London) 215, 163–79.
Bisby, M. A., Fillenz, M. andSmith, A. D. (1973) Evidence for the presence of dopamine β-hydroxylase in both populations of noradrenaline storage vesicles in sympathetic nerve terminals of the rat vas deferens.Journal of Neurochemistry 20, 245–8.
Bodian, D. (1966) Electron microscopy: two major synaptic types on spinal motoneurons.Science 151, 1093–4.
Bodian, D. (1970) An electron microscope characterization of classes of synaptic vesicles by means of controlled aldehyde fixation.Journal of Cell Biology 44, 115–24.
Bone, Q. andDenton, E. J. (1971) The osmotic effects of electron microscope fixatives.Journal of Cell Biology 49, 571–81.
Boyne, A. F., Bohan, T. P. andWilliams, T. (1974) Effects of calcium-containing fixation solutions on cholinergic synaptic vesicles.Journal of Cell Biology 63, 780–95.
Chen-Yen, S. H., Yen, S. S., Thureson-Klein, Å. andKlein, R. L. (1974) Physico-chemical properties of the fast pool of norepinephrine release from purified adrenergic vesicles.Federation Proceedings 33, 523A.
Chubb, I. W., De Potter, W. P. andDe Schaepdryver, A. F. (1970) Two populations of noradrenaline containing particles in the spleen.Nature (London) 228, 1023–4.
Dahlström, A. andHäggendal, J. (1973) The possible importance of young (large) amine storage granules for adrenergic nerve terminal function. InFrontiers in Catecholamine Research (edited byUsdin, E. andSnyder, S.), pp. 409–10. Oxford: Pergamon Press.
De Potter, W. P. (1971) Noradrenaline storage particles in the splenic nerve.Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London, Series B 261, 313–17.
De Potter, W. P., Chubb, I. W. andDe Schaepdryver, A. F. (1972) Pharmacological aspects of peripheral noradrenergic transmission.Archives Internationales de Pharmacodynamie et de Therapie 196, 258–87.
De Potter, W. P., Smith, A. D. andDe Schaepdryver, A. F. (1970) Subcellular fractionation of splenic nerve: ATP, chromogranin A and dopamine β-hydroxylase in noradrenergic vesicles.Tissue and Cell 2, 529–46.
Documenta Geigy Scientific Tables (1970) 7th edition (edited byDiem, K. andLentner, C.). Basle: J. R. Geigy S. A.
Euler, U. S. Von (1958) The presence of the adrenergic neurotransmitter in intraaxonal structures.Acta physiologica scandinavica 43, 155–66.
Euler, U. S. Von andLishajko, F. (1963) Effect of adenine nucleotides on catecholamine release and uptake in isolated adrenergic nerve granules.Acta physiologica scandinavica 59, 454–61.
Fillenz, M. andWest, D. P. (1974) Changes in vesicular dopamine β-hydroxylase resulting from transmitter release.Journal of Neurochemistry 23, 411–16.
Gray, E. G. (1969a) Round and flat synaptic vesicles in the fish central nervous system. In:Cellular Dynamics of the Neuron (edited byBarondes, S. H.), pp. 211–27. New York and London: Academic Press.
Gray, E. G. (1969b) Electron microscopy of excitatory and inhibitory synapses: a brief review.Progress in Brain Research 8, 141–53.
Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (1964) 45th edition (editor-in-chiefWeast, R. C.), Cleveland, Ohio: The Chemical Rubber Co.
Helle, K. B. (1973) Biochemical studies of the chromaffin granule. III Redistribution of lipid phosphate, dopamine β-hydroxylase and chromogranin A after freezing and thawing of the isolated granule membranes.Biochemica et Biophysica Acta 318, 167–80.
Helle, K. B. andSerck-Hanssen, G. (1975) The adrenal medulla: a model for studies of hormonal and neuronal storage and release mechanisms.Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry 6, 127–46.
Hillarp, N. Å. (1958) Enzymic systems involving adenosinephosphates in the adrenaline and noradrenaline containing granules of the adrenal medulla.Acta physiologica scandinavica 42, 144–65.
Hillarp, N. Å. andNilsson, B. (1954) The structure of the adrenaline and noradrenaline containing granules in the adrenal medullary cells with reference to the storage and release of the sympathomimetic amines.Acta physiologica scandinavica 113, Supplementum 31, 79–107.
Klein, R. L. (1973) A large second pool of norepinephrine in the highly purified vesicle fraction from bovine splenic nerve. InFrontiers in Catecholamine Research (edited byUsdin, E. andSnyder, S.), pp. 423–5. Oxford: Pergamon Press.
Klein, R. L. andHarden, T. K. (1975) Newly synthesized norepinephrine accumulation in the readily releasable pool of a purified adrenergic vesicle fraction.Life Sciences 16, 315–22.
Klein, R. L. andThureson-Klein, Å. (1971) An electron microscopic study of noradrenaline storage vesicles isolated from bovine splenic nerve trunk.Journal of Ultrastructure Research 34, 473–91.
Klein, R. L. andThureson-Klein, Å. (1974) Pharmacomorphological aspects of large dense-core adrenergic vesicles.Federation Proceedings 33, 2195–206.
Korneliussen, H. (1972a) Elongated profiles of synaptic vesicles in motor endplates. Morphological effects of fixative variations.Journal of Neurocytology I, 279–96.
Korneliussen, H. (1972b) Ultrastructure of normal and stimulated motor endplates. With comments on the origin and fate of synaptic vesicles.Zeitschrift für Zellforschung und mickroskopische Anatomie 130, 28–57.
Korneliussen, H. (1973) Ultrastructure of motor nerve terminals on different types of muscle fibers in the Atlantic hagfish (Myxine glutinosa, L.)Zeitschrift für Zellforschung und mikroskopische Anatomie 147, 87–105.
Lagercrantz, H. (1973) Can the sympathetic large dense core vesicles be transformed to small vesicles by depletion of their soluble contentin vitro?Acta physiologica scandinavica 87, 23A-24A.
Lagercrantz, H., Kirksey, D. F. andKlein, R. L. (1974) On the development of sympathetic nerve trunk vesicles during axonal transport: Density gradient analysis of dopamine β-hydroxylase in bovine splenic nerve.Journal of Neurochemistry 23, 769–73.
Lagercrantz, H., Klein, R. L. andStjärne, L. (1970) Improvements in the isolation of noradrenaline storage vesicles from bovine splenic nerves.Life Sciences 9, 639–50.
Lagercrantz, H., Stjärne, L., Flatmark, T. andHelle, K. B. (1973) Artifactual subcellular distribution of dopamine β-hydroxylase: Effects of dilution and non-specific protein on the dopamine β-hydroxylase activity of membranes of adrenomedullary and sympathetic nerve vesicles.Biochemical Pharmacology 22, 3005–11.
Lagercrantz, H. andThureson-Klein, Å. (1975) On the soluble phase of adrenergic nerve vesicles: Correlation of matrix density and biochemical composition.Histochemie 43, 173–83.
Machado, A. B. M. (1967) Straight OsO4 versus glutaraldehyde-OsO4 in sequence as fixatives for the granular vesicles in sympathetic axons of the rat pineal body.Stain Technology 42, 293–300.
Maser, M. D., Powell, T. E. III andPhilpott, C. W. (1967) Relationships among pH, osmolarity and concentration of fixative solutions.Stain Technology 42, 175–82.
Maunsbach, A. K. (1966) The influence of different fixatives and fixation methods on the ultrastructure of rat kidney proximal tubule cells. II. Effect of varying osmolarity, ionic strength, buffer system and fixative concentration of glutaraldehyde solutions.Journal of Ultrastructure Research 15, 283–309.
Nelson, D. L. andMolinoff, P. B. (1974) The use of dopamine β-hydroxylase as a marker for adrenergic storage granules.The Pharmacologist 16, 235A.
Pfenninger, K. H. (1973) Synaptic morphology and cytochemistry.Progress in Histochemistry and Cytochemistry 5, 1–86.
Pfenninger, K. H. andRovainen, C. M. (1974) Stimulation- and calcium-dependence of vesicle attachment sites in presynaptic membrane; a freeze-cleave study of the lamprey spinal cord.Brain Research 72, 1–23.
Poisner, A. M., Douglas, W. W. andTrifaro, J. M. (1967) The role of ATP and ATPase in the release of catecholamines from the adrenal medulla. I. ATP-evoked release of catecholamines, ATP and protein from isolated chromaffin granules.Molecular Pharmacology 3, 561–71.
Rasmussen, K. E. (1974) Fixation in aldehydes. A study on the influence of the fixative, buffer and osmolarity upon the fixation of the rat retina.Journal of Ultrastructure Research 46, 87–102.
Schultz, R. L. andKarlsson, U. (1965) Fixation of the central nervous system for electron microscopy by aldehyde perfusion. II. Effect of osmolarity, pH of perfusate, and fixative concentration.Journal of Ultrastructure Research 12, 187–206.
Smith, A. D. (1968) Biochemistry of adrenal chromaffin granules. InA Symposium on the Interaction of Drugs and Subcellular Components in Animal Cells, edited byCampbell, P. N.), pp. 239–92. London: Churchill Ltd.
Smith, A. D. (1972) Subcellular localization of noradrenaline in sympathetic neurons.Pharmacological Reviews 24, 435–57.
Smith, A. D., De Potter, W. P., Moerman, E. J. andde Schaepdryver, A. F. (1970) Release of dopamine β-hydroxylase and chromogranin A upon stimulation of the splenic nerve.Tissue and Cell 2, 547–68.
Stjärne, L. (1964) Studies of catecholamine uptake, storage and release mechanisms.Acta physiologica scandinavica 228, Supplementum 62, 1–60.
Streit, P., Akert, K., Sandri, C., Livingston, R. B. andMoor, H. (1972) Dynamic ultrastructure of presynaptic membranes at nerve terminals in the spinal cord of rats. Anesthetized and unanesthetized preparations compared.Brain Research 48, 11–26.
Taugner, G. (1971) The membrane of catecholamine storage vesicles of adrenal medulla. Catecholamine fluxes and ATP-ase activity.Naunyn-Schmiedebergs' Archiv für Pharmakologie 270, 392–406.
Taugner, G. andWähler, A. (1974) Effects of lipid-modification on catecholamine fluxes and ATPase activity in storage vesicles from adrenal medulla.Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Archiv für Pharmakologie 282, 261–78.
Thureson-Klein, Å., Chen-Yen, S. H. andKlein, R. L. (1974) Retention of matrix density in adrenergic vesicles after extensive norepinephrine depletion.Experientia 30, 935–7.
Thureson-Klein, Å., Klein, R. L. andLagercrantz, H. (1973a) Highly purified splenic nerve vesicles: Early post-mortem effects on ultrastructure.Journal of Neurocytology 2, 13–27.
Thureson-Klein, Å., Klein, R. L. andYen, S. S. (1973b) Ultrastructure of highly purified sympathetic nerve vesicles: correlation between matrix density and norepinephrine content.Journal of Ultrastructure Research 43, 18–35.
Tranzer, J. P. (1973) New aspects of the localization of catecholamines in adrenergic neurons. InFrontiers in Catecholamine Research (edited byUsdin, E. andSynder, S.), pp. 453–8. Oxford: Pergamon Press.
Uchizono, K. (1965) Characteristics of excitatory and inhibitory synapses in the central nervous system of the cat.Nature (London) 207, 642–3.
Uchizono, K. (1969) Synaptic organization of the mammalian cerebellum. InNeurobiology of Cerebellar Evolution and Development (edited byLlinás, R.), pp. 549–81. Chicago: American Medical Association.
Valdivia, O. (1971) Methods of fixation and the morphology of synaptic vesicles.Journal of Comparative Neurology 142, 257–74.
Walberg, F. (1963) An electron microscopic study of the inferior olive of the cat.Journal of Comparative Neurology 120, 1–17.
Weinshilbaum, R. M. (1974) Subcellular localization of dopamine β-hydroxylase and norepinephrine in guinea pig vas deferens.Federation Proceedings 33, 497A.
Whittaker, V. P. (1971) Origin and function of synaptic vesicles.Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences 183, 21–32.
Whittaker, V. P. (1973) The structural and chemical properties of synaptic vesicles. InProteins of the Nervous System (edited bySchneider, D. J.), pp. 155–69. New York: Raven Press.
Whittaker, V. P. andGray, E. G. (1962) The synapse: biology and morphology.British Medical Bulletin 18, 223–8.
Whittaker, V. P., Michaelson, J. A. andKirkland, R. J. A. (1964) The separation of synaptic vesicles from nerve-ending particles (‘synaptosomes’).Biochemical Journal 90, 293–303.
Winkler, H., Hörtnagl, Heidi, Hörtnagl, H. andSmith, A. D. (1970) Membranes of the adrenal medulla. Characterization of insoluble proteins of chromaffin granules by gel electrophoresis.Biochemical Journal 118, 303–10.
Yen, S. S., Klein, R. L. andChen-Yen, S. H. (1973) Highly purified splenic nerve vesicles: Early postmortem effects on norepinephrine content and pools.Journal of Neurocytology 2, 1–12.
Zimmerman, H. andWhittaker, V. P. (1974a) Effect of electrical stimulation on the yield and composition of synaptic vesicles from the cholinergic synapses of the electric organ ofTorpedo: A combined biochemical, electrophysiological and morphological study.Journal of Neurochemistry 22, 435–50.
Zimmerman, H. andWhittaker, V. P. (1974b) Different recovery rates of the electrophysiological, biochemical and morphological parameters in the cholinergic synapses ofTorpedo electric organ after stimulation.Journal of Neurochemistry 22, 1109–14.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Thureson-Klein, Å., Klein, R.L. & Chen Yen, SH. Morphological effects of osmolarity on purified noradrenergic vesicles. J Neurocytol 4, 609–627 (1975). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01351540
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01351540