Abstract
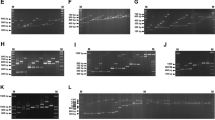
The factor XIIIB gene was examined to determine the nature of a previously described 300 bp restriction fragment length polymorphism (RFLP) seen in the human population. Polymerase chain reaction analysis of different regions within the factor XIIIB gene was carried out to define a high resolution map of the region encompassing the polymorphism, followed by DNA sequence analysis. AnAlu insertion was found to be the source of this variation. ThisAlu repeat is a member of the human specific-1 (HS-1) subfamily, although one of the five diagnostic nucleotides is a cattarhine specific (CS) subfamily mutation, suggesting that it may represent an intermediate form in the evolution between these two subfamilies. Subsequently, we developed a PCR-based assay to detect the polymorphism, rendering it a more useful marker for genetic linkage studies and genome mapping. This insertion is also a valuable polymorphism for human population studies, as demonstrated by the large variations in allele frequencies seen in three population groups.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Antonarakis, S. E., P. Oettgen, A. Chrakravarti, S. L. Halloran, R. R. Hudson, L. Feisee & S. K. Karathanasis, 1988. DNA polymorphism haplotypes of the human apolioprotein APOA1-APOC3-APOA4 gene cluster. Hum. Genet. 80:265–273.
Ausabel, F. M., R. Brent, R. E. Kingston, D. D. Moore, J. G. Seidman, J. A. Smith & K. Struhl, 1987. Current Protocols in Molecular Biology. Wiley, New York.
Bailey, A. D. & C.-K. J. Shen, 1993. Sequential insertion of Alu family repeats into specific genomic sites of higher primates. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 90:7205–7209.
Batzer, M. A., C. W. Schmid & P. L. Deininger, 1993. Evolutionary analyses of repetitive DNA sequences. Methods Enzymol. 224: 213–232.
Batzer, M. A., M. Alegria-Hartman, H. Bazan, D. H. Kass, T. H. Shaikh, G. E. Novick, P. A. Ioannou, D. A. Boudreau, W. D. Scheer, R. J. Herrera, M. Stoneking & P. L. Deininger, 1993. Alu repeats as markers for human population genetics, pp. 49–57 in Proceedings from the 4th International Symposium on Human Identification. Promega Publishing.
Batzer, M. A. & P. L. Deininger, 1991. A human-specific subfamily of Alu sequence. Genomics 9:481–487.
Batzer, M. A., V. A. Gudi, J. C. Mena, D. W. Foltz, R. J. Herrera & P. L. Deininger, 1991. Amplification dynamics of human-specific (HS) Alu family members. Nucleic Acids Res. 19:3619–3623.
Batzer, M. A., G. E. Kilroy, P. E. Richard, T. H. Shaikh, T. D. Desselle, C. L. Hoppens & P. L. Deininger, 1990. Structure and variability of recently inserted Alu family members. Nucleic Acids Res. 18:6793–6798.
Board, P. G., G. C. Webb, J. McKee & A. Ichinose, 1988. Localization of the coagulation factor XIII A subunit gene (F13A) to chromosome bands6p24-25. Cytogenet. Cell Genet. 48:25–27.
Bottenus, R. E., A. Ichinose & E. W. Davie, 1990. Nucleotide sequence of the gene for the b subunit of human factor XIII. Biochemistry 29:11195–11209.
Britten, R. J., W. F. Baron, D. B. Stout & E. H. Davidson, 1988. Sources and evolution of human Alu repeated sequences. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 85:4770–4774.
Cambien, F., O. Poirier, L. Lecerf, A. Evans, J.-P. Cambou, D. Arveiler, G. Luc, J.-M. Bard, L. Bara, R. Ricard, L. Tiret, P. Amouyel, F. Alhenc-Gelas & F. Soubrier, 1992. Deletion polymorphism in the gene for angiotensin-convering enzyme is a potent risk factor for myocardial infarction. Nature 359: 641–644.
Daniels, G. R. & P. L. Deininger, 1985. Integration site preferences of the Alu family and similar repetitive DNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 13:8939–8954.
Deininger, P. L., 1989. SINEs, short interspersed repeated DNA elements in higher eucaryotes, pp. 619–636 in Mobile DNA edited by M. Howe & D. Berg. ASM Press, Washington, DC.
Deininger, P. L. & M. A. Batzer, 1993. Evolution of retroposons, pp. 157–196 in Evolutionary Biology Vol. 27, edited by M./ K. Hecht, R. J. MacIntyre & M. T. Clegg. Plenum Press, New York.
Deininger, P. L., M. A. Batzer, C. A. Hutchison III & M. H. Edgell, 1992. Master genes in mammalian repetitive DNA amplification. Trends Genet. 8:307–311.
Economou-Pachnis, A. & P. N. Tsichlis, 1985. Insertion of an Alu SINE in the human homologue of the MIvi-2 locus. Nucleic Acids Res. 13:8379–8387.
Edwards, M. C. & M. C. Gibbs, 1992. A human dimorphism resulting from loss of an Alu. Genomics 14:590–597.
Friezner-Degen, S. J., B. Rajput & E. Reich, 1986. The human tissue plasminogen activator gene. J. Biol. Chem. 261:6972–6985.
Goldberg, Y. P., J. M. Rommens, S. E. Andrew, G. B. Hutchinson, B. Lin, J. Theilmann, R. Graham, M. L. Glaves, E. Starr, H. McDonald, J. Nasir, K. Schappert, M. A. Kalchman, L. A. Clarke & M. R. Hayden, 1993. Identification of an Alu retrotransposition event in close proximity to a strong candidate gene for Huntington's disease. Nature 362:370–373.
Hutchinson, G. B., S. E. Andrew, H. McDonald, Y. P. Goldberg, R. Graham, J. M. Rommens & Rommens M. R. and Hayden, 1993. An Alu element retroposition in two families with Huntington disease defines a new active Alu subfamily. Nucleic Acids Res. 21: 3379–3383.
Jurka, J., 1993. A new subfamily of recently retroposed Alu-repeats. Nucleic Acids Res. 21:2252.
Jurka, J. & A. Milosavljevic, 1991. Reconstruction and analysis of human Alu genes. J. Mol. Evol. 32:105–121.
Jurka, J. & T. Smith, 1988. A fundamental division in the Alu family of repeated sequences. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 85:4775–4778.
Matera, A. G., U. Hellmann, M. F. Hintz & C. W. Schmid, 1990. Recently transposed Alu repeats result from multiple source genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 18:6019–6023.
Matera, A. G., U. Hellmann & C. W. Schmid, 1990. A transpositionally and transcriptionally competent Alu subfamily. Mol. Cell. Biol. 10:5424–5432.
Mietus-Snyder, M., P. Charmley, B. Korf, J. A. A. Ladias, R. A. Gatti & S. K. Karathanasis, 1990. Genetic linkage of the human apolipoprotein AI-CIII-AIV gene cluster and the neural cell adhesion molecule (NCAM) gene. Genomics 7:633–637.
Miyamoto, M. M., J. L. Slightom & M. Goodman, 1987. Phylogenetic relations of humans and African apes from DNA sequences in the ψN-globin region. Science 238:369–373.
Mizutani, K., H. Nishimukai, T. Yasugi, I. Iwahashi, K. Tsunekawa & T. Shinomiya, 1991. Polymorphisms of serum proteins in Japanese patients with vascular diseases. I. Factor XIIIB, plasminogen and complementtypes in primary varicose veins. Hum. Hered. 41:270–275.
Muratani, K., T. Hada, Y. Yamamoto, T. Kaneko, Y. Shigeto, T. Ohue, J. Furuyama & K. Higashino, 1991. Inactivation of the cholinesterase geen by Alu insertion: Possible mechanism for human gene transposition. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 88: 11315–11319.
Nakamura, Y., M. Leppert, P. O'Connell, R. Wolff, T. Holm, M. Culver, C. Martin, E. Fujimoto, M. Hoff, E. Kumlin & R. White, 1987. Variable number of tandem repeat (VNTR) markers for human gene mapping. Science 235:1616–1622.
Perna, N. T., M. A. Batzer, P. L. Deininger & M. Stoneking, 1992. Alu insertion polymorphism: A new type of marker for human population studies. Hum. Biol. 64:641–648.
Quentin, Y., 1988. The Alu family developed through successive waves of fixation closely connected with primate lineage history. J. Mol. Evol. 27:194–202.
Ryan, S. C. & A. Dugaiczyk, 1989. Newly arisen DNA repeats in primate phylogeny. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 86:9360–9364.
Sanger, F., S. Nicklen & A. R. Coulson, 1977. DNA sequencing with chain terminating inhibitors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 74:5463–5467.
Sawada, I. & C. W. Schmid, 1986. Primate evolution of the α-globin gene cluster and its Alu-like repeats. J. Mol. Biol. 192:693–703.
Sawada, I., C. Willard, C.-K. J. Shen, B. Chapman, A. C. Wilson & C. W. Schmid, 1985. Evolution of Alu family repeats since the divergence of human chimpanzee. J. Mol. Evol. 22:316–322.
Schwartz, M. L., V. P. Salvatore, R. L. Hill & P. A. MacKee, 1973. Human factor XIII from plasma and platelets. J. Biol. Chem. 246:5851–5854.
Shen, M. R., M. A. Batzer & P. L. Deininger, 1991. Evolution of the master Alu gene(s). J. Mol. Evol. 33:311–320.
Slagel, V. & P. L. Deininger, 1989. In vivo transcription of a cloned prosimian SINE sequence. Nucleic Acids Res. 17:8669–8682.
Slagel, V., E. Flemington, V. Traina-Dorge, H. Bradshaw & P. L. Deininger, 1987. Clustering and subfamily relationships of the Alu family in the human genome. Mol. Biol. Evol. 4:19–29.
Stoppa-Lyonnet, D., P. E. Carter, T. Meo & M. Tosi, 1990. Clusters of intragenic Alu repeats predispose the human C1 inhibitor locus to deleterious rearrangements. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 87:1551–1557.
Tiret, L., B. Riget, S. Visvikis, C. Breda, P. Corvol, F. Cambien & F. Soubrier, 1992. Evidence from combined segregation and linkage analysis, that a variant of the angiotensin I-converting enzyme (ACE) gene controls plasma ACE levels. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 51:197–205.
Vidaud, D., M. Vidaud, B. R. Bahnak, V. Siguret, S. G. Sanchez, Y. Laurin, D. Meyer, M. Goossens & J. M. Lavergne, 1993. Hemophilia B due to a de novo insertion of a human-specific Alu subfamily member within the coding region of the factor IX gene. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 1:30–36.
Wallace, M. R., L. B. Anderson, A. M. Saulino, P. E. Gregory, T. W. Glover & F. S. Collins, 1991. A de novo Alu insertion results in neurofibromatosis type 1. Nature 353:864–866.
Webb, G. C., M. Coggan, A. Ichinose & P. G. Board, 1989. Localization of the coagulation factor XIII B subunit gene (F13B) to chromosome bands 1q31-32.1 and restriction fragment length polymorphism at the locus. Hum. Genet. 81:157–160.
Weber, J. L. & P. E. May, 1989. Abundant class of human DNA polymorphisms which can be typed using the polymerase chain reaction. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 44:388–396.
Weiner, A. M., P. L. Deininger & A. Efstratiadis, 1986. Nonviral retroposons: Genes, pseudogenes and transposable elements generated by the reverse flow of genetic information. Ann. Rev. Biochem. 55:631–661.
Willard, C., H. T. Nguyen & C. W. Schmid, 1987. Existence of at least three distinct Alu subfamilies. J. Mol. Evol. 26:180–186.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kass, D.H., Aleman, C., Batzer, M.A. et al. Identification of a human specificAlu insertion in the factor XIIIB gene. Genetica 94, 1–8 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01429214
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01429214