Summary
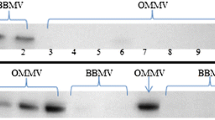
Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide (DCCD) and the 5-ethylisopropyl-6-bromo-derivative of amiloride (Br-EIPA) have been used as affinity and photoaffinity labels of the Na+/H+ exchanger in rat renal brush-border membranes. Intravesicular acidification by the Na−/H+ exchanger was irreversibly inhibited after incubation of vesicles for 30 min with DCCD. The substrate of the antiporter, Na+, and the competitive inhibitor, amiloride, protected from irreversible inhibition. The Na+-dependent transport systems for sulfate, dicarboxylates, and neutral, acidic, and basic amino acids were inhibited by DCCD, but not protected by amiloride. An irreversible inhibition of Na+/H+ exchange was also observed when brush-border membrane vesicles were irradiated in the presence of Br-EIPA. Na+ and Li+ protected. [14C]-DCCD was mostly incorporated into three brush-border membrane polypeptides with apparent molecular weights of 88,000, 65,000 and 51,000. Na+ did not protect but rather enhanced labeling. In contrast, amiloride effectively decreased the labeling of the 65,000 molecular weight polypeptide. In basolateral membrane vesicles one band was highly labeled by [14C]-DCCD that was identified as the α-subunit of the Na+, K+-ATPase. [14C]-Br-EIPA was mainly incorporated into a brushborder membrane polypeptide with apparent molecular weight of 65,000. Na+ decreased the labeling of this protein. Similar to the Na+/H+ exchanger this Na+-protectable band was absent in basolateral membrane vesicles. We conclude that a membrane protein with an apparent molecular weight of 65,000 is involved in rat renal Na+/H+ exchange.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aronson, P.S. 1983. Mechanism of active H+ secretion in the proximal tubule.Am. J. Physiol. 245:F647-F659
Aronson, P.S. 1985. Kinetic properties of the plasma membrane Na+−H+ exchanger.Annu. Rev. Physiol. 47:545–560
Aronson, P.S., Igarashi, P. 1986. Molecular properties and physiological roles of the renal Na+−H+ exchanger.In: Current Topics in Membranes and Transport. P.S. Aronson and W.F. Boron, editors. Vol. 26, pp. 57–75. Academic, New York
Azzi, A., Casey, R.P., Nalecz, M.J. 1984. The effect of N,N′-dicyclohexylcarbodiimide on enzymes of bioenergetic relevance.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 768:209–226
Azzi, A., Nalecz, M.J. 1984. Is dicyclohexylcarbodiimide a probe for proton translocating enzymes?TIBS 9:513–514
Banks, T.E., Blossey, B.K., Shafer, J.A. 1969. Inactivation of α-chymotrypsin by a water-soluble carbodiimide.J. Biol. Chem. 244:6323–6333
Benos, D.J., Mandel, L.J. 1978. Irreversible inhibition of sodium entry sites in frog skin by a photosensitive amiloride analog.Science 199:1205–1206
Biber, J., Stieger, B., Haase, W., Murer, H. 1981. A high yield preparation for rat kidney brush border membranes; different behaviour of lysosomal markers.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 647:169–176
Bradford, M. 1976. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding.Anal. Biochem. 72:248–254
Burnham, C., Münzesheimer, C., Rabon, E., Sachs, G. 1982. Ion pathways in renal brush border membranes.Biochim Biophys. Acta 685:260–272
Carraway, K.L., Koshland, D.E., Jr. 1968. Reaction of tyrosine residues in proteins with carbodiimide reagents.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 160:272–274
Carraway, K.L., Triplett, R.B. 1970. Reaction of carbodiimides with protein sulfhydryl groups.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 200:564–566
Cassel, D., Whiteley, B., Zhuang, Y.X., Glaser, L. 1985. Mitogen-independent activation of Na+/H+ exchange in human epidermoid carcinoma A431 cells: Regulation by medium osmolarity.J. Cell. Physiol. 122:178–186
Cragoe, E.J., Jr., Woltersdorf, O.W., Bicking, J.B., Kwong, S.F., Jones, J.H. 1967. Pyrazine diuretics. II. N-amidino-3-amino-5-substituted 6-halopyrazinecarboxamides.J. Med. Chem. 10:66–75
Cobb, M.H., Scott, W.N. 1981. Irreversible inhibition of sodium transport by the toad urinary bladder following photolysis of amiloride analogs.Experientia 37:68–69
Cuthbert, A.W., Edwardson, J.M. 1979. Synthesis, properties and biological activity of tritiated N-benzylamidino-3,5-diamino-6-chloro-pyrazine carboxamide—A new ligand for epithelial sodium channels.J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 31:382–386
Damiano, E., Bassilana, M., Leblanc, G. 1985. Chemical modification of the Na+−H+ antiport inEscherichia coli membrane vesicles.Eur. J. Biochem. 148:183–188
Frelin, C., Vigne, P., Lazdunski, M. 1983. The amiloridesensitive Na+/H+ antiport in 3T3 fibroblasts.J. Biol. Chem. 258:6272–6276
Frelin, C., Vigne, P., Lazdunski, M. 1984. The role of the Na+/H+ exchange system in cardiac cells in relation to the control of the internal Na+ concentration.J. Biol. Chem. 259:8880–8885
Friedrich, T., Sablotni, J., Burckhardt, G. 1985. Affinity labeling of the Na+−H+ exchanger in rat renal brush-border membrane vesicles by dicyclohexylcarbodiimide (DCCD).Pfluegers Arch. 405:R32 (Abstract)
Gorga, F.R. 1985. Inhibition of (Na+, K+)-ATPase by dicyclohexylcarbodiimide. Evidence for two carboxyl groups that are essential for enzymatic activity.Biochemistry 24:6783–6788
Grillo, F.G., Aronson, P.S. 1986. Inactivation of the renal microvillus membrane Na+−H+ exchanger by histidine-specific reagents.J. Biol. Chem. 261:1120–1125
Grinstein, S., Cohen, S., Rothstein, A. 1985. Chemical modification of the Na+/H+ exchanger of thymic lymphocytes. Inhibition by N-ethylmaleimide.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 812:213–222
Grinstein, S., Goetz-Smith, J.D., Stewart, D., Beresford, B.J., Mellors, A. 1986. Protein phosphorylation during activation of Na+/H+ exchange by phorbol esters and by osmotic shrinking.J. Biol. Chem. 261:8009–8016
Grinstein, S., Rothstein, S. 1986. Mechanisms of regulation of the Na+/H+ exchanger.J. Membrane Biol. 90:1–12
Haggerty, J.G., Cragoe, E.J., Jr., Slayman, C.W., Adelberg, E.A. 1985. Na+/H+ exchanger activity in the pig kidney epithelial cell line, LLC-PK1: Inhibition by amiloride and its derivatives.Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 127:759–767
Hoare, D.G., Koshland, D.E., Jr. 1967. A method for the quantitative modification and estimation of carboxylic groups in proteins.J. Biol. Chem. 10:2447–2453
Hopfer, U., Nelson, K., Perrrotto, J., Isselbacher, K.J. 1973. Glucose transport in isolated brush border membrane from rat small intestine.J. Biol. Chem. 248:25–33
Igarashi, P., Slayman, C.W., Aronson, P.S. 1986. Covalent modification of the renal Na/H exchanger by dicyclohexylcarbodiimide.Kidney Int. 29:369 (Abstract)
Ives, H.E., Yee, V.J., Warnock, D.G. 1983. Asymmetric distribution of the Na+/H+ antiporter in the renal proximal tubule epithelial cell.J. Biol. Chem. 258:13513–13516
Jean, T., Frelin, C., Vigne, P., Barbry, P., Lazdunski, M. 1985. Biochemical properties of the Na+/H+ exchange system in rat brain synaptosomes.J. Biol. Chem. 260:9678–9684
Khorana, H.G. 1953. The chemistry of carbodiimides.Chem. Rev. 53:145–166
Kinsella, J., Wehrle, J., Sacktor, B. 1985. Inhibition of rat renal Na+−H+ exchange by N,N′-dicyclohexylcarbodiimide in isolated brush border membrane vesicles.Fed. Proc. 44:1897 (Abstract)
Kleyman, T.R., Yulo, T., Ashbaugh, C., Landry, D., Cragoe, E.J., Jr., Karlin, A., Al-Awqati, Q. 1986. Photoaffinity labeling of the epithelial sodium channel.J. Biol. Chem. 261:2839–2843
Krulwich, T.A. 1983. Na+/H+ antiporters.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 726:245–264
Laemmli, U.K. 1970. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4.Nature (London) 227:680–685
L'Allemain, G., Franchi, A., Cragoe, E.J., Jr., Pouysségur, J. 1984. Blockage of the Na+/H+ antiport abolishes growth factor-induced DNA synthesis in fibroblasts.J. Biol. Chem. 259:4313–4319
Lazorick, K., Miller, C., Sariban-Sohrabi, S., Benos, D. 1986. Synthesis and characterization of methylbromoamiloride, a potential biochemical probe of epithelial Na+ channels.J. Membrane Biol. 86:69–77
Löw, I., Friedrich, T., Burckhardt, G. 1984. Properties of an anion exchanger in rat renal basolateral membrane vesicles.Am. J. Physiol. 246:F334-F342
Murer, H., Hopfer, U., Kinne, R. 1976. Sodium/proton antiport in brush border membrane vesicles from rat small intestine and kidney.Biochem. J. 154:597–604
Nord, E.P., Goldfarb, D., Mikhail, N., Moradeshagi, P., Hafezi, A., Vaystub, S., Cragoe, E.J., Jr., Fine, L.G. 1986. Characteristics of the Na+−H+ antiporter in the intact renal proximal tubular cell.Am. J. Physiol. 250:F539-F550
O'Farrell, P.H.D. 1975. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins.J. Biol. Chem. 250:4007–4021
Pick, U., Racker, E. 1979. Inhibition of the (Ca2+)ATPase from sarcoplasmic reticulum by dicyclohexylcarbodiimide: Evidence for location of the Ca2+ binding site in a hydrophobic region.Biochemistry 18:108–113
Pouysségur, J. 1985. The growth factor-activatable Na+/H+ exchange system: A genetic approach.TIBS 10:453–455
Rocco, V.K., Yick, D.G., Yee, V.J., Cragoe, E.J., Jr., Warnock, D.G. 1986. Amiloride protects the rabbit renal Na+/H+ antiporter against inactivation by ethoxycarbonyl-ethoxy-dihydroquinoline.Kidney Int. 29:405 (Abstract)
Sabolié, I., Burckhardt, G. 1983. Proton pathways in rat renal brush-border and basolateral membrane vesicles.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 734:210–220
Schoner, W., Schmidt, H. 1969. Inhibition of (Na++K+)-activated ATPase by N,N′-dicyclohexylcarbodiimide.FEBS Lett. 5:285–287
Schuldiner, S., Rottenberg, H., Avron, M. 1972. Determination of ΔpH in chloroplasts. 2. Fluorescent amines as a probe for the determination of ΔpH in chloroplasts.Eur. J. Biochem. 25:64–70
Solioz, M. 1984. Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide as a probe for proton translocating enzymes.TIBS 9:309–312
Vigne, P., Cragoe, E.J., Jr., Lazdunski, M. 1983. Ethylisopropylamiloride: A new and highly potent derivative of amiloride for the inhibition of the Na+/H+ exchange system in various cell types.Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 116:86–90
Vigne, P., Frelin, C., Audinot, M., Borsotto, M., Cragoe, E.J., Jr., Lazdunski, M. 1984. [3H]ethylpropylamiloride, a radio-labelled diuretic for the analysis of the Na+/H+ exchange system. Its use with kidney cell membranes.EMBO J. 3:2647–2651
Vigne, P., Frelin, C., Lazdunski, M. 1982. The amiloridesensitive Na+/H+ exchange system in skeletal muscle cells in culture.J. Biol. Chem. 257:9394–9400
Zhuang, Y.-X., Cragoe, E.J., Jr., Shaikewitz, T., Glaser, L., Cassel, D. 1984. Characterization of potent Na+/H+ exchange inhibitors from the amiloride series from A431 cells.Biochemistry 23:4481–4486
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Friedrich, T., Sablotni, J. & Burckhardt, G. Identification of the renal Na+/H+ exchanger with N,N′-dicyclohexylcarbodiimide (DCCD) and amiloride analogues. J. Membrain Biol. 94, 253–266 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01869721
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01869721