Abstract
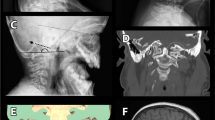
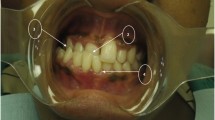
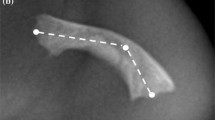
Basilar impression (BI) assessed by either plain lateral skull radiograph or computerized tomography (CT) sagittal reconstruction of the craniocervical junction is a common finding occurring in 25% of subjects with osteogenesis imperfecta (OI). It appears to occur with highest frequency in a group of subjects with OI type IVB, i.e. patients with mild/moderate liability to fractures, normal sclerae but dentinogenesis imperfecta. Neurologic signs indicating compression of posterior fossa structures occur predominantly in subjects with BI and OI type IV. Screening is recommended for all patients with OI but particularly OI type IVB.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
O'Connell JEA, Turner JWA (1950) Basilar impression of the skull. Brain 73: 405–426
Hurwitz LJ, McSwiney RR (1960) Basilar impression and osteogenesis imperfecta in a family. Brain 83: 138–149
Dirheimer Y, Babin E (1971) Basilar impression and hereditary fragility of the bones. Neuroradiology 3: 41–43
Frank E, Berger T, Tew JM (1982) Basilar impression in osteogenesis imperfecta tarda. Surg Neurol 17: 116–119
Pozo JL, Crockard HA, Ransford AO (1984) Basilar impression in osteogenesis imperfecta. J Bone Joint Surg [Br] 66: 233
Pauli RM, Gilbert EF (1986) Upper cervical cord compression as cause of death in osteogenesis imperfecta type II. J Pediatr 108: 579–581
Rush PJ, Berbrayer D, Reilly BJ (1989) Basilar impression and osteogenesis imperfecta in a three-year-old girl: CT and MRI. Pediatr Radiol 19: 142–143
Hunt TE, Dekaban AS (1982) Modified head-neck support for basilar invagination with brain-stem compression. CMA J 126: 947–948
Harkey HL, Crockard A, Stevens JM, Smith R, Ransford AO (1990) Operative management of basilar impression in osteogenesis imperfecta. Neurosurgery 27: 782–786
Sillence DO (1988) Osteogenesis imperfecta — nosology and genetics. Ann NY Acad Sci 543: 1–15
Taylor AR, Charkrovorti MS (1964) Clinical syndromes associated with basilar impression. Arch Neurol 10: 475–484
McGregor M (1948) Significance of certain measurements of skull in the diagnosis of basilar impression. Br J Radiol 21: 171–181
Chamberlain WE (1939) Basilar impression (platybasia): bizarre developmental anomaly of occipital bone and upper cervical spine with striking and misleading neurologic manifestations. Yale J Biol Med 11: 487–496
Bull JWD, Nixon WLB, Pratt RTC (1955) Radiologic criteria and familial occurrence of primary basilar impression. Brain 78: 229–247
Tsipouras P, Barabas G, Matthwes WS (1986) Neurologic correlates of osteogenesis imperfecta. Arch Neurol 43: 150–152
Byers PH, Wallis GA, Willing MC (1991) Osteogenesis imperfecta: translation of mutation to phenotype. J Med Genet 28: 433–442
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sillence, D.O. Craniocervical abnormalities in osteogenesis imperfecta: Genetic and molecular correlation. Pediatr Radiol 24, 427–430 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02011910
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02011910