Summary
The acute effects of captopril in cirrhosis are well known but there are few descriptions of the pattern of response to chronic administration of captopril in this disease. Nine nonuraemic cirrhotic patients with ascites and portal hypertension were studied after 1 week on fixed sodium and water intake (balance diet) and following acute and chronic treatment with captopril (three doses of 25 mg every 30 min and 75 mg · day−1 for three weeks, respectively).
Whilst on the balance diet, 7/9 patients were unable to excrete the amount of sodium ingested. After the acute administration of captopril, a significant reduction was seen in arterial blood pressure (86.9 vs 77 mm Hg), with no change in the intra-hepatic pressures (free suprahepatic pressure, FSHP: 15.0 vs 12.1 mmHg and wedged suprahepatic pressure, WSHP: 22.9 vs 20.7 mmHg).
After chronic captopril treatment, a drop was observed in portal pressure (FSHP: 9.4 mm Hg and WSHP 18.8 mmHg, NS) and the arterial pressure returned to its basal level.
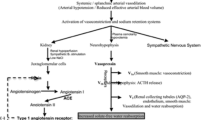
The plasma aldosterone concentration decreased, whilst noradrenaline and dopamine increased significantly, the latter more than the former, leading to a reduction in the noradrenaline/dopamine ratio (14.5 vs 5.0). Seven out of nine patients showed enhanced natriuresis and the remaining two, who previously had had a positive sodium balance failed to do so. These haemodynamic, hormonal and renal changes were interpreted as evidence of blockade of angiotensin II generation by captopril, and also as a homoeostatic response by the sympathetic nervous system.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bosch J, Arroyo V, Betriu A, Mas A, Carrilho F, Rivera F, Navarro-Lopez F, Rodes J (1980) Hepatic hemodynamics and the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system in cirrhosis. Gastroenterology 78: 92–99
Better OS, Schrier RW (1983) Disturbed volume homeostasis in patients with cirrhosis of the liver. Kidney Int 23: 303–311
Weinberger MH (1982) Role of sympathetic nervous system activity in the blood pressure response to long term captopril therapy in severely hypertensive patients. Am J Cardiol 49: 1542–1547
Riegger GAJ, Kochsiek K (1986) Vasopressin, renin and norepinephrine levels before and after captopril administration in patients with congestive heart failure due to idiopathic dilated cardiomyopathy. Am J Cardiol 58: 300–303
Caramelo C, Gomez Berne J, Salata H, Castrillo JM, Casado S, Lopez Novoa JM (1983) Captopril en et manejo hidroelectrolitico de enfermos cirroticos en descompensacion hidropica. Nefrologia III: 243–249
Lianos EA, Alavi N, Tobin M, Venuto R, Bentzel CL (1982) Angiotensin-induced sodium excretion patterns in cirrhosis: Role of renal prostaglandins. Kidney Int 21: 70–77
Hollenberg NK (1988) Renin, angiotensin and the kidney: Assessment by pharmacological interruption of the renin angiotensin system, In: Epstein M (ed) The Kidney in liver diseases. Williams & Wilkins, Baltimore
Arroyo V, Bosch J, Gaya Beltran J, Kravetz D, Estrada L, Rivera F, Rodes J (1981) Plasma renin activity and urinary sodium excretion as prognostic indicators-in non azotemic cirrhosis with ascites. Ann Intern Med 94:198–201
Armando I, Levin G, Barontini M (1983) Evaluation of sympathetic nervous system and adrenomedullary activity in normal children. J Anton Nerv System 8: 57–62
Snedecor GW, Cochran WG (1967) Statistical methods. 6th edn. IOWA State University Press, Ames, Iowa
Pariente EA, Bataille C, Bercoff E, Lebrec D (1985) Acute effects of captopril on systemic and renal hemodynamics and on renal function in cirrhotic patients with ascites. Gastroenterology 88:1255–1259
Arroyo V, Bosch J, Mauri M, Rivera F, Navarro Lopez F, Rodes J (1981) Effect of angiotensin II blockade on systemic and hepatic hemodynamics in cirrhosis with ascites. Eur J Clin Inv 11: 221–229
Erikkson SL, Kagedal B, Wohren J (1984) Effect of captopril on hepatic venous pressure and blood flow in patients with liver cirrhosis. Am J Med 31: 66–71
Schoreky K, Brenner B (1982) Body fluid homeostasis in congestive heart failure and cirrhosis with ascites. Am J Med 72: 323–338
Horovitz ZP (1980) Pharmacology and mechanism of action of inhibitors of the renin angiotensin system. In: Gross F, Liedtke RW (eds) Pharmacology and clinical use of angiotensin I converting enzyme inhibitors. Fischer, Stuttgart New York, pp 9–16
Morgunov M, Baines A (1981) Renal nerves and catecholamines excretion. Am J Physiol 240: F75-F81
Yoshimura M, Yamazaki H, Takashina R, Kambara S, Iyoda I, Sasaki S, Takahashi H, Takeda K, Hijichi H (1986) The significance of duration of salt loading on cardiovascular response and urinary excretion of catecholamine in rats. Endocrinol Japan 33: 169–175
Kim JK, Linas SL, Schrier RW (1979) Catecholamines and sodium transport in the kidney. Pharmacol Rev 31: 169–172
Morganti A, Graziani G, Salerno F, Incerti PL, Bolla G, Lorenzano E, Casati S, Ghimardi P (1985) The dopaminergic response of patients with liver cirrhosis. Kidney Int 27: 94–95
Palatini P, Dabbeni-Sala F, Finotti P (1989) Inhibition of dopamine-beta-hydroxylase by captopril. Biochem Pharmacol 38:1011–1013
Usberti M, Di Minno G, Ungaro B, Cianciaruso B, Federico S, Ardillo G, Gargiulo A, Martucci F, Pannain M, Cerbone AM, Conte G, Pecoraro C, Andreucci VE (1986) Angiotensin II inhibition with captopril on plasma ADH, PG synthesis, and renal function in humans. Am J Physiol 250: F986-F990
Suki W, Rouse D (1988) Renal tubular actions of antihypertensive agents. Kidney Int [Suppl] 25:160–161
Margolius HS, Horwitz D, Geller RG, Alexander RW, Gill JR, Pisano JJ, Keiser HR (1974) Urinary kallikrein excretion in normal man. Relationships to sodium intake and sodium retaining steroids. Cir Res 35: 812–819
Cunningham RJ, Brouhard BH (1980) Captopril and kallikrein. Lancet 1:832
Maria-Grez M, Bonner G, Gross F (1980) Captopril, kallikrein and hypertension. Lancet 1:1033
Perez Ayuso RM, Arroyo V, Camps J, Rimola A, Costa J, Gaya J, Rivera F, Rodes J (1984) Renal kallikrein excretion in cirrhotics with ascites: relationship to renal hemodynamics. Hepatology 4: 247–252
Mimran A, Jover B, Casellas D (1984) Renal adaptation to sodium deprivation. Effect of captopril in the rat. Am J Med 76: 14–21
McCaa RE, Hall JE, McCaa CS (1978) The effects of angiotensin I converting enzyme inhibitors on arterial blood pressure and urinary sodium excretion. Cir Res [Suppl 1143: 32–39
Re RN (1987) The renin angiotensin system. In: Frohlich ED (ed) Medical clinics of North America. Saunders, Philadelphia, pp 877–898
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ibarra, E.R., Afione, C., Garzon, D. et al. Portal pressure, renal function and hormonal profile after acute and chronic captopril treatment in cirrhosis. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 43, 477–482 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02285088
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02285088