Abstract
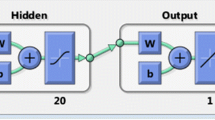
An artificial-neural-network-based detector of pharyngeal wall vibration (PWV) is presented. PWV signals the imminent occurrence of obstructive sleep apnoea (OSA) in adults who suffer from OSA syndrome. Automated detection of PWV is very important in enhancing continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) therapy by allowing automatic adjustment of the applied airway pressure by a procedure called automatic positive airway pressure (APAP) therapy. A network with 15 inputs, one output, and two hidden layers, each with two Adaline nodes, is used as part of a PWV detection scheme. The network is initially trained using nasal mask pressure data from five positively diagnosed OSA patients. The performance of the ANN-based detector is evaluated using data from five different OSA patients. The results show that on the average it correctly detects the presence of PWV events at a rate of ≅92% and correctly distinguishes normal breaths ≅98% of the time. Further, the ANN-based detector accuracy is not affected by the pressure level required for therapy.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acebo, C., Watson, R. K., Bakos, L., andThoman, E. B. (1991): ‘Sleep and apnoea in the elderly: reliability and validity of 24-hour recordings in the home’,Sleep,14, (1), pp. 56–64
Axe, J. R., Behbehani, K., Burk, J. R., Lucas, E. A., andYen, F. C. (1993): ‘Methods and apparatus for controlling sleep disorder breathing’, US patent number 5,203,343
Behbehani, K., andKang, T. (1990): ‘A microprocessor-based sleep apnoea device’. Proceedings of 11th Annual International Conference of IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology, Seattle, Washington State, pp. 332–333
Behbehani, K., Yen, F. C., Axe, J., Burk, J., andLucas, E. (1993): ‘Adaptive positive airway pressure (APAP) therapy for obstructive sleep apnoea’. Proceedings of the 15th IEEE Conference in Medicine and Biology, pp. 970–971
Behbehani, K., Yen, F.-C., Burk, J. R., Lucas, E. A., andAxe, J. R. (1995): ‘Automatic control of airway pressure for treatment of obstructive sleep apnoea’,IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng.,42, (10), pp. 1007–1016
Berthon-Jones, M. (1993): ‘Feasibility of a self-setting CPAP machine’,Sleep,16, pp. S120-S123
Berry, R. B., andBlock, A. J. (1984): ‘Positive nasal airway pressure eliminates snoring as well as obstructive sleep apnoea’,Chest,85, (1), pp. 15–20
Burk, J. R., Lucas, E. A., Axe, J. R., Behbehani, K., andYen, F. (1992): ‘Auto-CPAP in the treatment of obstructive sleep apnoea; a new approach’. 1992 Annual Meeting Abstracts, Association of Professional Sleep Societies, 6th Annual Meeting, p. 61
Daniels, B., andHarris, C. (1989): ‘Technical tidings: a simple device for detection of snoring’,APSS Newsletter,4 (1), p. 37
Fairbanks, D. N. F., Fujita, S., Ikematsu, T., andSimmons, F. B. (1987): ‘Snoring and obstructive sleep apnoea’, (Raven Press, New York)
Hoffstein, V., Chaban, R., andRubinstein, I. (1988): ‘Snoring and upper airway properties’,Chest,94, (1), pp. 87–89
Hoffstein, V., Wright, N., Zamel, N., andBradley, T. D. (1991): ‘Pharyngeal function and snoring characteristics in apenic and nonapenic snorers’,Am. Rev. Respir. Dis.,143, pp. 1294–1299
Kerby, G. R., Mayer, L. S., andPingleton, S. K. (1987): ‘Nocturnal positive pressure ventilation via nasal mask’,Am. Rev. Resp. Dis.,135, pp. 738–740
Listro, G., Stanescu, D., andVeriter, C. (1991): ‘Pattern of simulated snoring is different through mouth and nose’,J. Appl. Phy.,70, (6), pp. 2736–2741
Lugaresi, E., Cirignotta, F., Coccagna, G., andPiana, C. (1980): ‘Some epidemiological data on snoring and cardiocirculatory disturbances’,Sleep,3, pp. 221–224
Martin, R. J. (1990): ‘Cardiorespiratory disorders during sleep’, (Futura Publishing Company, Mount Kisto, NY)
Metes, A., Ohki, M., Cole, P., Haight, J. S. J., andHoffstien, V. (1991): ‘Snoring, apnoea and nasal resistance in men and women’,J. Otolaryngology,20, (1), pp. 57–61
Pasterkamp, H., Kraman, S. S., DeFrain, P. D., andWodicka, G. R. (1993): ‘Measurement of respiratory acoustical signals: comparison of sensors’,Chest,104, pp. 1518–1525
Perez-Guerra, F. (1987): ‘The treatment of obstructive sleep apnoea’,Texas Med.,83, pp. 30–33
Rechtschaffen A., andKales A. (1968): ‘A manual of standardized terminology, techniques and scoring system for sleep stages of human subjects’ (US Government Printing Office (National Institutes of Health Publication No. 204, Bethesda, MD)
Stoohs, R., andGuilleminault, C. (1992): ‘MESAM 4: an ambulatory device for the detection of patients at risk for obstructive sleep apnoea syndrome (OSAS)’,Chest,101, pp. 1221–1227
Stoohs, R., Skrobal, A., andGuilleminault, C. (1993): ‘Does snoring intensity predict flow limitations of respiratory effort during sleep’,Respiration Phys.,92, pp. 27–38
Yen, F. C. (1991): ‘Real-time detection of obstructive sleep apnoea using airway pressure’. Masters Thesis, Biomedical Engineering, The University of Texas at Arlington
Young, T., Palta, M., Dempsey, J., Skatrud, J., Weber, S., andBadr, S. (1993): ‘Prevalence and correlates of sleep disordered breathing in the Wisconsin sleep cohort study’,New England J. Med.,328, pp. 1230–1235
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Behbehani, K., Lopez, F., Yen, F.C. et al. Pharyngeal wall vibration detection using an artificial neural network. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 35, 193–198 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02530037
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02530037