Abstract
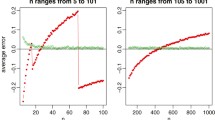
Multinomial sampling, in which the total number of sampled subjects is fixed, is probably one of the most commonly used samplig schemes in categorical data analysis. When we apply multinomial sampling to collect subjects who are subject to a random exclusion from our data analysis, the number of subjects falling into each comparison group is random and can be small with a positive probability. Thus, the application of the traditional statistics derived from large sample theory for testing equality between two independent proportions can sometimes be theoretically invalid. On the other hand, using fisher's exact test can always assure that the true type I error is less than or equal to a nominal α-level. Thus, we discuss here power and sample size calculation based on this exact test. For a desired power at a given α-level, we develop an exact sample size calculation procedure, that accounts for a random loss of sampled subjects, for testing equality between two independent proportions under multinomial sampling. Because the exact sample size calculation procedure requires intensive computations when the underlying required sample size is large, we also present an approximate sample size formula using large sample theory. On the basis of Monte Carlo simulation, we note that the power of using this approximate sample size formula generally agrees well with the desired power on the basis of the exact test. Finally, we propose a trial-and-error procedure using the approximate sample size as an initial estimate and Monte Carlo simulation to expedite the procedure for searching the minimum required sample size.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bennett, B. andHsu, P. (1960). On the power function of the exact test for the 2×2 contingency table.Biometrika, 47:393–398.
Bishop, Y., Fienberg, S., andHolland, P. (1975).Discrete Multivariate Analysis, Theory and Practice. MIT Press, Cambridge.
Casagrande, J., Pike, M., andSmith, P. (1978a). The power function of the “exact” test for comparing two binomial distributions.Applied Statistics, 27:176–180.
Casagrande, J., Pike, M., andSmith, P. (1978b). An improved approximate formula for comparing two binomial distributions.Biometrics, 34:483–486.
Fisher, R. (1935). The logic of inductive inference.Journal of Royal Statistical Society. Series A, 98:39–54.
Fleiss, J. (1981).Statistical Methods for Rates and Proportions, 2nd edn. Wiley and Sons, New York.
Fleiss, J. L., Tytun, A., andUry, H. K. (1980). A simple approximation for calculating sample sizes for comparing independent proportions.Biometrics, 36:343–346.
Gail, M. andGart, J. (1973). The determination of sample sizes for use with the exact conditional test in 2×2 comparative trials.Biometrics, 29:441–448.
Gordon, I. (1994). Sample size for two independent proportions: a review.Australian Journal of Statistics, 36:199–209.
Haseman, J. (1978). Exact sample sizes for use with the Fisher-Irwin test for 2×2 tables.Biometrics, 34:106–109.
Irwin, J. D. (1935). Test of significance for differences between percentages based on small numbers.Metron, 12:83–94.
Lui, K.-J. (1994). The effect of retaining probability variation on sample size calculations for normal variates.Biometrics, 50:297–300.
Sahai, H. andKhurshid, A. (1996). Formulas and tables for determination of sample sizes and power in clinical trials for testing differences in proportions for the two-sample design: a review.Statistics in Medicine, 15:1–21.
Skalski, J. (1992). Sample size calculations for normal variates under binomial censoring.Biometrics, 48:877–882.
Yates, F. (1934). Contingency tables involving small numbers and the χ2 test.Journal of the Royal Statistical Society, Supplement 1, pp. 217–235.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lui, KJ., Cumberland, W.G. Power and sample size calculation for 2×2 tables under multinomial sampling with random loss. Test 12, 141–152 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02595816
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02595816