Abstract
Objective:To determine the methods of evaluation used routinely by training programs and to obtain information concerning the frequencies with which various evaluation methods were used.
Design:Survey of residents who had recently completed internal medicine training.
Participants:5,693 respondents who completed residencies in 1987 and 1988 and were registered as first-time takers for the 1988 Certifying Examination in Internal Medicine. This constituted a 76% response rate.
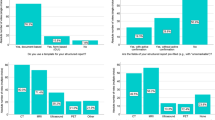
Main results:Virtually all residents were aware that routine evaluations were submitted on inpatient rotations, but were more uncertain about the evaluation process in the outpatient setting and the methods used to assess their bumanistic qualities. Most residents had undergone a Clinical Evaluation Exercise (CEX); residents’ clinical skills were less likely to be evaluated by direct observation of history or physical examination skills. Resident responses were aggregated within training programs to determine the pattern of evaluation across programs. The majority of programs used Advanced Cardiac Life Support (ACLS) certification, medical record audit, and the national In-Training Examination to assess most of their residents. Performance-based tests were used selectively by a third or more of the programs. Breast and pelvic examination skills and ability to perform sigmoidoscopy were thought not to be adequately assessed by the majority of residents in almost half of the programs.
Conclusions:While most residents are receiving routine evaluation, including a CEX, increased efforts to educate residents about their evaluation system, to strengthen evaluation in the outpatient setting, and to evaluate certain procedural skills are recommended.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Blank L, Grosso L, Benson J. A survey of clinical skills evaluation practices in internal medicine residency programs. J Med Educ. 1984;59:401–6.
Futcher P, Sanderson E, Tusler P. Evaluation of clinical skills for a specialty board during residency training. J Med Educ. 1977;52:567–77.
American Board of Internal Medicine. Guide to evaluation of residents in internal medicine 1988–89. Portland, OR: ABIM, 1988.
American Board of Internal Medicine. Evaluation of humanistic qualities in the internist. Ann Intern Med. 1983;99:720–4.
Norcini JJ, Swanson DB, Grosso LJ, Shea JA, Webster GD. A comparison of knowledge, synthesis, and clinical judgment. Eval Health Professions. 1984;7:485–500.
Lowenstein SR, Hansbrough JF, Libby LS, Hill DM, Mountain RD, Scoggin CH. Cardiopulmonary resuscitation by medical and surgical house-officers. Lancet. 1981;2:679–81.
Stillman PL, Swanson DB, Smee S, et al. Assessing clinical skills of residents with standardized patients. Ann Intern Med. 1986;105:762–71.
Stillman PL, Swanson DB. Ensuring the clinical competence of medical school graduates through standardized patients. Arch Intern Med. 1987;147:1049–52.
Swanson DB. A measurement framework for performance based tests. In: Hart IR, Hart R, Harden RM, eds. Further developments in assessing clinical competence Montreal, Quebec: Can-Heal Publications Ltd., 1987;13–45.
Mazzaferri EL, Butterfield P, Sachs L. Using nurses to evaluate residents’ humanistic behavior. Final report submitted to the American Board of Internal Medicine, 1988.
Tintinalli JE. Evaluation of emergency medicine residents by nurses. Acad Med. 1989;64:49–50.
Romm FJ, Fletcher SW, Hulka BS. The periodic health examination: comparison of recommendations and internists’ performance. South Med J 1981;74:265–71.
Lynch GR, Prout MD. Screening for cancer by residents in an internal medicine program. J Med Educ. 1986;61:387–93.
Additional information
Received from the American Board of Internal Medicine, 3624 Market Street, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania 19104. Dr. Swanson is currently on the staff of the National Board of Medical Examiners, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania.
Supported by the American Board of Internal Medicine, but this paper does not necessarily reflect the Board’s opinions or policies.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Day, S.C., Grosso, L.J., Norcini, J.J. et al. Residents’ perception of evaluation procedures used by their training program. J Gen Intern Med 5, 421–426 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02599432
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02599432