Abstract
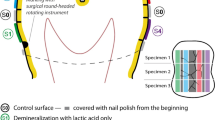
The aim of this study was to measure the strontium levels in surface and subsurface artificially decalcified enamel exposed in situ to a strontiumsupplemented toothpaste. Twenty healthy premolar teeth extracted for orthodontic reasons were cut into blocks and demineralized. The samples were cemented to the teeth of six volunteers who brushed with a hydroxyapatite (HAP) and HAP strontium-supplemented toothpaste for 3 and 6 mo. The strontium content in the enamel surface and in the lateral wall of the enamel samples was evaluated using energy-dispersive spectrometry microanalysis. After 3 mo, the strontium content in the enamel surface increased significantly compared to baseline values. On the lateral enamel surfaces, the strontium level was the same in all of the layers after 6 mo and was higher than the level observed after 3 mo. Regular toothbrushing with a strontium-supplemented toothpaste has been found to increase the strontium content in the exposed enamel, which can be an advantage in the prevention of cariogenesis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. E. J. Curzon and F. L. Losee, Strontium content of enamel and dental caries, Caries Res. 11(6), 321–326 (1977).
P. J. Marie, Effects of strontium on bone and bone cells, J. Trace Elements Med. Biol. 9, 227 (1995).
M. G. Dedhiya, F. Young, and W. I. Higuchi, Mechanism of hydroxyapatite dissolution. The synergistic effect of solution fluoride, strontium, and phosphate, J. Phys. Chem. 78(13), 1273–1279 (1974).
R. Z. Le Geros, M. A. Miravite, G. B. Quirologico, and M. E. J. Curzon, The effect of some trace elements on the lattice parameters of human and synthetic apatites, Calcif. Tissue Res. 22, 362–366 (1977).
M. E. J. Curzon and P. C. Spector, Strontium uptake and enamel dissolution in bovine and human enamel, Caries Res, 17(3), 249–252 (1983).
R. J. Herbison, and S. L. Handelman, Effect of trace elements on dissolution of hydroxyapatite by cariogenic streptococci, J. Dent. Res. 54(6), 1107–1114 (1975).
M. E. Curzon, P. C. Spector, and H. P. Iker, An association between strontium in drinking water supplies and low caries prevalence in man, Arch. Oral Biol. 23, 317–321 (1978).
M. E. J. Curzon, The relation between caries prevalence and strontium, concentrations in drinking water, plaque, and surface enamel, J. Dent. Res. 64(12), 1386–1388 (1985).
M. F. Little, and K. Barret, Trace element content of surface and subsurface enamel relative to caries prevalence on the west coast of the United States of America, Arch. Oral. Biol. 21, 651–657 (1976).
A. Surdacka, and T. Matthews-Brzozowska, Utilization of Sr ions in remineralization of artificial enamel lesion: in situ investigations, J. Dent. Res. 81 (B), 259 (2002).
A. Surdacka, The effects of strontium and saliva on in situ mineralisation of artificial enamel lesion, J. Dent. Res., 82 (C), 567 (2003).
D. Vaughan, Energy-Dispersive X-ray Microanalysis: An Introduction, Kavex Instruments, Inc., San Carlos, CA (1989).
M. J. Larsen, Chemical events during tooth dissolution, J. Dent. Res. 69, 575–580 (1990).
J. Arends, and J. Christoffersen, The nature of early lesion in enamel, J. Dent. Res. 65(1), 2–11 (1986).
C. Robinson, A. S. Hallsworth, R. C. Shore, and S. J. Kirkham, Effect of surface zone deproteinisation on the access of mineral ions into subsurface carious lesions of human enamel, Caries Res, 24(4), 226–230 (1990).
D. T. Zero, M. E. J. Curzon, and H. A. Zander, Physical and chemical effects of toothpastes on dental enamel, J. Dent. Res. 61, 451–455 (1982).
J. P. W. Valk, P. P. E. Duijsters, and C. L. Davidson, Toothbrush resistance and fluoride retention of sound, etched, fluoridated, and remineralized bovine enamel, Am. J. Orthodont. 89(4), 298–301 (1986).
M. G. Dedhiya, F. Young, and W. I. Higuchi, Mechanism for the retardation of acid dissolution rate of hydroxyapatite by strontium, J. Dent. Res. 52(5), 1097–1109 (1973).
J. D. B. Featherstone, C. P. Shields, B. Khademazad, and M. D. Oldershaw, Acid reactivity of carbonated apatites with strontium and fluoride substitutions, J. Dent. Res. 62(10), 1049–1053 (1983).
I. Gedalia, D. Almog, and S. Yariv, Effects of strontium and fluoride uptakes on solubility of powdered enamel, Caries Res. 11(5), 287–292 (1977).
F. C. M. Driessens, Mineral Aspects of Dentistry, Howard M., Myers, Philadelphia, pp. 148–153 (1982).
J. R. Mellberg, and W. G. Chomicki, Fluoride uptake by artificial caries lesions from fluoride dentifrices in vivo, J. Dent. Res. 62(5), 540–542 (1983).
C. P. Shields, M. E. J. Curzon, and J. D. B. Featherstone, Strontium concentrations in plaque and solids, Caries Res. 18(6), 495–498 (1984).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Surdacka, A., Stopa, J. & Torlinski, L. In Situ effect of strontium toothpaste on artificially decalcified human enamel. Biol Trace Elem Res 116, 147–153 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02685927
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02685927