Abstract
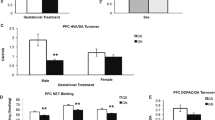
Two experiments were performed to investigate the interactive effects of prenatal coadministration of cocaine hydrochloride (C) and nicotine tartrate (N). Experiment I was designed to determine doses of C and N that could be coadministered without altering maternal gestational parameters and/or fetal viability. Exposure of Sprague-Dawley rats to combined high-dose C (20 mg/kg) and high-dose N (5.0 mg/kg) on gestation days 8–21 was not more toxic to dam or fetus than that of exposure to C alone. Experiment II investigated pregnancy outcome, postnatal development, and behavior of the offspring following drug exposure to either high-dose cocaine (20 mg/kg: CS), high-dose nicotine (5.0 mg/kg: NS), or both (NC) on gestation days 8–21. N was administered by osmotic minipump and C by sc injection. Saline-injected dams, fitted with saline-filled pumps (SS), and untreated dams, pair-fed (PF) to NC females, served as controls. Alterations in maternal variables were limited to a 10–15% decrease in food consumption in NC and CS groups. Pregnancy outcome and birth statistics were unaffected by prenatal treatment, as was offspring body weight during the first four postnatal weeks. However, the development of surface righting was delayed in CS pups, and only CS offspring were underresponsive to the stimulatory effects of dopamine agonists on activity and stereotypy. Behavioral responses to N challenge were similar in all groups. In addition, only CS offspring showed altered behavioral responses in a spontaneous alternation task. Treatment effects on dopamine D1 and D2 binding in the caudate nucleus were not observed. The combination of N and C did not exacerbate any of the behavioral changes seen in CS offspring. These results support the hypothesis that C is a behavioral teratogen in rodents, and suggest that in the present model, nicotine can mitigate some of the consequences ofin utero exposure to cocaine.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ali S. F., Slikker W. Jr., Newport G. D., and Goad P. T. (1986) Cholinergic and dopaminergic alterations in the mouse central nervous system following acute trimethyltin exposure.Acta Pharmacol. Toxicol. 59, 179–188.
Anday E. K., Cohen M. E., Kelley N. E., and Leitner D. S. (1989) Effect of in utero cocaine exposure on startle and its modification.Dev. Pharmacol. Ther. 12, 137–145.
Britos S. A. and Orsingher O. A. (1991) Prenatal nicotine exposure increased susceptibility to electroconvulsive shock (ECS) in adult rats.Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 13, 271–273.
Butler N. R. and Goldstein H. (1973) Smoking in pregnancy and subsequent child development.Br. Med. J. 4, 573,574.
Chasnoff I. J., Burns W. J., Schnoll S. H., and Bruns K. A. (1985) Cocaine use in pregnancy.N. Engl. J. Med. 313, 666–669.
Chasnoff I. J., Griffith D. R., Freier C., and Murray J. (1992) Cocaine/polydrug use in pregnancy: two-year follow-up.Pediatrics 89, 284–289.
Chavez G. F., Mulinare J., and Cordero J. F. (1989) Maternal cocaine use during early pregnancy as a risk factor for congenital urogential anomalies.JAMA 262, 795–798.
Cherukuri R., Minkoff H., Feldman J., Pardkh A., and Glass L. (1988) A cohort study of alkaloidal cocaine “crack” in pregnancy.Obstet. Gynecol. 72, 147–151.
Church M. W., Holmes P. A., Overbeck G. W., Tilak J. P., and Zajac C. S. (1991) Interactive effects of prenatal alcohol and cocaine exposures on postnatal mortality, development and behavior in the Long-Evans rat.Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 13, 377–386.
Church M. W. and Overbeck G. W. (1991) Sensorineural hearing loss as evidenced by the auditory brainstem response following prenatal cocaine exposure in the Long-Evans rat.Teratology 43, 561–570.
Church M. W. and Overbeck G. W. (1990a) Prenatal cocaine exposure in the Long-Evans rat: III. Developmental effects on the brainstem auditory-evoked potential.Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 12, 345–351.
Church M. W. and Overbeck G. W. (1990b) Prenatal cocaine exposure in the Long-Evans rat: II. Dose-dependent effects on offspring behavior.Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 12, 335–343.
Church M. W., Overbeck G. W., and Andrezejczak A. L. (1990) Prenatal cocaine exposure in the Long-Evans rat: I. Dose-dependent effects on gestation, mortality, and postnatal maturation.Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 12, 327–334.
Church M. W. and Rauch H. C. (1992) Prenatal cocaine exposure in the laboratory mouse: effects on maternal water consumption and offspring outcome.Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 14, 313–319.
Clow D. W., Hammer R. P. Jr. Kirstein C. L., and Spear L. P. (1991) Gestational cocaine exposure increases opiate receptor binding in weanling offspring.Brain Res. Dev. Brain Res. 59, 179–185.
Cohen M. E., Anday E. K., and Leitner D. S. (1989) Effects of in utero cocaine exposure on sensorineural reactivity. inPrenatal Use of Licit and Illicit Drugs (Hutchings D. E., ed.), New York Academy of Sciences, New York pp. 344–346.
Douglas R. J., Peterson J. J., and Douglas D. P. (1973) The ontogeny of a hippocampus-dependent response in two rodent species.Behav. Biol. 8, 27–37.
Dow-Edwards D. L. (1991) Cocaine effects on fetal development: a comparison of clinical and animal research findings.Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 13, 347–352.
Duhart H. M., Fogel C. M., Gillam M. P., Bailey J. R., Slikker W. Jr., and Paule M. G. (1993) Pharmacokinetics of cocaine in pregnant and nonpregnant rhesus monkeys.Reproduct. Toxicol. 7, 429–437.
Edwards J. A. and Warburton D. M. (1984) Smoking, nicotine, and electrocortical activity, inNicotine and the Smoking Habit (International Encyclopedia of Pharmacology and Tobacco Therapeutics) (Balfour D. J. K., ed.), Pergamon NY pp. 113–131.
Ellis J. E., Byrd L. D., Sexson W. R., and Patterson-Barnett C. A. (1993) In utero exposure to cocaine: a review.S. Med. J. 86, 725–731.
Eriksson M., Larsson G., Zetterstrom R. (1979) Abuse of alcohol, drugs and tobacco during pregnancy: consequences for the child.Paediatrician 8, 228–242.
Feng T. (1993) Substance abuse in pregnancy.Curr. Opin. Obstet. Gynecol. 5, 16–23.
Foss J. A. and Riley E. P. (1991a) Elicitation and modification of the acoustic startle reflex in animals prenatally exposed to cocaine.Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 13, 541–546.
Foss J. A. and Riley E. P. (1991b) Failure of acute cocaine administration to differentially affect acoustic startle and activity in rats prenatally exposed to cocaine.Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 13, 547–551.
Fulroth R., Phillips B., and Duran D. J. (1989) Perinatal outcome of infants exposed to cocaine and/or heroin in utero.Am. J. Dis. Child 143, 905–910.
Fung Y. K. (1989) Postnatal effects of maternal nicotine exposure on the striatal dopaminergic system in rats.J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 41, 576–578.
Fung Y. K. and Lau Y. S. (1989) Effects of prenatal nicotine exposure on rat striatal dopaminergic and nicotine systems.Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 33, 1–6.
Graham K., Feigenbaum A., Pastuszak A., Nulman I., Weksberg R., Einarson T., Goldberg S., Ashby S., and Koren G. (1992) Pregnancy outcome and infant development following gestational cocaine use by social cocaine users in Toronto, Canada.Clin. Invest. Med. 15, 384–394.
Henderson M. G., McConnaughey M. M., and McMillen B. A. (1991) Long-term consequences of prenatal exposure to cocaine or related drugs: effects on rat brain monoaminergic receptors.Brain Res. Bull. 26, 941–945.
Henderson M. G. and McMillen B. A. (1990) Effects of prenatal exposure to cocaine or related drugs on rat developmental and neurological indices.Brain Res. Bull. 24, 207–212.
Heyser C. J., Chen W. J., Miller J., Spear N. E., and Spear L. P. (1990) Prenatal cocaine exposure induces deficits in Pavlovian conditioning and sensory preconditioning among infant rat pups.Behav. Neurosci. 104, 955–963.
Heyser C. J., Molina V. A., and Spear L. P. (1992) A fostering study of the effects of prenatal cocaine exposure: I. Maternal behaviors.Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 415–421.
Hoyme H. E., Jones K. L., and Dixon S. D. (1990) Prenatal cocaine exposure and fetal vascular disruption.Pediatrics 85, 743–747.
Hutchings D. E., Fico T. A., and Dow-Edwards D. L. (1989) Prenatal cocaine: maternal toxicity, fetal effects and locomotor activity in rat offspring.Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 11, 65–69.
Johns J. M., Means L. W., Means M. J., and McMillen B. A. (1992a) Prenatal exposure to cocaine. I: Effects on gestation, development and activity in Sprague-Dawley rats.Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 14, 337–342.
Johns J. M., Means M. J., Anderson D. R., Means L. W., and McMillen B. A. (1992b) Prenatal exposure to cocaine II: Effects on open-field activity and cognitive behavior in Sprague-Dawley rats.Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 15, 342–349.
Kain Z. N., Kain T. S., and Scarpelli E. M. (1992) Cocaine exposure in utero: perinatal development and neonatal manifestations—review.J. Toxicol. Clin. Toxicol. 30, 607–636.
King J. A., Davilla-Gracia M., Azmitia E. C., and Strand F. L. (1991) Differential effects of prenatal and postnatal ACTH or nicotine exposure on 5-HT high affinity uptake in the neonatal rat brain.Int. J. Dev. Neurosci. 9, 281–286.
Kirk R. E. (1968)Experimental Design: Procedures for the Behavioral Sciences. Brooks/Cole, Belmont, CA.
Lester B. M., Corwin M. J., Sepkosi C., Seifer R., Peucker M., McLaughlin S., and Golub H. L. (1991) Neurobehavioral syndromes in cocaine-exposed newborn infants.Child Dev. 62, 694–705.
Levin E. D., Briggs S. J., Christopher N. C., and Rose J. E. (1993) Prenatal nicotine exposure and cognitive performance in rat.Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 15, 251–260.
Lichtensteiger W., Ribary U., Schlumpf M., Odermatt B., and Widmer H. R. (1988) Prenatal adverse effects of nicotine on the developing brain.Prog. Brain Res. 73, 137–157.
Longo L. O. (1977) The biological effects of carbon monoxide on the pregnant women, fetus, and the newborn infant.Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 129, 69–103.
Lord F. M. (1953) On the statistical treatment of football numbers.Am. Psychol. 8, 750,751.
Lowry O. H., Rosenbrough N. I., Farr A. L., and Randall R. J. (1951) Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent.J. Biol. Chem. 193, 265–275.
Martin J. C. and Becker R. F. (1971) The effects of maternal nicotine absorption or hypoxic episodes upon appetitive behavior of rat offspring.Dev. Psychobiol. 4, 133–147.
Meyer D. C. and Carr L. A. (1987) The effects of perinatal exposure to nicotine on plasma LH levels in prepubertal rats.Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 9, 95–98.
Miller L. G. (1990) Cigarettes and drug therapy: pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic considerations.Clin. Pharm. 9, 125–135.
Naeye R. L. (1978) Effects of maternal cigarette smoking on the fetus and placenta.Br. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 85, 732–737.
Navarro H. A., Mils E., Seidler F. J., Baker F. E., Lappi S. E., Tayyeb M. I., Spencer J. R., and Slotkin T. A. (1990a) Prenatal nicotine exposure impairs beta-adrenergic function: persistent chronotropic subsensitivity despite recovery from deficits in receptor binding.Brain Res. Bull. 25, 233–237.
Navarro H. A., Slotkin T. A., Tayyeb M. I., Lappi S. E., and Seidler F. J. (1990b) Effects of fetal nicotine exposure on development of adrenergic receptor binding in rat brain regions: selective changes in alpha1-receptors.Res. Commun. Subst. Abuse 11, 95–104.
Nayak P. K., Misra A. L., and Mule S. J. (1976) Physiological disposition and biotransformation of [3H]cocaine in acutely and chronically treated rats.J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 196, 556–569.
Riley E. P. and Foss J. A. (1991) Exploratory behavior and locomotor activity: a failure to find effects in animals prenatally exposed to cocaine.Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 13, 553–558.
Rose K. J. and Strand F. L. (1991) A sensitive period in gestation for nicotine acceleration of neuromuscular maturation.Int. J. Dev. Neurosci. 9, 297–305.
Ryan L., Ehrlich S., and Finnegan L. (1987) Cocaine abuse in pregnancy: effects on the fetus and the newborn.Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 9, 295–299.
Sastry B. V. R. (1991) Placental toxicology: tobacco smoke, abused drugs, multiple chemical interaction, and placental function.Reprod. Fertil. Dev. 3, 355–372.
Scalzo F. M. and Holson R. R. (1992) The ontogeny of behavioral sensitization to phencyclidine.Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 14, 7–14.
Scalzo F. M., Ali S. F., Frambes N. A., and Spear L. P. (1990) Wealling rats exposed prenatally to cocaine exhibit an increase in striatal D2 dopamine binding associated with an increase in ligand affinity.Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 33, 371–373.
Scanlon J. W. (1991) the neuroteratology of cocaine: background theory and clinical implications.Reproduct. Toxicol. 5, 89–98.
Segarra A. C. and Strand F. L. (1989) Perinatal administration of nicotine alters subsequent sexual behavior and testosterone levels of male rats.Brain Res. 480, 151–159.
Seifert M. F. and Church M. W. (1991) Long term effects of prenatal cocaine exposure on bone in rats.Life Sci. 48, 569–574.
Siegel S. (1956)Nonparametric Statistics for the Behavioral Sciences McGraw-Hill, New York.
Smith R. F., Mattran K. M., Kurkjian M. F., and Kurtz S. L. (1989) Alterations in offspring behavior induced by chronic prenatal cocaine dosing.Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 11, 35–38.
Sobrian S. K. and Nandedkar A. K. N. (1986) Prenatal antiepileptic drug exposure alters seizure susceptibility in rats.Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 24, 1383–1391.
Sobrian S. K., Burton L. E., Robinson N. L., Ashe W. K., James H., Stokes D. L., and Turner L. M. (1990) Neurobehavioral and immunological effects of prenatal cocaine exposure in rat.Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 35, 617–629.
Sorenson C. A., Raskin L. A., and Suh Y. (1991) The effects of prenatal nicotine on radial-arm maze performance in rats.Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 40, 991–994.
Spear L. P., Frambes N. A., and Kirstein C. L. (1989a) Fetal and maternal brain and plasma levels of cocaine and benzoylecgonine following chronic and subcutaneous administration of cocaine during gestation in rats.Psychopharmacology 97, 427–431.
Spear L. P., Kirstein C. L., Bell J., Yoottanasumpun V., Greenbaum R., O’Shea J., Hoffman H., and Spear N. E. (1989b) Effects of prenatal cocaine exposure on behavior during the early postnatal period.Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 11, 57–63.
Spear L. P., Kirstein C. L. and Frambes N. A. (1989c) Cocaine effects on the developing central nervous system: behavioral, psychopharmacological, and neurochemical studies.Ann. NY Acad. Sci. 562, 290–307.
Wang C. H. and Schnoll S. H. (1987) Prenatal cocaine use associated with down regulation of receptors in human placenta.Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 9, 301–304.
Wilson J. G. (1965) Embryological considerations in teratology, inTeratology: Principles and Techniques (Wilson J. G. and Warkany J., eds.), University of Chicago Press, chicago, IL, pp. 251–277.
Zahalka E. A., Seidler F. J., Lappi S. E., McCook E. C., Yanai J., and Slotkin T. A. (1992) Deficits in development of central cholinergic pathways caused by fetal nicotine exposure: differential effects on choline acetyltransferase activity and [3H]hemicholinium-3 binding.Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 14, 375–382.
Zahalka E. A., Seidler F., Yanai J., and Slotkin T. A. (1993) Fetal nicotine exposure alters ontogeny of M1-receptors and their link to G-proteins.Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 15, 107–115.
Zuckerman B. and Bresnahan K. (1991) Developmental and behavioral consequences of prenatal drug and alcohol exposure.Pediatr. Clin. North Am. 38, 1387–1406.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sobrian, S.K., Ali, S.F., Slikker, W. et al. Interactive effects of prenatal cocaine and nicotine exposure on maternal toxicity, postnatal development, and behavior in the rat. Mol Neurobiol 11, 121–143 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02740690
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02740690