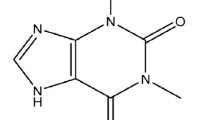
Summary
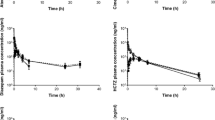
Six beagles received intravenous and oral doses of 50 mg/kg phenacetin. Plasma concentrations of phenacetin, paracetamol, andp-phenetidin were determined and pharmacokinetic parameters calculated.
Phenacetin showed rate constants for absorption and elimination of 0.025 and 0.033 (min−1) and an apparent metabolic clearance rate of about 350 ml/min. Paracetamol andp-phenetidin elimination rate constants were 0.02 and 0.015 (min−1), respectively.
There was no difference in pharmacokinetics or metabolic pattern between both routes of phenacetin administration.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kampffmeyer, H. G., 1974, Metabolic rate of phenacetin and of paracetamol in dogs before and after treatment with phenobarbital or SKF 525 A. Biochem. Pharmacol.,23, 713–724.
Kiese, M., Renner, G., 1966, The hydrolysis of acetanilide and some of its derivatives by enzymes in the microsomal and soluble fraction prepared from livers of various species. Arch. exp. Path. Pharmak.,252, 480–500.
Brodie, B. B., Axelrod, J., 1948, The estimation of acetanilide and its metabolic products, aniline, N-acetyl-p-aminophenol andp-aminophenol (free and total conjugated) in biological fluids and tissues. J. Pharmac. exp. Ther.,94, 22–28.
Brodie, B. B., Axelrod, J., 1949, The fate of acetophenetidin (phenacetin) in man and methods for the estimation of acetophenetidin and its metabolites in biological material. J. Pharmac. exp. Ther.,97, 58–67.
Kampffmeyer, H. G., 1971, Elimination of phenacetin and phenazone by man before and after treatment with phenobarbital. Europ. J. clin. Pharmacol.,3, 113–118.
Kiese, M., 1959, Oxidation of Anilin zu Nitrosobenzol im Hunde. Arch. exp. Path. Pharmak.,235, 354–359.
Albert, K. S., Sedman, A. J., Wagner, J. G., 1974, Pharmacokinetics of orally administered acetaminophen in man. J. Pharmacokin. Biopharm.,2, 381–393.
Wagner, J. G., 1974, Application of the Wagner-Nelson absorption method to the two-compartment open model. J. Pharmacokin. Biopharm.,2, 469–486.
Shoemaker, W. C, 1960, Measurement of hepatic blood flow in the unanesthetized dog by a modified bromsul-phthalein method. J. Appl. Physiol.,15, 473–478.
Smith, R. L., Timbrell, J. A., 1974, Factors affecting the metabolism of phenacetin. I. Influence of dose, chronic dosage, route of administration and species on the metabolism of (1−14C-acetyl) phenacetin. Xenobiotica,8, 489–501.
Pantuck, E. J., Hsiao, K. C., Kuntzmann, R., Conney, A. H., 1975, Intestinal metabolism of phenacetin in the rat: Effect of charcoal-broiled beef and rat chow. Science,187, 744–746.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Souchay, S., Wörner, A., Kampffmeyer, H.G. et al. Comparison of the pharmacokinetics of phenacetin in beagles after oral or intravenous administration. European Journal of Drug Metabolism and Pharmacokinetics 1, 21–24 (1976). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03192275
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03192275