Abstract
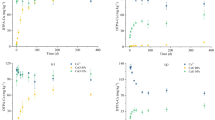
The bioavailability of copper in contaminated soils has received more attention due to the safety concern of food chain. The bioavailability of metals is determined by its fractions which are affected by the soil properties and its aging time. This paper focused on the aging effect on the bioavailability of copper added to the soil. The garden soil (fluvo aquic soil) was treated with 100 mg/kg and 1000 mg/kg of copper(II) sulfate and incubated for 14, 21, 28, 42, 63, 120, 200, 300 and 400 days in the laboratory respectively. The sequential extraction procedure was used to characterize copper bioavailability in the soil. Meanwhile, the barley was cultured on the same soil incubated and its toxicity was assessed according to the guideline of International Organization for Standardization. The findings show that the exchangeable and carbonate-bound copper decreased with the aging time after addition of copper(II) sulfate to soil. Meanwhile, the percentages of Fe-Mn oxides- and organic-bound copper increased. The residual copper was changed little during the aging course. The copper fractions became stable in soils after 60 days. The kinetic equations showed that the Power function and the Elovich equation were well fitted to the experimental data, and the r2 values ranged from 0.840 to 0.982 and 0.741 to 0.975, respectively. The barley test showed that the barley root length was more sensitive to reflect copper toxicity than the shoot biomass, and the exchangeable and carbonate-bound copper were significantly correlated with the barley root length.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alexander, M., (2000). Ageing, Bioavailability and Overestimation of Risk from Environmental Pollutants. Environ. Sci. Tech., 34(20), 4259–4265 (7 pages).
Ammann, L.; Bergaya, F.; Lagaly, G., (2005). Determination of the cation exchange capacity of clays with copper complexes revisited. Clay Minerals, 40(4), 441–453 (13 pages).
Arias-Estévez, M.; Nóvoa-Muńoz, J. C.; Pateiro, M.; López-Periago, E., ( 2007). Influence of aging on copper fractionation in an acid soil. Soil Sci., 172(3), 225–232 (8 pages).
Ayari, F.; Hamdi, H.; Jedidi, N.; Gharbi, N.; Kossai, R., (2010). Heavy metal distribution in soil and wheat plants in municipal solid waste compost-amended plots. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Tech., 7(3), 465–472 (8 pages).
Balasoiu, C. F.; Zagury, G. J.; Deschznes, L., (2001). Partitioning and speciation of chromium, copper, and arsenic in CCA-contaminated soils: influence of soil composition. Sci. Total Environ., 280(1–3), 239–255 (17 pages).
Chhabra, R.; Pleysier, J.; Cremers, A., (1975). The measurement of the cation exchange capacity and exchangeable cation in soils: A new method. Proceedings International Clay Conference, Mexico City, Mexico, 439–449 (11 pages).
Chojnacka, K.; Chojnacki, A.; Góecka, H.; Góecki, H., (2005). Bioavailability of heavy metals from polluted soils to plants. Sci. Total Environ., 337(1–3), 175–182 (8 pages).
Elzinga, E. J.; Rouff, A. A.; Reeder, R. J., (2006). The long-term fate of Cu2+, Zn2+, and Pb2+ adsorption complexes at the calcite surface: An X-ray absorption spectroscopy study. Geochim. Cosmochim. Ac., 70(11), 2715–2725 (11 pages).
Filgueiras, A. V.; Lavilla, I.; Bendicho, C., (2002). Chemical sequential extraction for metal partitioning in environmental solid samples. J. Environ. Monitor., 4(6), 823–857 (35 pages).
Ginocchio, R.; Sinchez, P.; de la Fuente, L. M.; Camus, I.; Bustamante, E. S. Y.; Urrestarazu, P.; Torres, J. C.; Rodriguez, P. H., (2006). Agricultural soils spiked with copper mine wastes and copper concentrate: Implications for copper bioavailability and bioaccumulation. Environ. Toxicol. Chem., 25(3), 712–718 (7 pages).
International Organization for Standardization, (1993). Soil quality—Determination of the effects of pollutants on soil flora—Part 1: Method for the measurement of inhibition of root growth. Geneva, Switzerland.
International Organization for Standardization, (1995). iSoil quality—Determination of the effects of pollutants on soil flora—Part 2: Effects of chemicals on the emergence and growth of higher plants. Geneva, Switzerland.
Jalali, M.; Khanlari, Z. V., (2008). Effect of aging process on the fractionation of heavy metals in some calcareous soils of Iran. Geoderma, 143(1–2), 26–40 (15 pages).
Kidd, P. S.; Domķnguez-Rodrķguez, M. J.; Dķez, J.; Monterroso, C., (2007). Bioavailability and plant accumulation of heavy metals and phosphorus in agricultural soils amended by long-term application of sewage sludge. Chemosphere, 66(8), 1458–1467 (10 pages).
Li, H. F.; Gray, C.; Mico, C.; Zhao, F. J.; McGrath, S. P., (2009). Phytotoxicity and bioavailability of cobalt to plants in a range of soils. Chemosphere, 75(7), 979–986 (8 pages)
Lu, A. X.; Zhang, S. H.; Qin, X. Y.; Wu, W. Y.; Liu, H. L., (2009). Aging effect on the mobility and bioavailability of copper in soil. J. Environ. Sci., 21(2), 173–178 (6 pages).
Ma, Y. B.; Lombi, E.; Oliver, I. W.; Nolan, A. L.; McLaughlin, M. J., (2006a). Long-term aging of copper added to soils. Environ. Sci. Tech., 40(20), 6310–6317 (8 pages).
Ma, Y. B.; Lombi, E.; Nolan, A. L.; McLaughlin, M. J., (2006b). Short-term natural attenuation of copper in soils: Effects of time, temperature, and soil characteristics. Environ. Toxicol. Chem., 25(3), 652–658 (7 pages).
McGrath, S. P.; Cunliffe, C. H., (1985). A simplified method for the extraction of the metals Fe, Zn, Cu, Ni, Cd, Pb, Cr, Co, and Mn from soils and sewage sludges. J. Sci. Food Agr., 36(9), 794–798 (5 pages).
Nabulo, G.; Oryem Origa, H.; Nasinyama, G. W.; Cole, D., (2008). Assessment of Zn, Cu, Pb and Ni contamination in wetland soils and plants in the Lake Victoria basin. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Tech., 5(1), 65–74 (10 pages).
Navas, A.; Lindhorfer, H., (2003). Geochemical speciation of heavy metals in semiarid soils of the central Ebro Valley (Spain). Environ. Int., 29(1), 61–68 (8 pages).
Nouri, J., (1980). Heavy metals in sewage sludge, soils amended with sludge and their uptake by crop plants. Ph.D. Thesis, University of London, London, UK.
Nouri, J.; Lorestani, B.; Yousefi, N.; Khorasani, N.; Hasani, A. H.; Seif, S.; Cheraghi, M., (2011). Phytoremediation potential of native plants grown in the vicinity of Ahangaran lead-zinc mine (Hamedan, Iran). Environ. Earth Sci., 62(3), 639–644 (6 pages).
Oorts, K.; Gesquiere, U.; Swinnen, K.; Smolders, E., (2006). Soil properties affecting the toxicity of CuCl2 and NiCl2 for soil microbial processes in freshly spiked soils. Environ. Toxicol. Chem., 25(3), 836–844 (9 pages).
Petersen, T. A.; Hansen, H. C. B.; Nybroe, O., (2004). Time and moisture effects on total and bioavailable copper in soil water extracts. J. Environ. Qual., 33(2), 505–512 (8 pages).
Quazi, S.; Sarkar, D.; Datta, R., (2010). Effect of soil aging on arsenic fractionation and bioaccessibility in inorganic arsenical pesticide contaminated soils. Appl. Geochem., 25(9), 1422–1430 (8 pages).
Rooney, C. P.; Zhao, F. J.; Mcgrath, S. P., (2006). Soil factors controlling the expression of copper toxicity to plants in a wide range of European soils. Environ. Toxicol. Chem., 25(3), 726–732 (7 pages).
Rooney, C. P.; Zhao, F. J.; Mcgrath, S. P., (2007). Phytotoxicity of nickel in a range of European soils: Influence of soil properties, Ni solubility and speciation. Environ. Poll., 145(2), 596–605 (10 pages).
Schat, H.; Ten Bookum, W. M., (1992). Genetic control of copper tolerance in Silene vulgaris. Heredity, 68, 219–229 (11 pages).
Shirvani, M.; Shariatmadari, H.; Kalbasi, M., (2007). Kinetics of cadmium desorption from fibrous silicate clay minerals:Influence of organic ligands and aging. Appl. Clay Sci., 37(1–2), 175–184 (10 pages).
Stone, M.; Marsalek, J., (1996). Trace metal composition and speciation in street sediment: Sault Ste. Marie, Canada. Water Air Soil Poll., 87(1–4), 149–169 (21 pages).
Tagami, K.; Uchida, S., (1998). Aging effect on bioavailability of Mn, Co, Zn and Tc in Japanese agricultural soils under waterlogged conditions. Geoderma, 84(1–3), 3–13 (11 pages).
Tessier, A.; Campbell, P. G.; Blsson, M., (1979). Sequential extraction procedure for the speciation of particulate trace metals. J. Analys. Chem., 51(7), 844–851 (8 pages).
Xu, M. G.; Wang, B. Q.; Zhou, S. W.; Li, S. Q.; Chen, M. M.; Duan, G. L., (2008). Aging characteristics of copper and zinc added to typical soils of China. Environ. Sci., 29(11), 3213–3218 (6 pages).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, G., Yuan, T., Wang, W. et al. Effect of aging on bioavailability of copper on the fluvo aquic soil. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 8, 715–722 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03326256
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03326256