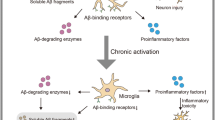
Abstract
The role of interleukin 1 (IL-1) and interleukin 6 (IL-6) in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is reviewed within the framework of “inflammaging”, i.e., the characteristic chronic pro-inflammatory status which develops in old age, and neuroinflammation, i.e., the peculiar inflammatory process which is present in the brain of AD patients. In particular, the data suggesting that several IL-1 and IL-6 gene polymorphisms can contribute to the risk of developing AD are reviewed. The possibility as well as the difficulty in identifying a pro-inflammatory phenotype, and its importance for the prevention, diagnosis and therapy of AD and other age-related pathologies are discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chapman P.F., Falinska A.M., Knevett S.G., Ramsay M.F.: Genes, models and Alzheimer’s disease. Trends Genet. 17: 254–261, 2001
Akiyama H., Barger S., Barnum S., Bradt B., Bauer J., Cole G.M., Cooper N.R., Eikelenboom P., Emmerling M., Fiebich B.L., Finch C.E., Frautschy S., Griffin W.S., Hampel H., Hull M., Landreth G., Lue L., Mrak R., Mackenzie I.R, McGeer P.L, O’Banion M.K., Pachter J., Pasinetti G., Plata-Salaman C., Rogers J., Rydel R., Shen Y., Streit W., Strohmeyer R., Tooyoma I., Van Muiswinkel F.L., Veerhuis R., Walker D., Webster S., Wegrzyniak B., Wenk G., Wyss-Coray T.: Inflammation and Alzheimer disease. Neurobiol. Aging 21: 383–421, 2000.
Selkoe D.J.: Alzheimer’s disease: genes, proteins, and therapy. Physiol. Rev. 81: 741–766, 2001.
Franceschi C., Motta L., Valensin S., Rapisarda R., Franzone A., Berardelli M., Motta M., Monti D., Bonafé M., Ferrucci L., Deiana L., Pes G., Carru C., Desole S., Barbi C., Gemelli C., Lescai F., Olivieri F., Marchegiani F., Cardelli M., Cavallone L., Gueresi P., Cossarizza A., Troiano L., Pini G., Sansoni P., Passeri G., Lisa R., Spazzafumo L., Amadio L., Giunta S., Stecconi R., Morresi R., Viticchi C., Mattace R., De Benedictis G., Baggio G. and the Italian Multicenter Study on Centenarians (IMUSCE): Do men and women follow different trajectories to reach extreme longevity? Aging Clin. Exp. Res. 12: 77–84, 2000.
Carrieri G., Bonafè M., De Luca M., Rose G., Varcasia O., Bruni A., Nacmias B., Sorbi S., Corsonello F., Feraco E., Andreev K.F., Yashin A.I., Franceschi C., De Benedictis G.: Mitochondrial DNA haplogroups and ApoE4 allele are non independent variables in sporadic Alzheimer’s disease. Hum. Genet. 108: 194–198, 2001.
Bonilla E., Kurenai T., Hirano M., Tuan H.V., Di Mauro S., Shon E.A.: Mitochondrial involvement in Alzheimer’s disease. Biochem. Biophys. Acta 1410: 1712–182, 1999.
Ruiz-Pesini E., Lapena A.C., Dièz-Sanchez C., Pérez-Martos A., Mantoya J., Alvarez E., Diaz M., Urriés A., Montoro L., Lopez-Perez M.J., Enriquez J.A.: Human mtDNA haplogroups associated with high or reduced spermatozoa motility. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 67:682-696, 2000.
Esposito L.A., Melov S., Panov A., Cottrell B. A., Wallace D.C.: Mitochondrial disease in mouse results in increased oxidative stress. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 96: 4820–4825, 1999.
Fassbender K., Masters C., Beyreuther K.: Alzheimer disease: an inflammatory disease? Neurobiol. Aging 21: 433–436, 2000.
Ravaglia G., Forti P., De Ronchi D., Maioli F., Nesi B., Cucinotta D., Bernardi M., Cavalli G.: Prevalence and severity of dementia among northern Italian centenarians. Neurology 53: 416–418, 1999.
Franceschi C., Bonafè M., Valensin S, Olivieri F., De Luca M., Ottaviani E., De Benedictis G.: Inflamm-aging: an evolutionary perspective of immunosenescence. Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. 908: 208–218, 2000.
Franceschi C., Valensin S., Bonafè M., Paolisso P., Yashin A., De Benedictis G.: The network and the remodelling theories of aging. Exp. Gerontol. 35: 879–896, 2000.
Franceschi C., Valensin S., Fagnoni F., Barbi C., Bonafè M.: Biomarkers of immunosenescence within an evolutionary perspective: the challenge of heterogeneity and the role of anti-genic load. Exp. Gerontol. 34: 911–921, 1999.
Franceschi C., Bonafè M., Valensin S.: Human immunose-nescence: the prevailing of innate immunity, the failing of clonotypic immunity, and the filling of immunological space. Vaccine 18:1717-1720, 2000.
Ottaviani E., Franchini A., Franceschi C.: Pro-opiome-lanocortin-derived peptides, cytokines and nitric oxide in immune responses and stress: an evolutionary approach. Int. Rev. Cytol. 170: 79–142, 1997.
Ottaviani E., Franceschi C.: The invertebrate phagocytic immunocyte: clues to a common evolution of the immune and the endocrine systems. Immunol. Today 18: 169–174, 1997.
Raine C.S.: Inflammation in Alzheimer’s disease: a view from the periphery. Neurobiol. Aging 21: 437–440, 2000.
Fagiolo U., Cossarizza A., Scala E., Fanales-Belasio E., Ortolani C., Cozzi E., Monti D., Franceschi C., Paganelli R.: Increased cytokine production in mononuclear cells of healthy elderly people. Eur. J. Immunol. 23: 2375–2378, 1993.
Bruunsgaard H., Pedersen M., Pedersen B.K.: Aging and proinflammatory cytokines. Curr. Opin. Hematol. 8: 131–136, 2001.
Dumont P., Balbeur L., Remacle J., Toussaint O.: Appearance of biomarkers of in vitro ageing after successive stimulation of WI-38 fibroblasts with IL-1 and TNF-: senescence associated-galactosidase activity and morphotype transition. J. Anat. 197: 529–537, 2000.
Ershler W.B., Keller E.T.: Age-associated increased inter-leukin-6 gene expression, late-life diseases, and frailty. Annu. Rev. Med. 51: 245–270, 2000.
Baggio G., Donazzan S., Monti D., Mari D., Martini S., Gabelli C., Dalla Vestra M., Previato L., Guido M., Pigozzo S., Cortella I., Crepaldi G., Franceschi C.: Lipoprotein(a) and lipoprotein profile in healthy centenarians: a reappraisal of vascular risk factors. FASEB J. 12: 433–437, 1998.
Bethin K.E., Vogt S.K., Muglia L.J.: Interleukin-6 is an essential, corticotropin-releasing hormone-independent stimulator of the adrenal axis during immune system activation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 97: 9317–9322, 2000.
Xing Z., Gauldie J., Cox G., Baumann H., Jordana M., Lei X-F., Achong M.K.: IL-6 is an Antiinflammatory Cytokine Required for Controlling Local or Systemic Acute Inflammatory Responses. J. Clin. Invest. 101: 311–320, 1998.
Mysliwska J., Bryl E., Foerster J., Mysliwski A.: Increase of interleukin 6 and decrease of interleukin 2 production during the ageing process are influenced by the health status. Mech. Ageing Dev. 100: 313–328, 1998.
Young D.G., Skibinski G., Mason JI., James K.: The influence of age and gender on serum dehydroepiandrosterone sulphate (DHEA-S), IL-6, IL-6 soluble receptor (IL-6 sR) and transforming growth factor 1 (TGF-1) levels in normal healthy blood donors. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 117: 476–481, 1999.
Ferrucci L., Harris T.B., Guralnik J.M., Tracy R.P., Corti M.C., Cohen H.J., Penninx B., Pahor M., Wallace R., Havlik R.J.: Serum IL-6 level and the development of disability in older persons. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 47: 639–646, 1999.
Harris T.B., Ferrucci L., Tracy R.P., Corti M.C., Wacholder S., Ettinger W.H.Jr., Heimovitz H., Cohen H.J., Wallace R.: Associations of elevated interleukin-6 and C-reactive protein levels with mortality in the elderly. Am. J. Med. 106: 506–512, 1999.
Kado S., Nagase T., Nagata N.: Circulating levels of inter-leukin-6, its soluble receptor and interleukin-6/interleukin-6 receptor complexes in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Acta Diabetol. 36: 67–72, 1999.
Ross R.: Atherosclerosis—an inflammatory disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 340: 115–126, 1999.
Griffin W.S., Nicoll J. A., Grimaldi L.M., Sheng J.G., Mrak R.E.: The pervasiveness of interleukin-1 in Alzheimer pathogenesis: a role for specific polymorphisms in disease risk. Exp. Gerontol. 35: 481–487, 2000.
Bauer J., Strauss S., Schreiter-Gasser U., Ganter U., Schlegel P., Witt I., Yolk B., Berger M.: Interleukin-6 and alpha-2-macroglobulin indicate an acute-phase state in Alzheimer’s disease cortices. FEBS Lett. 285: 111–114, 1991.
Strauss S., Bauer J., Ganter U., Jonas U., Berger M., Volk B.: Detection of interleukin-6 and alpha 2-macroglobulin immunoreactivity in cortex and hippocampus of Alzheimer’s disease patients. Lab Invest. 66: 223–230, 1992.
Huell M., Strauss S., Volk B., Berger M., Bauer J.: Interleukin-6 is present in early stages of plaque formation and is restricted to the brains of Alzheimer’s disease patients. Acta Neuropathol. (Berl) 89: 544–551, 1995.
Licastro F., Campbell I.L., Kincaid C., Veinbergs I., Van Uden E., Rockenstein E., Mallory M., Gilbert J.R., Masliah E.: A role for ApoE in regulating the levels of alpha-1-antichy-motrypsin in the aging mouse brain and in Alzheimer’s disease. Am. J. Pathol. 155: 869–875, 1999.
Grimaldi L.M., Casadei V.M., Ferri C., Veglia F., Licastro F., Annoni G., Biunno I., De Bellis G., Sorbi S., Mariani C., Canal N., Griffin W.S., Franceschi M.: Association of early-onset Alzheimer’s disease with an interleukin-1 gene polymorphism. Ann. Neurol. 47: 361–365, 2000.
Nicoll J. A., Mrak R.E., Graham D.I., Stewart J., Wilcock G., MacGowan S., Esiri M.M., Murray L.S., Dewar D., Love S., Moss T., Griffin W.S.: Association of interleukin-1 gene polymorphisms with Alzheimer’s disease. Ann. Neurol. 47: 365–368, 2000.
Rebeck G.W.: Confirmation of the genetic association of in-terleukin-1A with early onset sporadic Alzheimer’s disease. Neurosci. Lett. 293: 75–77, 2000.
Du Y., Dodel R.C., Eastwood B.J., Bales K.R., Gao F., Lohmuller F., Muller U., Kurz A., Zimmer R., Evans R.M., Hake A., Gasser T., Oertel W.H., Griffin W.S., Paul S.M., Farlow M.R.: Association of an interleukin-1 alpha polymorphism with Alzheimer’s disease. Neurology 55: 480–483, 2000.
Licastro F., Pedrini S., Ferri C., Casadei V., Govoni M., Pession A., Sciacca F.L., Veglia F., Annoni G., Bonafe M., Olivieri F., Franceschi C., E. Grimaldi L.M.: Gene polymorphism affecting alpha1-antichymotrypsin and interleukin-1 plasma levels increases Alzheimer’s disease risk. Ann. Neurol. 48: 388–391, 2000.
Bhojak T.J., DeKosky S.T., Ganguli M., Kamboh M.I.: Genetic polymorphisms in the cathespin D and interleukin-6 genes and the risk of Alzheimer’s disease. Neurosci. Lett. 288: 21–24, 2000.
Papassotiropoulos A., Bagli M., Feder O., Jessen F., Maier W., Rao M.L., Ludwig M., Schwab S.G., Heun R.: Genetic polymorphism of cathepsin D is strongly associated with the risk for developing sporadic Alzheimer’s disease. Neurosci. Lett. 262: 171–174, 1999.
Bagli M., Papassotiropoulos A., Knapp M., Jessen F., Luise Rao M., Maier W., Heun R.: Association between an inter-leukin-6 promoter and 3′ flanking region haplotype and reduced Alzheimer’s disease risk in a German population. Neurosci. Lett. 283: 109–112, 2000.
Bonafé M., Olivieri F., Cavallone L., Giovanetti S., Marchigiani F., Cardelli M., Pieri C., Marra M., Antonicelli R., Lisa R., Rizzo M. R., Prolisso G., Monti D., Franceschi C.: The genetic predisposition to produce high levels of IL-6 is a detrimental gender-specific factor for longevity. Eur. J. Immunol. 2001 (in press).
Remarque E.J., Bollen E.L., Weverling-Rijnsburger A.W., Laterveer J.C., Blauw G.J., Westendorp R.G.: Patients with Alzheimer disease display a pro-inflammatory phenotype. Exp. Geront. 36: 171–176, 2001.
McGeer P.L., McGeer E.G.: Inflammation of the brain in Alzheimer’s disease: implications for therapy. J. Leukoc. Biol. 65: 409–415, 1999.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Franceschi, C., Valensin, S., Lescai, F. et al. Neuroinflammation and the genetics of Alzheimer’s disease: The search for a pro-inflammatory phenotype. Aging Clin Exp Res 13, 163–170 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03351475
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03351475