Abstract
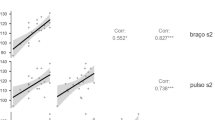
Blood pressure is usually determined by arm sphygmomanometry. However, this technique does not allow continuous blood pressure monitoring. Over the last years, a technique introduced by Peñaz makes it feasible to determine blood pressure noninvasively and continuously from the finger artery. Study on 46 normotensives showed that both methods have high retest-reliabilities for systolic blood pressure while for diastolic blood pressure, arm sphygmomanometry resulted in lower reliabilities than the Peñaz-method. Between-method-comparisons showed only small correlations. Diastolic blood pressure levels were significantly lower in the Peñaz-method than in arm sphygmomanometry. In conclusion, blood pressure levels determined by arm sphygmomanometry and the Peñaz-method differ systematically because of different methodologies. If blood pressure or blood pressure changes are determined, the method and the circumstances of its application need to be carefully reported.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Larochelle P, Hamet P. Blood pressure measurement in animals and humans. In: Genest J, Kuchel O, Hamet P, Cantin M, eds. Hypertension — Physiopathology and treatment. New York: McGraw-Hill 1983
Steptoe A. Blood pressure. In: Martin I, Venables PH, eds. Technique in psychophysiology. Chichester: Wiley & Sons 1980
Wesseling KH, Peñaz J. Indirect blood pressure measurement in the finger: physiological background of a recent development. Scripta Medica 1986; 59: 203–206
Hartmann B, Bassenge E. Noninvasive, continuous measurement of the finger arterial pressure with the servo-plethysmomanometer Finapres. Herz 1989; 14: 251–259
Imholz BPM, Wieling W, Langewouters GJ, Van Montfrans GA. Continuous finger arterial pressure: utility in the cardiovascular laboratory. Clinical Autonomic Research 1991; 1: 43–53
Wesseling KH. Finapres, continuous noninvasive finger arterial pressure based on the method of Peñaz. In: Rüddel H, Curio L eds. Non-invasive continuous blood pressure measurement. Frankfurt, Lang 1991
Weber F, Anlauf M. The accuracy of the automatic blood pressure measuring device Tonomed: a comparison of direct and indirect measurements. Herz Kreislauf 1982; 14: 279–283
Mancia G, Parati G, Pomidossi G, Grassi G, Casadei R, Zanchetti A. Alerting reaction and rise in blood pressure during measurement by physician and nurse. Hypertension 1987; 9: 209–215
Kugler J, Schmitz N, Seelbach H, Rollnik J, Krüskemper GM. Rise in systolic blood pressure during sphygmomanometry depends on the maximum inflation pressure of the arm cuff. J Hypertens 1994; 12: 825–829
Lal SKL, Mihailidou AS, Cejnar M, Henderson RJ, Jones M, Hunyor SN. Continuous, non-invasive volume clamp blood pressure: determinants of performance. J Hypertens 1993; 11: 1413–1422
Kirkendall WM, Feinleb M, Freis ED, Mark AL. American Heart Association report: recommendations for human blood pressure determinations by sphygmomanometers. Circulation 1980; 62: 1145–55A
Perloff D, Grim C, Flack J, Frohlich ED, Mill M, McDonald M, Morgenstern BZ. Human blood pressure determination by sphygmomanometry. Circulation 1993; 88: 2460–2470
Schandry R. Psychophysiologie. U&U, München 1981
Kugler J, Schmitz N, Seelbach H, Kröber A, Brunk B, Krüskemper GM. Comparison of Peñaz-Method and sphygmomanometry in normo- and mild hypertensives. Am J Hypertens 1992; 5: 128A
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kugler, J., Rollnik, J. & Schmitz, N. Retest-reliability and convergent validity of noninvasive blood pressure determination: arm sphygmomanometry vs. Peñaz-method. Int. J. Clin. Mon. Comp. 14, 251–254 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03356570
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03356570