Abstract
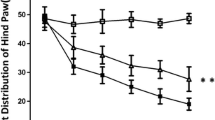
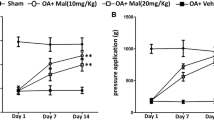
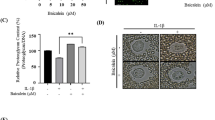
Osteoarthritis (OA) is the most common degenerative joint disease, and causes major pain and disability in adults. It has been reported that muscle weakness and inflammation contribute to osteoarthritis development and progression. Oxidative stress plays important roles in muscle dysfunction and inflammation in osteomyelitis. Baicalin, the major active constituent of the isolated root of Scutellarialateriflora Georgi, has been shown to have anti-oxidative and anti-inflammatory effects. In this study, we evaluated the potential effects of baicalin on osteoarthritis. We established experimental osteoarthritis rat model, applied baicalin to the rats, and then explored the potential protective effect of baicalin on osteoarthritis severity, muscle dysfunction, and oxidative stress. Baicalin alleviated severity of OA in rats. Baicalin application attenuated muscle dysfunction in OA rats by increasing citrate synthase activity, myosin heavy chain IIa expression, and decreasing interleukin 6 production. Baicalin decreased muscular reactive oxygen species generation in OA rats. Baicalin inhibited nuclear factor erythroid-derived 2-like 2 expression in OA rats. Baicalin attenuated osteoarthritis in rat by inhibiting oxidative stress.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Callahan DM, Miller MS, Sweeny AP et al (2014) Muscle disuse alters skeletal muscle contractile function at the molecular and cellular levels in older adult humans in a sex-specific manner. J Physiol 592:4555–4573
Chen D, Shen J, Zhao W et al (2017) Osteoarthritis: toward a comprehensive understanding of pathological mechanism. Bone Res 5:16044
Cherng CH, Lee KC, Chien CC et al (2014) Baicalin ameliorates neuropathic pain by suppressing HDAC1 expression in the spinal cord of spinal nerve ligation rats. J Formos Med Assoc 113:513–520
Dong SJ, Zhong YQ, Lu WT et al (2015) Baicalin inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation through signaling NF-kappaB pathway in HBE16 airway epithelial cells. Inflammation 38:1493–1501
Gao Z, Huang K, Xu H (2001) Protective effects of flavonoids in the roots of Scutellaria baicalensis Georgi against hydrogen peroxide-induced oxidative stress in HS-SY5Y cells. Pharmacol Res 43:173–178
Gong L, Zhu J (2018) Baicalin alleviates oxidative stress damage in trabecular meshwork cells in vitro. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 391:51–58
Hootman JM, Helmick CG (2006) Projections of US prevalence of arthritis and associated activity limitations. Arthritis Rheum 54:226–229
Hsu DZ, Chu PY, Wu PT et al (2015) Oxidative stress participates in quadriceps muscle dysfunction during the initiation of osteoarthritis in rats. Int J Clin Exp Pathol 8:12491–12499
Hsu DZ, Chu PY, Jou IM (2016) Daily sesame oil supplement attenuates joint pain by inhibiting muscular oxidative stress in osteoarthritis rat model. J Nutr Biochem 29:36–40
Ikeda S, Tsumura H, Torisu T (2005) Age-related quadriceps-dominant muscle atrophy and incident radiographic knee osteoarthritis. J Orthop Sci 10:121–126
Ikezoe T, Chen SS, Heber D et al (2001) Baicalin is a major component of PC-SPES which inhibits the proliferation of human cancer cells via apoptosis and cell cycle arrest. Prostate 49:285–292
Kaplowitz N, Aw TY, Ookhtens M (1985) The regulation of hepatic glutathione. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 25:715–744
Lei M, Guo C, Hua L et al (2017) Crocin attenuates joint pain and muscle dysfunction in osteoarthritis rat. Inflammation 40:2086–2093
Lepetsos P, Papavassiliou AG (2016) ROS/oxidative stress signaling in osteoarthritis. Biochim Biophys Acta 1862:576–591
Lin M, Li L, Zhang Y et al (2014) Baicalin ameliorates H2O2 induced cytotoxicity in HK-2 cells through the inhibition of ER stress and the activation of Nrf2 signaling. Int J Mol Sci 15:12507–12522
Liu J, Wei Y, Luo Q et al (2016) Baicalin attenuates inflammation in mice with OVA-induced asthma by inhibiting NF-kappaB and suppressing CCR7/CCL19/CCL21. Int J Mol Med 38:1541–1548
Lixuan Z, Jingcheng D, Wenqin Y et al (2010) Baicalin attenuates inflammation by inhibiting NF-kappaB activation in cigarette smoke induced inflammatory models. Pulm Pharmacol Ther 23:411–419
Ma Q (2013) Role of nrf2 in oxidative stress and toxicity. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 53:401–426
Mapp PI, Sagar DR, Ashraf S et al (2013) Differences in structural and pain phenotypes in the sodium monoiodoacetate and meniscal transection models of osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage 21:1336–1345
Mihara M, Higo S, Uchiyama Y et al (2007) Different effects of high molecular weight sodium hyaluronate and NSAID on the progression of the cartilage degeneration in rabbit OA model. Osteoarthritis Cartilage 15:543–549
O’Reilly SC, Muir KR, Doherty M (1999) Effectiveness of home exercise on pain and disability from osteoarthritis of the knee: a randomised controlled trial. Ann Rheum Dis 58:15–19
Pereira YC, do Nascimento GC, Iyomasa DM et al (2015) Muscle characterization of reactive oxygen species in oral diseases. Acta Odontol Scand 73:81–86
Shen YC, Chiou WF, Chou YC et al (2003) Mechanisms in mediating the anti-inflammatory effects of baicalin and baicalein in human leukocytes. Eur J Pharmacol 465:171–181
Spassov A, Gredes T, Gedrange T et al (2011) Increased oxidative stress in dystrophin deficient (mdx) mice masticatory muscles. Exp Toxicol Pathol 63:549–552
Tonge DP, Bardsley RG, Parr T et al (2013) Evidence of changes to skeletal muscle contractile properties during the initiation of disease in the ageing guinea pig model of osteoarthritis. Longev Healthspan 2:15
Velasquez MT, Katz JD (2010) Osteoarthritis: another component of metabolic syndrome? Metab Syndr Relat Disord 8:295–305
Wang HZ, Wang HH, Huang SS et al (2014) Inhibitory effect of baicalin on collagen-induced arthritis in rats through the nuclear factor-kappaB pathway. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 350:435–443
Wen ZH, Tang CC, Chang YC et al (2016) Calcitonin attenuates cartilage degeneration and nociception in an experimental rat model of osteoarthritis: role of TGF-beta in chondrocytes. Sci Rep 6:28862
Wojdasiewicz P, Poniatowski LA, Szukiewicz D (2014) The role of inflammatory and anti-inflammatory cytokines in the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis. Mediators Inflamm 2014:561459
Xing D, Gao H, Liu Z et al (2017) Baicalin inhibits inflammatory responses to interleukin-1beta stimulation in human chondrocytes. J Interferon Cytokine Res 37:398–405
Xu G, Dou J, Zhang L et al (2010) Inhibitory effects of baicalein on the influenza virus in vivo is determined by baicalin in the serum. Biol Pharm Bull 33:238–243
Yamada T, Mishima T, Sakamoto M et al (2006) Oxidation of myosin heavy chain and reduction in force production in hyperthyroid rat soleus. J Appl Physiol (1985) 100:1520–1526
Yang X, Yang J, Zou H (2013) Baicalin inhibits IL-17-mediated joint inflammation in murine adjuvant-induced arthritis. Clin Dev Immunol 2013:268065
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Research Involving Human Participants and/or Animals
All applicable international, national, and/or institutional guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed.
Informed Consent
Not applicable.
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, Ds., Cao, Jg., Zhu, B. et al. Baicalin Attenuates Joint Pain and Muscle Dysfunction by Inhibiting Muscular Oxidative Stress in an Experimental Osteoarthritis Rat Model. Arch. Immunol. Ther. Exp. 66, 453–461 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00005-018-0518-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00005-018-0518-6