Abstract
Objective
In the current study of murine colitis, the potential roles of thromboxane and the thromboxane-prostanoid (TP) receptor were investigated, in as much as thromboxane signaling has been implicated in human inflammatory bowel disease.
Methods
Colitis was induced in C57BL/6 mice via ingestion of dextran sodium sulfate (DSS), with or without co-administration of the thromboxane synthase inhibitor ozagrel (25 mg/kg/day) or the TP receptor antagonist vapiprost (2.5 mg/kg/day).
Results
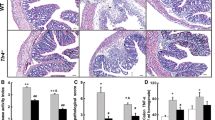
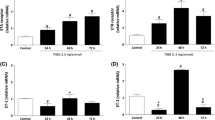
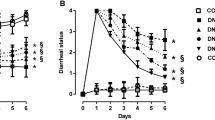
Immunohistochemistry of colonic tissue demonstrated a DSS-induced increase in TP receptor expression, but not of thromboxane synthase. Moreover, tissue levels of the metabolite thromboxane B2 were unchanged by DSS. Vapiprost, but not ozagrel, partially attenuated histologic signs of inflammation induced by DSS, with vapiprost allowing a smaller increase in colon weight per unit length than ozagrel. Vapiprost also tended to attenuate DSS-induced alterations in intestinal transit.
Conclusions
In summary, TP receptor antagonism was more effective than thromboxane synthase inhibition in alleviating DSS-induced colitis in mice.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Carty E, Nickols C, Feakins RM, Rampton DS. Thromboxane synthase immunohistochemistry in inflammatory bowel disease. J Clin Pathol. 2002;55:367–70.
Ligumsky M, Karmeli F, Sharon P, Zor U, Cohen F, Rachmilewitz D. Enhanced thromboxane A2 and prostacyclin production by cultured rectal mucosa in ulcerative colitis and its inhibition by steroids and sulfasalazine. Gastroenterology. 1981;81:444–9.
Hawkey CJ, Karmeli F, Rachmilewitz D. Imbalance of prostacyclin and thromboxane synthesis in Crohn’s disease. Gut. 1983;24:881–5.
Lauritsen K, Laursen LS, Bukhave K, Rask-Madsen J. In vivo profiles of eicosanoids in ulcerative colitis, Crohn’s colitis, and Clostridium difficile colitis. Gastroenterology. 1988;95:11–7.
Tytgat GN, Van Nueten L, Van De Velde I, Joslyn A, Hanauer SB. Efficacy and safety of oral ridogrel in the treatment of ulcerative colitis: two multicentre, randomized, double-blind studies. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2002;16:87–99.
Carty E, Rampton DS, Schneider H, Rutgeerts P, Wright JP. Lack of efficacy of ridogrel, a thromboxane synthase inhibitor, in a placebo-controlled, double-blind, multi-centre clinical trial in active Crohn’s disease. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2001;15:1323–9.
Dogne JM, de Leval X, Hanson J, Frederich M, Lambermont B, Ghuysen A, et al. New developments on thromboxane and prostacyclin modulators part I: thromboxane modulators. Curr Med Chem. 2004;11:1223–41.
Feletou M, Huang Y, Vanhoutte PM. Vasoconstrictor prostanoids. Pflugers Arch. 2010;459(6):941–50.
Gomi T, Ikeda T, Sasaki Y, Kosugi T, Shibuya Y, Sakurai J. Protective effect of thromboxane synthetase inhibitor on hypertensive renal damage in Dahl salt-sensitive rats. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol Suppl. 1995;22:S371–3.
Gomi T, Ikeda T, Ishimitsu T, Uehara Y. Effects of OKY-046, a selective thromboxane synthetase inhibitor, on blood pressure and thromboxane synthesis in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids. 1989;37:139–44.
Tanaka T, Fukuta Y, Higashino R, Sato R, Nomura Y, Fukuda Y, et al. Antiplatelet effect of Z-335, a new orally active and long-lasting thromboxane receptor antagonist. Eur J Pharmacol. 1998;357:53–60.
Dieleman LA, Palmen MJ, Akol H, Bloemena E, Pena AS, Meuwissen SG, et al. Chronic experimental colitis induced by dextran sulphate sodium (DSS) is characterized by Th1 and Th2 cytokines. Clin Exp Immunol. 1998;114:385–91.
Holma R, Salmenpera P, Virtanen I, Vapaatalo H, Korpela R. Prophylactic potential of montelukast against mild colitis induced by dextran sulphate sodium in rats. J Physiol Pharmacol. 2007;58:455–67.
Vowinkel T, Mori M, Krieglstein CF, Russell J, Saijo F, Bharwani S, et al. Apolipoprotein A-IV inhibits experimental colitis. J Clin Invest. 2004;114:260–9.
Sato K, Ohkura S, Kitahara Y, Ohama T, Hori M, Sato M, et al. Involvement of CPI-17 downregulation in the dysmotility of the colon from dextran sodium sulphate-induced experimental colitis in a mouse model. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2007;19:504–14.
Zipser RD, Patterson JB, Kao HW, Hauser CJ, Locke R. Hypersensitive prostaglandin and thromboxane response to hormones in rabbit colitis. Am J Physiol. 1985;249:G457–63.
Appleyard CB, Alvarez A, Percy WH. Temporal changes in colonic vascular architecture and inflammatory mediator levels in animal models of colitis. Dig Dis Sci. 2002;47:2007–14.
Vilaseca J, Salas A, Guarner F, Rodriguez R, Malagelada JR. Participation of thromboxane and other eicosanoid synthesis in the course of experimental inflammatory colitis. Gastroenterology. 1990;98:269–77.
Taniguchi T, Tsukada H, Nakamura H, Kodama M, Fukuda K, Tominaga M, et al. Effects of a thromboxane A2 receptor antagonist in an animal model of inflammatory bowel disease. Digestion. 1997;58:476–8.
Harris NR, Whatley JR, Carter PR, Specian RD. Venular constriction of submucosal arterioles induced by dextran sodium sulfate. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2005;11:806–13.
Mori M, Stokes KY, Vowinkel T, Watanabe N, Elrod JW, Harris NR, et al. Colonic blood flow responses in experimental colitis: time course and underlying mechanisms. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2005;289:G1024–9.
Schultheiss G, Diener M. Inhibition of spontaneous smooth muscle contractions in rat and rabbit intestine by blockers of the thromboxane A2 pathway. Zentralbl Veterinarmed A. 1999;46:123–31.
Diener M, Gabato D. Thromboxane-like actions of prostaglandin D2 on the contractility of the rat colon in vitro. Acta Physiol Scand. 1994;150:95–101.
Okada Y, Hara A, Ma H, Xiao CY, Takahata O, Kohgo Y, et al. Characterization of prostanoid receptors mediating contraction of the gastric fundus and ileum: studies using mice deficient in prostanoid receptors. Br J Pharmacol. 2000;131:745–55.
Borjesson L, Delbro DS. Neurogenic and non-neurogenic mechanisms in response of rat distal colon muscle to dextran sulphate sodium treatment. Auton Neurosci. 2003;107:74–80.
Gonzalez A, Sarna SK. Different types of contractions in rat colon and their modulation by oxidative stress. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2001;280:G546–54.
Murakami I, Hamada Y, Yamane S, Fujino H, Horie S, Murayama T. Nicotine-induced neurogenic relaxation in the mouse colon: changes with dextran sodium sulfate-induced colitis. J Pharmacol Sci. 2009;109:128–38.
Howes LG, James MJ, Florin T, Walker C. Nv-52: a novel thromboxane synthase inhibitor for the treatment of inflammatory bowel disease. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2007;16:1255–66.
Hirota Y, Suzuki M, Katsube N. Thromboxane A2 up-regulates neutrophil elastase release in Syrian hamsters with trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid-induced colitis. J Pharmacol Sci. 2005;98:430–8.
Acknowledgments
This study was performed with funding from the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (P01DK043785-18; Project 2 plus Cores B and C).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Ian Ahnfelt-Rønne.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Carter, P.R., McElhatten, R.M., Zhang, S. et al. Thromboxane-prostanoid receptor expression and antagonism in dextran-sodium sulfate-induced colitis. Inflamm. Res. 60, 87–92 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00011-010-0240-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00011-010-0240-2