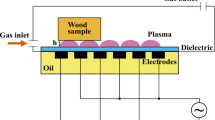
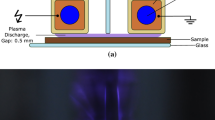
Abstract
Sample material from spruce (Picea abies), beech (Fagus sylvatica) and ash (Fraxinus excelsior) with radial and tangential section was treated by diffuse coplanar surface barrier discharge (DCSBD) plasma generated in air at atmospheric pressure. Plasma activated samples exhibited significantly lower water uptake times of 50 μl droplets and minimal differences in wetting between the two cutting planes (radial and tangential), when compared to the untreated surface. Simultaneously, more uniform spreading of the droplets and increased area of wetting on the activated surface were achieved. The plasma treatment had no effect on the water absorption coefficient of the wood samples. FTIR measurements confirmed the presence of oxygen containing functional groups and structural changes in lignin on the activated wood surface. The minimal heating of the treated samples suggests this method to be applicable to treat heat sensitive wooden materials.
Zusammenfassung
Fichte- (Picea abies), Buche- (Fagus sylvatica) und Escheproben (Fraxinus excelsior) mit den Schnittrichtungen radial und tangential wurden mit einem Atmosphärendruck DCSBD-Plasma behandelt. Im Vergleich zu den unbehandelten Oberflächen zeigten die plasmaaktivierten Proben deutlich geringere Wassereindringzeiten für ein 50 μl Tröpfchen und das Benetzungsverhalten zwischen den beiden Schnittebenen (radial und tangential) wies nur minimale Unterschiede auf. Gleichzeitig wurde eine gleichmäßigere Ausbreitung und eine größere benetzte Fläche auf den aktivierten Oberflächen erreicht. Die Plasmabehandlung hatte keinen Einfluss auf den Wasseraufnahmekoeffizienten der Holzproben. Die FTIR-Messungen zeigten die Bildung von funktionellen Gruppen, die polaren Sauerstoff enthalten, sowie strukturelle Veränderungen im Lignin auf der aktivierten Holzoberfläche. Durch die geringe Erwärmung der behandelten Proben ergibt sich die Möglichkeit der Behandlung von temperaturempfindlichen Holzwerkstoffen.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Asandulesa M, Topala I, Dumitrascu N (2010) Effect of helium DBD plasma treatment on the surface of wood samples. Holzforschung: Int J Biol Chem, Phys Technol Wood 64(2):223–227. doi:10.1515/hf.2010.025
Avramidis G, Nothnick E, Wolkenhauer A, Militz H, Viöl W (2010) Holzoberflächenmodifikation mittels Atmosphärendruckplasma. Vakuum in Forschung und Praxis 22(1):25–29
Avramidis G, Klarhöfer L, Maus-Friedrichs W, Militz H, Viöl W (2012a) Influence of air plasma treatment at atmospheric pressure on wood extractives. Polym Degrad Stab 97(3):469–471
Avramidis G, Militz H, Avar I, Viöl W, Wolkenhauer A (2012b) Improved absorption characteristics of thermally modified beech veneer produced by plasma treatment. Eur J Wood Prod 70(5):545–549
Busnel F, Blanchard V, Prégent J, Stafford L, Riedl B, Blanchet P, Sarkissian A (2010) Modification of sugar maple (Acer saccharum) and black spruce (Picea mariana) wood surfaces in a dielectric barrier discharge (DBD) at atmospheric pressure. J Adhes Sci Technol 24(8):1401–1413
Černák M, Černáková L, Hudec I, Kováčik D, Zahoranová A (2009) Diffuse coplanar surface barrier discharge and its applications for in-line processing of low-added-value materials. Eur Phys J Appl Phys 47(2):22806–22811. ISSN 1286-0042
EN ISO 15148 (2002) Hygrothermal performance of building materials and products—determination of water absorption coefficient by partial immersion
Frihart CR (2012) Wood Adhesion and Adhesives. In: Rowell R (ed) Handbook of wood chemistry and wood composites, 2nd edn. CRC Press, Taylor and Francis group, Boca Raton, FL, USA, pp 255–319
Homola T, Matoušek J, Hergelová B, Kormunda M, Wu LYL, Černák M (2012) Activation of poly(methyl methacrylate) surfaces by atmospheric pressure plasma. Polym Degrad Stab 97(6):886–892
Jamali A, Evans PD (2011) Etching of wood surfaces by glow discharge plasma. Wood Sci Technol 45(1):169–182
Klarhöfer L, Viöl W, Maus-Friedrichs W (2010) Electron spectroscopy on plasma treated lignin and cellulose. Holzforschung: Int J Biol Chem Phys Technol Wood 64(3):331–336
Mahlberg R, Niemi HEM, Denes F, Rowell RM (1998) Effect of oxygen and hexamethyldisiloxane plasma on morphology, wettability and adhesion properties of polypropylene and lignocellulosics. Int J Adhes Adhes 18(4):283–297
Mertens N, Wolkenhauer A, Leck M, Viöl W (2006) UV laser ablation and plasma treatment of wooden surfaces—a comparing investigation. Laser Phys Lett 3(8):380–384
Niemz P, Mannes D, Herbers Y, Koch W (2010a) Untersuchungen zum Wasseraufnahmekoeffizienten von Holz bei Variation von Holzart und Flüssigkeit. Bauphysik 32(3):149–153
Niemz P, Mannes D, Koch W, Herbers Y (2010b) Eindringverhalten verschiedener Flüssigkeiten in Holz: einfluss von Netzmitteln und Aufbringungsart. Holztechnologie 51(6):5–11
Niemz P, Sonderegger W, Häring D, Joščák M, Krackler V (2012) Untersuchungen zur Wasseraufnahme von Vollholz und Holzwerkstoffen. Bauphysik 34(3):101–106
Odrášková M, Ráhel’ J, Zahoranová A, Tiňo R, Černák M (2008) Plasma activation of wood surface by diffuse coplanar surface barrier discharge. Plasma Chem Plasma Process 28(2):203–211
Pandey KK, Pitman AJ (2003) FTIR studies of the changes in wood chemistry following decay by brown-rot and white-rot fungi. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 52(3):151–160
Podgorski L, Chevet B, Onic L, Merlin A (2000) Modification of wood wettability by plasma and corona treatments. Int J Adhes Adhes 20(2):103–111
Prysiazhnyi V, Vasina P, Panyala NR, Havel J, Cernak M (2012) Air DCSBD plasma treatment of Al surface at atmospheric pressure. Surf Coat Technol 206(11–12):3011–3016
Ráhel’ J, Szalay Z, Odrášková M, Tiňo R, Tóth A, Černák M (2008) Modification of wood surfaces by the coplanar barrier discharge. In: Dubovský J, Kúdela J (eds) Interaction of wood with various forms of energy. Technical University in Zvolen, Zvolen, pp 99–103
Rehn P, Viöl W (2003) Dielectric barrier discharge treatments at atmospheric pressure for wood surface modification. Holz Roh Werkst 61(2):145–150
Rehn P, Wolkenhauer A, Bente M, Förster S, Viöl W (2003) Wood surface modification in dielectric barrier discharges at atmospheric pressure. Surf Coat Technol 174–175:515–518
Sakata I, Morita M, Tsuruta N, Morita K (1993) Activation of wood surface by corona treatment to improve adhesive bonding. J Appl Polym Sci 49(7):1251–1258
Šimor M, Ráhel’ J, Vojtek P, Černák M, Brablec A (2002) Atmospheric-pressure diffuse coplanar surface discharge for surface treatments. Appl Phys Lett 81:2716–2718
Thomas PA (2000) Trees: Their Natural History. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK
Tóth A, Černáková L, Černák M, Kunovská K (2007) Surface analysis of groundwood paper treated by diffuse coplanar surface barrier discharge (DCSBD) type atmospheric plasma in air and in nitrogen. Holzforschung 61(5):528–531
Tshabalala MA, Jakes J, VanLandingham MR, Wang S, Peltonen J (2012) Surface characterization. In: Rowell R (ed) Handbook of wood chemistry and wood composites, 2nd edn. CRC Press, Taylor and Francis group, Boca Raton, FL, USA, pp 217–252
Wolkenhauer A, Avramidis G, Cai Y, Militz H, Viöl W (2007) Investigation of wood and timber surface modification by dielectric barrier discharge at atmospheric pressure. Plasma Process Polym 4(S1):S470–S474
Wolkenhauer A, Militz H, Vi l W (2008) Increased PVA-glue adhesion on particle board and fibre board by plasma treatment. Holz Roh Werkst 66(2):143–145
Wolkenhauer A, Avramidis G, Hauswald E, Militz H, Viöl W (2009) Sanding vs. plasma treatment of aged wood: a comparison with respect to surface energy. Int J Adhes Adhes 29(1):18–22
Acknowledgments
In memoriam Prof. Hans K. Pulker. The presented work was financially supported by the “Tiroler Standortagentur” under the project “Physikalisch-chemische Untersuchungen der silikatischen Nano-Infiltration von Hölzern nach Mikrowellentrocknung” within the Translational-Research program, further by the grant “Action Austria-Slovakia” of the Slovak Academic Information Agency (SAIA) No. 2010-10-15-0015 and by the project R&D center for low-cost plasma and nanotechnology surface modifications CZ.1.05/2.1.00/03.0086 funded by European Regional Development Fund.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Hans K. Pulker: Deceased.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lux, C., Szalay, Z., Beikircher, W. et al. Investigation of the plasma effects on wood after activation by diffuse coplanar surface barrier discharge. Eur. J. Wood Prod. 71, 539–549 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00107-013-0706-3
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00107-013-0706-3