Abstract
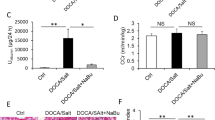
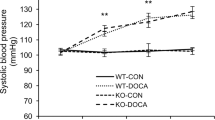
Mineralocorticoids stimulate renal tubular Na+ reabsorption, enhance salt appetite, increase blood pressure, and favor the development of renal fibrosis. The effects of mineralocorticoids on renal tubular Na+ reabsorption and salt appetite involve the serum- and glucocorticoid-inducible kinase 1 (SGK1). The kinase is highly expressed in fibrosing tissue. The present experiments thus explored the involvement of SGK1 in renal fibrosis. To this end, SGK1-knockout mice (sgk1 −/−) and their wild-type littermates (sgk1 +/+) were implanted with desoxycorticosterone acetate (DOCA)-release pellets and offered 1% saline as drinking water for 12 weeks. The treatment led to significant increases in fluid and Na+ intake and urinary output of fluid and Na+ in sgk1 +/+ mice, effects blunted in sgk1 −/− mice. Blood pressure increased within the first 7 weeks to a similar extent in both genotypes, but within the next 5 weeks, it increased further only in sgk1 +/+ mice. Creatinine clearance did not change significantly but albuminuria increased dramatically in sgk1 +/+ mice, an effect significantly blunted in sgk1 −/− mice. Histology after 12 weeks treatment revealed marked glomerular sclerosis and tubulointerstitial damage with interstitial fibrosis and inflammation in kidneys from sgk1 +/+ mice, but not from sgk1 −/− mice. In conclusion, a lack of SGK1 protects against DOCA/high-salt-induced albuminuria and renal fibrosis.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Reilly RF, Ellison DH (2000) Mammalian distal tubule: physiology, pathophysiology, and molecular anatomy. Physiol Rev 80:277–313
Stellar E, Epstein AN (1991) Neuroendocrine factors in salt appetite. J Physiol Pharmacol 42:345–355
Vallon V, Huang DY, Grahammer F, Wyatt AW, Osswald H, Wulff P, Kuhl D, Lang F (2005) SGK1 as a determinant of kidney function and salt intake in response to mineralocorticoid excess. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 289:R395–R401
Connell JM, Fraser R, MacKenzie S, Davies E (2003) Is altered adrenal steroid biosynthesis a key intermediate phenotype in hypertension? Hypertension 41:993–999
Bader M, Peters J, Baltatu O, Muller DN, Luft FC, Ganten D (2001) Tissue renin-angiotensin systems: new insights from experimental animal models in hypertension research. J Mol Med 79:76–102
Berger S, Bleich M, Schmid W, Greger R, Schutz G (2000) Mineralocorticoid receptor knockout mice: lessons on Na+ metabolism. Kidney Int 57:1295–1298
Goldschimdt I, Grahammer F, Warth R, Schulz-Baldes A, Garty H, Greger R, Bleich M (2004) Kidney and colon electrolyte transport in CHIF knockout mice. Cell Physiol Biochem 14:113–120
Swynghedauw B (1999) Molecular mechanisms of myocardial remodeling. Physiol Rev 79:215–262
Vallon V, Wyatt AW, Klingel K, Huang DY, Hussain A, Berchtold S, Friedrich B, Grahammer F, BelAiba RS, Görlach A, Wulff P, Daut J, Dalton ND, Ross Jr J, Flögel U, Schrader J, Osswald H, Kandolf R, Kuhl D, Lang F (2006) SGK1-dependent cardiac CTGF formation and fibrosis following DOCA treatment. J Mol Medicine 84:396–404
Bravo EL (2003) Aldosterone and specific aldosterone receptor antagonists in hypertension and cardiovascular disease. Curr Hypertens Rep 5:122–125
Quinkler M, Zehnder D, Eardley KS, Lepenies J, Howie AJ, Hughes SV, Cockwell P, Hewison M, Stewart PM (2005) Increased expression of mineralocorticoid effector mechanisms in kidney biopsies of patients with heavy proteinuria. Circulation 112:1435–1443
Brilla CG, Weber KT (1992) Reactive and reparative myocardial fibrosis in arterial hypertension in the rat. Cardiovasc Res 26:671–677
Young MJ, Funder JW (1996) The renin–angiotensin–aldosterone system in experimental mineralocorticoid-salt-induced cardiac fibrosis. Am J Physiol 271:E883–E888
Chen SY, Bhargava A, Mastroberardino L, Meijer OC, Wang J, Buse P, Firestone GL, Verrey F, Pearce D (1999) Epithelial sodium channel regulated by aldosterone-induced protein sgk. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 96:2514–2519
Djelidi S, Beggah A, Courtois-Coutry N, Fay M, Cluzeaud F, Viengchareun S, Bonvalet JP, Farman N, Blot-Chabaud M (2001) Basolateral translocation by vasopressin of the aldosterone-induced pool of latent Na-K-ATPases is accompanied by alpha1 subunit dephosphorylation: study in a new aldosterone-sensitive rat cortical collecting duct cell line. J Am Soc Nephrol 12:1805–1818
Muller OG, Parnova RG, Centeno G, Rossier BC, Firsov D, Horisberger JD (2003) Mineralocorticoid effects in the kidney: correlation between alphaENaC, GILZ, and Sgk-1 mRNA expression and urinary excretion of Na+ and K+. J Am Soc Nephrol 14:1107–1115
Naray-Fejes-Toth A, Canessa C, Cleaveland ES, Aldrich G, Fejes-Toth G (1999) Sgk is an aldosterone-induced kinase in the renal collecting duct. Effects on epithelial Na+ channels. J Biol Chem 274:16973–16978
Pearce D (2003) SGK1 regulation of epithelial sodium transport. Cell Physiol Biochem 13:013–020
Verrey F, Loffing J, Zecevic M, Heitzmann D, Staub O (2003) SGK1: aldosterone-induced relay of Na+ transport regulation in distal kidney nephron cells. Cell Physiol Biochem 13:021–028
Firestone GL, Giampaolo JR, O’Keeffe BA (2003) Stimulus-dependent regulation of the serum and glucocorticoid inducible protein kinase (Sgk) transcription, subcellular localization and enzymatic activity. Cell Physiol Biochem 13:1–12
Waldegger S, Barth P, Raber G, Lang F (1997) Cloning and characterization of a putative human serine/threonine protein kinase transcriptionally modified during anisotonic and isotonic alterations of cell volume. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 94:4440–4445
Diakov A, Korbmacher C (2004) A novel pathway of epithelial sodium channel activation involves a serum- and glucocorticoid-inducible kinase consensus motif in the C terminus of the channel’s alpha-subunit. J Biol Chem 279:38134–38142
Yoo D, Kim BY, Campo C, Nance L, King A, Maouyo D, Welling PA (2003) Cell surface expression of the ROMK (Kir 1.1) channel is regulated by the aldosterone-induced kinase, SGK-1, and protein kinase A. J Biol Chem 278:23066–23075
Yun CC, Palmada M, Embark HM, Fedorenko O, Feng Y, Henke G, Setiawan I, Boehmer C, Weinman EJ, Sandrasagra S, Korbmacher C, Cohen P, Pearce D, Lang F (2002) The serum and glucocorticoid-inducible kinase SGK1 and the Na(+)/H(+) exchange regulating factor NHERF2 synergize to stimulate the renal outer medullary K(+) channel ROMK1. J Am Soc Nephrol 13:2823–2830
Setiawan I, Henke G, Feng Y, Bohmer C, Vasilets LA, Schwarz W, Lang F (2002) Stimulation of Xenopus oocyte Na(+),K(+)ATPase by the serum and glucocorticoid-dependent kinase sgk1. Pflugers Arch 444:426–431
Feng Y, Wang Q, Wang Y, Yard B, Lang F (2005) SGK1-mediated fibronectin formation in diabetic nephropathy. Cell Physiol Biochem 16:237–244
Lang F, Klingel K, Wagner CA, Stegen C, Warntges S, Friedrich B, Lanzendorfer M, Melzig J, Moschen I, Steuer S, Waldegger S, Sauter M, Paulmichl M, Gerke V, Risler T, Gamba G, Capasso G, Kandolf R, Hebert SC, Massry SG, Broer S (2000) Deranged transcriptional regulation of cell-volume-sensitive kinase hSGK in diabetic nephropathy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 97:8157–8162
Lang F, Cohen P (2001) Regulation and physiological roles of serum-and glucocorticoid-induced protein kinase isoforms. Sci STKE 2001:RE17
Kumar JM, Brooks DP, Olson BA, Laping NJ (1999) Sgk, a putative serine/threonine kinase, is differentially expressed in the kidney of diabetic mice and humans. J Am Soc Nephrol 10:2488–2494
Friedrich B, Wärntges S, Klingel K, Sauter M, Kandolf R, Risler T, Müller GA, Witzgall R, Kriz W, Gröne HJ, Lang F (2002) Up-regulation of the human serum and glucocorticoid-dependent kinase 1 in glomerulonephritis. Kidney Blood Press Res 25:303–307
Waldegger S, Klingel K, Barth P, Sauter M, Rfer ML, Kandolf R, Lang F (1999) h-sgk serine-threonine protein kinase gene as transcriptional target of transforming growth factor beta in human intestine. Gastroenterology 116:1081–1088
Wärntges S, Klingel K, Weigert C, Fillon S, Buck M, Schleicher E, Rodemann HP, Knabbe C, Kandolf R, Lang F (2002) Excessive transcription of the human serum and glucocorticoid dependent kinase hSGK1 in lung fibrosis. Cell Physiol Biochem 12:135–142
Fillon S, Klingel K, Warntges S, Sauter M, Gabrysch S, Pestel S, Tanneur V, Waldegger S, Zipfel A, Viebahn R, Haussinger D, Broer S, Kandolf R, Lang F (2002) Expression of the serine/threonine kinase hSGK1 in chronic viral hepatitis. Cell Physiol Biochem 12:47–54
Klingel K, Warntges S, Bock J, Wagner CA, Sauter M, Waldegger S, Kandolf R, Lang F (2000) Expression of cell volume-regulated kinase h-sgk in pancreatic tissue. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 279:G998–G1002
Wulff P, Vallon V, Huang DY, Volkl H, Yu F, Richter K, Jansen M, Schlunz M, Klingel K, Loffing J, Kauselmann G, Bosl MR, Lang F, Kuhl D (2002) Impaired renal Na(+) retention in the sgk1-knockout mouse. J Clin Invest 110:1263–1268
Meneton P, Ichikawa I, Inagami T, Schnermann J (2000) Renal physiology of the mouse. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 278:F339–F351
Wolf G, Schanze A, Stahl RA, Shankland SJ, Amann K (2005) p27(Kip1) Knockout mice are protected from diabetic nephropathy: evidence for p27(Kip1) haplotype insufficiency. Kidney Int 68:1583–1589
Schwarz U, Amann K, Orth SR, Simonaviciene A, Wessels S, Ritz E (1998) Effect of 1,25 (OH)2 vitamin D3 on glomerulosclerosis in subtotally nephrectomized rats. Kidney Int 53:1696–1705
Huang DY, Wulff P, Volkl H, Loffing J, Richter K, Kuhl D, Lang F, Vallon V (2004) Impaired regulation of renal K+ elimination in the sgk1-knockout mouse. J Am Soc Nephrol 15:885–891
Sandulache D, Grahammer F, Artunc F, Henke G, Hussain A, Nasir O, Mack A, Friedrich B, Vallon V, Wulff P, Kuhl D, Palmada M, Lang F (2005) Renal Ca2+ handling in sgk1-knockout mice. Pflugers Arch 452:444–452
Fiebeler A, Nussberger J, Shagdarsuren E, Rong S, Hilfenhaus G, Al Saadi N, Dechend R, Wellner M, Meiners S, Maser-Gluth C, Jeng AY, Webb RL, Luft FC, Muller DN (2005) Aldosterone synthase inhibitor ameliorates angiotensin II-induced organ damage. Circulation 111:3087–3094
Kang N, Walther T, Tian XL, Bohlender J, Fukamizu A, Ganten D, Bader M (2002) Reduced hypertension-induced end-organ damage in mice lacking cardiac and renal angiotensinogen synthesis. J Mol Med 80:359–366
Markmann A, Schafer S, Linz W, Lohn M, Busch AE, Wohlfart P (2005) Down-regulation of calpain 9 is linked to hypertensive heart and kidney disease. Cell Physiol Biochem 15:109–116
Shindo T, Kurihara H, Maemura K, Kurihara Y, Ueda O, Suzuki H, Kuwaki T, Ju KH, Wang Y, Ebihara A, Nishimatsu H, Moriyama N, Fukuda M, Akimoto Y, Hirano H, Morita H, Kumada M, Yazaki Y, Nagai R, Kimura K (2002) Renal damage and salt-dependent hypertension in aged transgenic mice overexpressing endothelin-1. J Mol Med 80:105–116
Wolf G, Schroeder R, Ziyadeh FN, Stahl RA (2004) Albumin up-regulates the type II transforming growth factor-beta receptor in cultured proximal tubular cells. Kidney Int 66:1849–1858
Zhang L, Cui R, Cheng X, Du J (2005) Antiapoptotic effect of serum and glucocorticoid-inducible protein kinase is mediated by novel mechanism activating I{kappa}B kinase. Cancer Res 65:457–464
Blom IE, Goldschmeding R, Leask A (2002) Gene regulation of connective tissue growth factor: new targets for antifibrotic therapy? Matrix Biol 21:473–482
Moussad EE, Brigstock DR (2000) Connective tissue growth factor: what’s in a name? Mol Genet Metab 71:276–292
Brigstock DR (2003) The CCN family: a new stimulus package. J Endocrinol 178:169–175
Ihn H (2002) Pathogenesis of fibrosis: role of TGF-beta and CTGF. Curr Opin Rheumatol 14:681–685
Coffman TM, Spurney RF, Mannon RB, Levenson R (1998) Thromboxane A2 modulates the fibrinolytic system in glomerular mesangial cells. Am J Physiol 275:F262–F269
Edgtton KL, Gow RM, Kelly DJ, Carmeliet P, Kitching AR (2004) Plasmin is not protective in experimental renal interstitial fibrosis. Kidney Int 66:68–76
Kanasaki K, Koya D, Sugimoto T, Isono M, Kashiwagi A, Haneda M (2003) N-acetyl-seryl-aspartyl-lysyl-proline inhibits TGF-beta-mediated plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 expression via inhibition of Smad pathway in human mesangial cells. J Am Soc Nephrol 14:863–872
Okada H, Watanabe Y, Kikuta T, Kobayashi T, Kanno Y, Sugaya T, Suzuki H (2004) Bradykinin decreases plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 expression and facilitates matrix degradation in the renal tubulointerstitium under angiotensin-converting enzyme blockade. J Am Soc Nephrol 15:2404–2413
Busjahn A, Aydin A, Uhlmann R, Krasko C, Bahring S, Szelestei T, Feng Y, Dahm S, Sharma AM, Luft FC, Lang F (2002) Serum- and glucocorticoid-regulated kinase (SGK1) gene and blood pressure. Hypertension 40:256–260
von Wowern F, Berglund G, Carlson J, Mansson H, Hedblad B, Melander O (2005) Genetic variance of SGK-1 is associated with blood pressure, blood pressure change over time and strength of the insulin-diastolic blood pressure relationship. Kidney Int 68:2164–2172
Dieter M, Palmada M, Rajamanickam J, Aydin A, Busjahn A, Boehmer C, Luft FC, Lang F (2004) Regulation of glucose transporter SGLT1 by ubiquitin ligase Nedd4-2 and kinases SGK1, SGK3, and PKB. Obes Res 12:862–870
Busjahn A, Seebohm G, Maier G, Toliat MR, Nurnberg P, Aydin A, Luft FC, Lang F (2004) Association of the serum and glucocorticoid regulated kinase (sgk1) gene with QT interval. Cell Physiol Biochem 14:135–142
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grants from Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft, La 315/4-6, Sonderforschungsbereich 423 (project Z2), the Department of Veterans Affairs, and the National Institutes of Health (DK56248, DK28602). O. Nasir was a recipient of a Deutscher Akademischer Austauschdienst fellowship.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Artunc, F., Amann, K., Nasir, O. et al. Blunted DOCA/high salt induced albuminuria and renal tubulointerstitial damage in gene-targeted mice lacking SGK1. J Mol Med 84, 737–746 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-006-0082-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-006-0082-0