Abstract
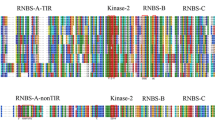
Ginger (Zingiber officinale Rosc.) production is seriously affected by many fungal and bacterial diseases to which no resistant source is available in the cultivated germplasm. Degenerate primers based on conserved motifs of plant resistance (R) genes were used to isolate analogous sequences called resistance gene candidates (RGCs) from cultivated and wild Zingiber species. Cloning and sequence characterization identified 42 Zingiber RGCs, which could be classified into five classes following phenetic analysis. Deduced amino acid sequences of Zingiber RGCs showed strong identity, ranging from 16 to 43%, to non-toll interleukin receptor (non-TIR) R-gene subfamily. Non-synonymous to synonymous nucleotide substitution (dN/dS) ratio for the NBS domains of Zingiber RGC classes showed evidence of purifying selection. RT-PCR analysis with 15 Zingiber RGC-specific primers demonstrated 8 of the 15 Zingiber RGCs to be expressed. The present study reports for the first time the isolation and characterization of RGCs from ginger and its wild relatives, which will serve as a potential resource for future improvement of this important vegetatively propagated spice crop.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aarts MG, Hekkert B, Holub EB, Beynon JL, Stiekema WJ, Pereira A (1998) Identification of R-gene homologous DNA fragments genetically linked to disease resistance loci in Arabidopsis thaliana. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 11:251–258
Afzal M, Al-Hadidi D, Menon M, Pesek J, Dhami MS (2001) Ginger: an ethnomedical, chemical and pharmacological review. Drug Metabol Drug Interact 18:159–190
Altschul SF, Gish W, Miller W, Myers EW, Lipman DJ (1990) Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol 215:403–410
Anandaraj M, Devasahayam S, Zachariah TJ, Santhosh JE, Sasikumar B, Thankamani CK (2001) Ginger (extension pamphlet). In: Sarma YR (ed), Indian Institute of Spices Research, Calicut pp 1–8
Anderson P, Lawrence G, Morrish B, Ayliffe M, Finnegan E, Ellis J (1997) Inactivation of the flax rust resistance gene M associated with the loss of a repeated unit within the leucine-rich repeat coding region. Plant Cell 9:641–651
Bai J, Pennill L, Ning J, Lee S, Ramalingam J, Webb C, Zhao B, Sun Q, Nelson J, Leach J, Hulbert S (2002) Diversity in nucleotide binding site-leucine-rich repeat genes in cereals. Genome Res 12:1871–1884
Brosius J, Gould S (1992) On “genomenclature”: a comprehensive (and respectful) taxonomy for pseudogenes and other “junk DNA”. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89:10706–10710
Cannon SB, Zhu H, Baumgarten AM, Spangler R, May G, Cook DR, Young ND (2002) Diversity, distribution and ancient taxonomic relationships within the TIR and non-TIR NBS-LRR resistance gene subfamilies. J Mol Evol 54:548–562
Clay K, Kover P (1996) The Red Queen Hypothesis and plant/pathogen interactions. Ann Rev Phytopathol 34:29–50
Cordero JC, Skinner DZ (2002) Isolation from alfalfa of resistance gene analogues containing nucleotide binding sites. Theor Appl Genet 104:1283–1289
Dake G (1995) Diseases of ginger (Zingiber officinale Rosc.) and their management. J Sp Arom Crops 4:40–48
Dangl JL, Jones DG (2001) Plant pathogens and integrated defence responses to infection. Nature 411:826–833
Deng Z, Gmitter FJ (2003) Cloning and characterization of receptor kinase class disease resistance gene candidates in Citrus. Theor Appl Genet 108:53–61
Deng Z, Huang S, Ling P, Chen C, Yu C, Weber C, Moore G, Gmiter FJ (2000) Cloning and characterization of NBS-LRR class resistance-gene candidate sequences in citrus. Theor Appl Genet 101:814–822
Dhamayanthi KPM, Sasikumar B, Remashree AB (2003) Reproductive biology and incompatibility studies in ginger (Zingiber officiniale Rosc.) Phytomorphology 53:123–131
Di Gaspero G, Cipriani G (2002) Resistance gene analogs are candidate markers for disease-resistance genes in grape (Vitis spp.). Theor Appl Genet 106:163–172
Dixon MS, Hatzixanthis K, Jones DA, Harrison K, Jones JDG (1998) The tomato Cf-5 disease resistance gene and six homologs show pronounced allelic variation in leucine-rich repeat copy number. Plant Cell 10:1915–1925
Ebert D, Hamilton W (1996) Sex against virulence: the co-evolution of parasitic diseases. Trends Ecol Evol 11:79–82
FAOSTAT Citation database results (2005) Food and Agricultural Organization, Rome. http://faostat.fao.org Cited 01 July 2006
Ferrier-Cana E, Geffroy V, Macadre C, Creusot F, Imbert-Bollore P, Sevignac M, Langin T (2003) Characterization of expressed NBS-LRR resistance gene candidates from common bean Theor Appl Genet 106:251–261
Feuillet C, Schachermayr G, Keller B (1997) Molecular cloning of a new receptor-like kinase gene encoded at the Lr10 disease resistance locus of wheat. Plant J 11:45–52
Flor HH (1971) The current status of gene for gene concept. Ann Rev Phytopathol 9:275–296
Fourmann M, Chariot F, Froger N, Delourme R, Brunel D (2001) Expression, mapping, and genetic variability of Brassica napus disease resistance gene analogues. Genome 44:1083–1099
Gish W, States DJ (1993) Identification of protein coding regions by database similarity search. Nature Genet 3:266–272
Goldman N, Yang Z (1994) A codon-based model of nucleotide substitution for protein-coding DNA sequences. Mol Biol Evol 11:725–736
Graham M, Marek L, Lohnes D, Cregan P, Shoemaker R (2000) Expression and genome organization of resistance gene analogs in soybean. Genome 43:86–93
Graham M, Marek L, Shoemaker R (2002) Organization, expression and evolution of a disease resistance gene cluster in soybean. Genetics 162:1961–1977
Grant MR, Godiard L, Straube E, Ashfield T, Lewald J, Sattler A, Innes RW, Dangl JL (1995) Structure of the Arabidopsis RPM1 gene enabling dual specificity disease-resistance. Science 269:843–846
Hall TA (1999) BioEdit: a user-friendly biological sequence alignment editor and analysis program for Windows 95/98/NT. Nucleic Acids Symp Ser 41:95–98
Hammond-Kosack KE, Jones JDG (1997) Plant disease resistance genes. Ann Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol 48:575–607
He CY, Tian AG, Zhang JS, Zhang ZY, Gai JY, Chen SY (2003) Isolation and characterization of a full-length resistance gene homolog from soybean. Theor Appl Genet 106:786–793
Hulbert SH, Webb CA, Smith SM, Sun Q (2001) Resistance gene complexes: evolution and utilization. Ann Rev Phytopathol 39:285–312
Irigoyen ML, Loarce Y, Fominaya A, Ferrer E (2004) Isolation and mapping of resistance gene analogues from the Avena strigosa genome. Theor Appl Genet 109:713–724
Johal G, Briggs S (1992) Reductase activity encoded by the HM1 disease resistance gene in maize. Science 258:985–987
Kanazin V, Marek LF, Shoemaker RC (1996) Resistance gene analogs are conserved and clustered in soybean. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93:11746–11750
Kumar S, Tamura K, Nei M (2004) MEGA3: integrated software for molecular evolutionary genetics analysis and sequence alignmnet. Brief Bioinform 5:150–163
Leister D, Ballvora A, Salamini F, Gebhardt C (1996) A PCR-based approach for isolating pathogen resistance genes from potato with potential for wide application in plants. Nat Genet 14:421–428
Liu J-J, Ekramoddoullah AKM (2003) Isolation, genetic variation and expression of TIR-NBS-LRR resistance gene analogs from western white pine (Pinus monticola Dougl Ex D Don.). Mol Genet Genom 270:432–441
Lopez CE, Zuluaga AP, Cooke R, Delseny M, Tohme J, Verdier V (2003) Isolation of resistance gene candidates (RGCs) and characterization of an RGC cluster in cassava. Mol Genet Genom 269:658–671
Mago R, Nair S, Mohan M (1999) Resistance gene analogues from rice: cloning, sequencing and mapping. Theor Appl Genet 99:50–57
McDowell J, Dhandaydham M, Long T, Aarts M, Goff S, Holubd E, Dangl J (1998) Intragenic recombination and diversifying selection contribute to the evolution of downy mildew resistance at the RPP8 locus of Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 10:1861–1874
Meyers B, Kozik A, Griego A, Kuang H, Michelmore R (2003) Genome wide analysis of NBS-LRR-encoding genes in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 15:809–834
Meyers BC, Dickerman AW, Michelmore RW, Sivaramakrishnan S, Sobral BW Young ND (1999) Plant disease resistance genes encode members of an ancient and diverse protein family within the nucleotide-binding super family. Plant J 20:317–332
Michelmore RW, Meyers BC (1998) Clusters of resistance genes in plants evolve by divergent selection and a birth-and-death process. Genome Res 8:1113–1130
Mysore K, Crasta O, Tuori R, Folkerts O, Swirsky P, Martin GB (2002) Comprehensive transcript profiling of Pto- and Prf-mediated host defense responses to infection by Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato. Plant J 32:299–315
Nei M, Gojobori T (1986) Simple methods for estimating the numbers of synonymous and nonsynonymous nucleotide substitutions. Mol Biol Evol 3:418–426
Noir S, Combes MC, Anthony F, Lashermes P (2001) Origin, diversity and evolution of NBS-type disease-resistance gene homologues in coffee trees (Coffea L.). Mol Genet Genom 265:654–662
Ohmori T, Murata M, Motoyoshi F (1998) Characterization of disease resistance gene-like sequences in near-isogenic lines of tomato. Theor Appl Genet 96:331–338
Pan Q, Wendel J, Fluhr R (2000) Divergent evolution of plant NBS-LRR resistance gene homologues in dicot and cereal genomes. J Mol Evol 50:203–213
Parniske M, Hammond-Kosack KE, Golsten C, Thomas CM, Jones DA, Harrison K, Wulff BBH, Jones JDG (1997) Novel disease resistance specificities result from sequence exchange between tandemly repeated genes at the Cf-4/9 locus of tomato. Cell 91:821–832
Rigden DJ, Mello LV, Bertioli DJ (2000) Structural modeling of a plant disease resistance gene product domain. Proteins 41:133–143
Rivkin MI, Vallejos CE, McClean PE (1999) Disease-resistance related sequences in common bean. Genome 42:41–47
Saitou N, Nei M (1987) The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol 4:406–425
Salmeron J, Oldroyd G, Rommens C, Scofield S, Kim H, Lavelle D, Dahlbeck D, Staskawicz B (1996) Tomato Prf is a member of the leucine-rich repeat class of plant disease resistance genes and lies embedded within the Pto kinase gene cluster. Cell 86:123–133
Salzman R, Fujita T, Zhu-Salzman K, Hasegawa P, Bressan R (1999) An improved RNA isolation method for plant tissues containing high levels of phenolic compounds or carbohydrates. Plant Mol Biol Rep 17:11–17
Shen KA, Meyers BC, Nurul Islam Faridi M, Chin DB, Stelly DM, Michelmore RW (1998) Resistance gene candidates identified by PCR with degenerate oligonucleotide primers map to clusters of resistance genes in lettuce. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 11:815–823
Song WY, Pi LY, Wang GL, Gardner J, Holsten T, Ronald PC (1997) Evolution of the rice Xa21 disease resistance gene family. Plant Cell 9:1279–1287
Soriano JM, Vilanova S, Romero C, Llacer G, Badenes ML (2005) Characterization and mapping of NBS-LRR resistance gene analogs in apricot (Prunus armeniaca L.). Theor Appl Genet 110:980–989
Stahl EA, Dwyer G, Mauricio R, Kreitman M, Bergelson J (1999) Dynamics of disease resistance polymorphism at the Rpm1 locus of Arabidopsis. Nature 400:667–671
Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Plewniak F, Jeanmougin F, Higgins DG (1997) The ClustalX windows interface: flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Res 24:4876–4882
van der Biezen E, Jones J (1998) The NB-ARC domain: a novel signalling motif shared by plant resistance gene products and regulators of cell death in animals. Curr Biol 8:226–227
Vicente J, King G (2001) Characteisation of disease resistance gene-like sequences in Brassica oleracea L. Theor Appl Genet 102:555–563
Wang Z, Yano M, Yamanouchi U, Iwamoto M, Monna L, Hayasaka H, Katayose Y, Sasaki T (1999) The Pib gene for rice blast resistance belongs to the nucleotide binding and leucine-rich repeat class of plant disease resistance genes. Plant J 19:55–64
Whitham S, Dinesh-Kumar SP, Choi D, Hehl R, Corr C, Baker B (1994) The product of the tobacco mosaic virus resistance gene N: similarity to Toll and the interleukin-1 receptor. Cell 78:1101–1115
Xiao J, Li J, Grandillo S, Ahn SN, Yuan L, Tanksley SD, McCouch SR (1998) Identification of trait-improving quantitative trait loci alleles from a wild rice relative, Oryza rufipogon. Genetics 150:899–909
Yang Z (1997) PAML: A program package for phylogenetic analysis by maximum likelihood. Comput Appl Biosci 13:555–556
Yoshimura S, Yamanouchi U, Katayose Y, Toki S, Wang Z, Kono I, Kurata N, Yano M, Iwata N, Sasaki T (1998) Expression of Xa1 a bacterial blight-resistance gene in rice, is induced by bacterial inoculation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:1663–1668
Zamir D (2001) Improving plant breeding with exotic genetic libraries. Nat Rev Genet 2:983–989
Acknowledgments
ANR gratefully acknowledges Council for Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR), Government of India for the research fellowship (F. No. 9/716(23)/2KI/EMR-I) and Travel Grant (No. TG/2079/06-HRD) received and GT acknowledges Department of Biotechnology (DBT), Government of India for the research grant.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by S. J. Knapp.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aswati Nair, R., Thomas, G. Isolation, characterization and expression studies of resistance gene candidates (RGCs) from Zingiber spp.. Theor Appl Genet 116, 123–134 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-007-0652-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-007-0652-8