Abstract
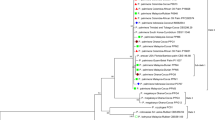
Restriction fragment length polymorphism (RFLP) and sequencing were used to elucidate the genetic relationship between phytoplasmas that cause white lead disease and grassy shoot disease in sugarcane and white leaf disease in gramineous weeds found in the cane-growing areas (Crowfoot grass, Bermuda grass and Brachiaria grass). A 1.35-kb DNA fragment encoding for the 16s rRNA was amplified by PCR using universal primers and analysed by digestion with nine restriction endonucleases. A DNA fragment containing the 3′ end of the 16s rRNA and the spacer region between the 16s rRNA and the tRNA(Ile) was amplified by PCR and sequenced. Analysis of the RFLP patterns and of the sequence showed that grassy shoot and white leaf diseases in sugarcane are caused by two different phytoplasmas. Sequence analysis of phytoplasma DNA obtained from three species of weeds showing symptoms of white leaf disease failed to detect any organism that is identical to those infecting the sugarcane. Moreover the phytoplasma species that infect the three types of gramineous weeds, although closely related, are nevertheless different
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 15 April 1997 / Accepted: 18 April 1997
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wongkaew, P., Hanboonsong, Y., Sirithorn, P. et al. Differentiation of phytoplasmas associated with sugarcane and gramineous weed white leaf disease and sugarcane grassy shoot disease by RFLP and sequencing. Theor Appl Genet 95, 660–663 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/s001220050609
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s001220050609