Abstract
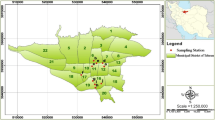
Polychlorinated biphenyl (PCB) concentrations in surface soil samples (0–10 cm) from 23 city parks (8 urban and 15 suburban) from Xi’An, China were presented. The average concentration of Σ7 PCBs among all the sites was 1.68 ng g−1 dry weight. High detection frequency (100 %) of PCB 28 and PCB 52 suggested wide occurrence of PCB contaminations in Xi’An. Among these PCBs, PCB 28, 52 and 153 were the most dominant compounds (14.9 %, 39.3 % and 9.5 % of the Σ7 PCBs on average, respectively). “Urban fractionation effect” was found in Xi’An. In other words, PCB concentrations were higher in the urban city park soils than those in suburban park soils. The PCB contamination in Xi’An city park soils were at a low level based on the Dutch guideline. However, dioxin-like PCB congeners were detected from 12 parks, which indicated further investigation was urgently required in future. Furthermore, total PCB concentrations were used to evaluate the cancer risk via ingestion, dermal and inhalation and the results showed that the total cancer risk was at the very low level in this area.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
ATSDR (1995) Public Health Assessment. Johnstown City Landfill, Johnstown, Fulton Country, (CERCLIS NO. NYD980506927). In: Department of health and human services PHS, Atlanta, editor: New York State Department of Health under cooperative agreement with the agency for toxic substances and disease registry
Breivik K, Sweetman A, Pacyna JM, Jones KC (2002) Towards a global historical emission inventory for selected PCB congeners-a mass balance approach 1. Global production and consumption. Sci Total Environ 290:181–198
Cachada A, Lopes LV, Hursthouse AS, Biasioli M, Grcman H, Otabbong E, Davidson CM, Duarte AC (2009) The variability of polychlorinated biphenyls levels in urban soils from five European cities. Environ Pollut 157(2):511–518
Fu S, Yang ZZ, Li K, Xu XB (2008) Polychlorinated biphenyl residues in sandstorm depositions in Beijing, China. Chemosphere 73:962–966
Gai N, Pan J, Tang H, Chen S, Chen DZ, Zhu XH, Lu GH, Yang YL (2014) Organochlorine pesticides and polychlorinated biphenyls in surface soils from Ruoergai high altitude prairie, east edge of Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Sci Total Environ 478:90–97
Ge J, Woodward LA, Li QX, Wang J (2013) Distribution, sources and risk assessment of polychlorinated biphenyls in Soils from the Midway Atoll. PLOS ONE, North Pacific Ocean. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0071521
Jiang Y, Wang X, Zhu K, Wu M, Sheng G, Fu J (2011) Polychlorinated biphenyls contamination in urban soil of Shanghai: level, compositional profiles and source identification. Chemosphere 83(6):767–773
Li ZY, Kong SF, Chen L, Bai ZP, Ji YQ, Liu JW, Lu B, Han B, Wang QW (2011) Concentrations, spatial distributions and congener profiles of polychlorinated biphenyls in soils from a coastal city-Tianjin, China. Chemosphere 85:494–501
Lu HX, Liu WG (2013) Occurrence of organochlorine pesticides in surface soils from college school yards of Xi’an, China. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 91:386–390
Mamontova EA, Mamontov AA, Tarasova EN, Kuzmin MI, Ganchimeg D, Khomutova MY, Gombosuren O, Ganjuurjav E (2013) Polychlorinated biphenyls in surface soil in urban and background areas of Mongolia. Environ Pollut 182:424–429
Meijer SN, Ockenden WA, Sweetman A, Breivik K, Grimalt JO, Jones KC (2003) Global distribution and budget of PCBs and HCB in background surface soils: implications for sources and environmental processes. Environ Sci Technol 37:667–672
Ren NQ, Qun MX, Li Y, Liu Y, Wan XN, Xu DD, Sverko E, Ma JM (2007) Polychlorinated biphenyls in Chinese surface soils. Environ Sci Technol 41:3871–3876
Toan VD, Thao VD, Walder J, Schmutz HR, Ha CT (2007) Level and distribution of polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) in surface soils from Hanoi, Vietnam. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 78:211–216
Wu S, Xia X, Yang L, Liu H (2011) Distribution, source and risk assessment of polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) in urban soils of Beijing, China. Chemosphere 82(5):732–738
Zhang HB, Luo YM, Wong MH, Zhao QG, Zhang GL (2006) Distributions and concentrations of PAHs in Hong Kong soils. Environ Pollut 141:107–114
Zhang HB, Luo YM, Wong MH, Zhao QG, Zhang GL (2007) Concentrations and possible sources of polychlorinated biphenyls in the soils of Hong Kong. Geoderma 138:244–251
Zhang L, Shi S, Dong L, Zhang T, Zhou L, Huang Y (2011) Concentrations and possible sources of polychlorinated biphenyls in the surface water of the Yangtze River Delta, China. Chemosphere 85(3):399–405
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the Key Research Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, Grants # KZZD-EW-04, the National Basic Research Program of China (No. 2013CB955901) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China Grants # 41103009 (H.X. Lu).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lu, H., Liu, W. Characterization and Risk Assessment of Polychlorinated Biphenyls in City Park Soils of Xi’An, China. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 94, 393–398 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-015-1463-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-015-1463-2