Abstract
The concept of the Nitrogen (N) cycle has been modified over the years based on certain new pathways, including comammox, anammox, and DNRA (dissimilatory nitrate reduction to ammonium). Comammox, nitrification, anammox, denitrification, DNRA, and nitrogen fixation pathways play key roles in the N cycle in paddy soils. Pesticides and chemical fertilizers’ effects on the N cycle in paddy soils together with the possible manifestation of these newly discovery pathways are the focus of this review. Both chemical fertilizers and pesticides’ overuse affect nitrifying archaea/bacteria and denitrifying and anammox bacteria, while heavy metals affect the nitrification rates in paddy soils. To add extra value to this study, we quantified the comammox amoA single copy gene from the Nitrospira strain ‘Nitrospira inopinata’. This review will help researchers access the latest information on the N cycle, particularly in the light of the most recent discoveries.


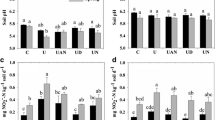
taken from our previous work (Nahar et al. 2020). A- Abundance of comammox N. inopinata, AOA, AOB, and NOB, B- Relative abundance of N. inopinata/ amoA gene copies per g dry soil in paddy soils

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alam MA, Rahman MM, Biswas JC, Akhter S, Maniruzzaman M et al (2019) Nitrogen transformation and carbon sequestration in wetland paddy field of Bangladesh. Paddy Water Environ 17:677–688
Ara L, Lewis M, Ostendorf B (2016) Spatio-temporal analysis of the impact of climate, cropping intensity and means of irrigation: an assessment on rice yield determinants in Bangladesh. Agric Food Secur 5:12. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40066-016-0061-9
Bai R, Xi D, He JZ, Hu HW, Fang YT, Zhang LM (2015) Activity, abundance and community structure of anammox bacteria along depth profiles in three different paddy soils. Soil Biol Biochem 91:212–221. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2015.08.040
Chao Y, Mao Y, Yu K, Zhang T (2016) Novel nitrifiers and comammox in a full-scale hybrid biofilm and activated sludge reactor revealed by metagenomics approach. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 100:8225–8237. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-016-7655-9
Cheng L, Li X, Lin X, Hou L, Liu M, Li Y, Liu S, Hu X (2016) Dissimilatory nitrate reduction processes in sediments of urban river networks: spatiotemporal variations and environmental implications. Environ Pollut 219:545–554
Daims H, Lebedeva EV, Pjevac P et al (2015) Complete nitrification by Nitrospira bacteria. Nature 528:504–509. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature16461
Hu H, He J (2017) Comammox—a newly discovered nitrification process in the terrestrial nitrogen cycle. J Soils Sediments 17:2709–2717
Islam MZ, Khalequzzaman M, Bashar MK, Ivy NA, Haque MM, Mian MAK (2016) Variability assessment of aromatic and fine rice germplasm in Bangladesh based on quantitative traits. Sci World J 14(2796720):20
Kalia A, Gosal SK (2011) Effect of pesticide application on soil microorganisms. Arch Agron Soil Sci 57(6):569–596. https://doi.org/10.1080/03650341003787582
Khan MI, Gwon HS, Alam MA, Song HJ, Das S, Kim J (2020) Short term effects of different green manure amendments on the composition of main microbial groups and microbial activity of a submerged rice cropping system. Appl Soil Ecol 147:103400
Khanom A, Azad MAK, Ali MM, Ali MY, Biswas SK, Rahman MM (2021) Plants and microbes’ responses to the net nitrification rates of chemical fertilizers in vegetable soils. Appl Soil Ecol 158:103783. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsoil.2020.103783
Kits KD, Sedlacek CJ, Lebedeva EV, Han P, Bulaev A, Pjevac P, Daebeler A, Romano S, Albertsen M, Stein LY, Daims H, Wagner M (2017) Kinetic analysis of a complete nitrifier reveals an oligotrophic lifestyle. Nature 549:269–272. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature23679
Kits KD, Jung MY, Vierheilig J, Pjevac P, Sedlacek CJ, Liu S, Herbold C, Stein LY, Richter A, Wissel H (2019) Low yield and abiotic origin of N2O formed by the complete nitrifier Nitrospira inopinata. Nat Commun 10:1836. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-09790-x
Liu WX, Shen LF, Liu JW, Wang YW, Li SR (2007) Uptake of toxic heavy metals by rice (Oryza sativa L.) cultivated in the agricultural soil near Zhengzhou City, People’s Republic of China. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 79:209–213
Liu T, Wang Z, Wang S, Zhao Y, Wright AL, Jiang X (2019) Responses of ammonia-oxidizers and comammox to different long-term fertilization regimes in a subtropical paddy soil. Eur J Soil Biol 93:103087. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejsobi.2019.103087
Lo CC (2010) Effect of pesticides on soil microbial community. J Environ Sci Health B 45:348–359. https://doi.org/10.1080/10934520903467873
Lu S, Sun Y, Lu B, Zheng D, Xu S (2020) Change of abundance and correlation of Nitrospira inopinata-like comammox and populations in nitrogen cycle during different seasons. Chemosphere 241:125098. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.125098
Mertens J, Broos K, Wakelin SA, Kowalchuk GA, Springael D et al (2009) Bacteria, not archaea, restore nitrification in a zinc-contaminated soil. ISME J 3:916–923
Nahar K, Ali MM, Khanom A, Alam MK, Md. Abul Kalam Azad MAK, Rahman MM (2020) Levels of heavy metal concentrations and their effect on net nitrification rates and nitrifying archaea/bacteria in paddy soils of Bangladesh. Appl Soil Ecol 156:103697. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsoil.2020.103697
Nicomrat D, Jharajk J, Kanthang P (2016) Pesticides contaminated in Rice Paddy soil affecting on cultivated microorganism community. Appl Mech Mater 848:135–138. https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMM.848.135
Pajares S, Bohannan BJ (2016) Ecology of nitrogen fixing, nitrifying, and denitrifying microorganisms in tropical forest soils. Front Microbiol 7:1045
Palomo A, Pedersen AG, Fowler SJ, Dechesne A, Sicheritz-Pontén T, Smets BF (2018) Comparative genomics sheds light on niche differentiation and the evolutionary history of comammox Nitrospira. ISME J 12:1779. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41396-018-0083-3
Pandey A, Suter H, He JZ, Hu HW, Chen D (2018) Nitrogen addition decreases dissimilatory nitrate reduction to ammonium in rice paddies. Appl Environ Microbiol 84(17):e00870-e918
Pjevac P, Schauberger C, Poghosyan L, Herbold CW, van Kessel MAHJ, Daebeler A et al (2017) AmoA-targeted polymerase chain reaction primers for the specific detection and quantification of comammox Nitrospira in the environment. Front Microbiol 8:1508
Rahman MM, Azad AK, Sima SN et al (2014a) Role of RNase on microbial community analysis in the rice and wheat plants soil by 16S rDNA-DGGE. J Crop Sci Biotechnol 17:229–237. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12892-014-0071-8
Rahman MM, Basaglia M, Vendramin E, Boz B, Fontana F, Gumiero B, Casella S (2014b) Bacterial diversity of a wooded riparian strip soil specifically designed for enhancing denitrification process. Biol Fertil Soils 50:25–35
Rahman F, Rahman MM, Rahman GKMM, Saleque MA, Hossain ATMS, Miah MG (2016) Effect of organic and inorganic fertilizers and rice straw on carbon sequestration and soil fertility under a rice-rice cropping pattern. Carbon Manag 7(1–2):41–53
Rahman MM, Shan J, Yang P, Shang X, Xia Y, Yan X (2018) Effects of long-term pig manure application on antibiotics, abundance of antibiotic resistance genes (ARGs), anammox and denitrification rates in paddy soils. Environ Pollut 240:368–377
Rahman MM, Nahar K, Ali MM, Sultana N, Karim MM, Adhikari UK, Rauf M, Azad MAK (2020) Effect of long-term pesticides and chemical fertilizers application on the microbial community specifically anammox and denitrifying bacteria in Rice field soil of Jhenaidah and Kushtia district, Bangladesh. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 104:828–833
Sato Y, Ohta H, Yamagishi T, Guo Y, Nishizawa T, Rahman MH, Kuroda H, Kato T, Saito M, Yoshinaga I, Inubushi K, Suwa Y (2012) Detection of anammox activity and 16S rRNA genes in ravine paddy field soil. Microbes Environ 27(3):316–319
Shan J, Zhao X, Sheng R, Xia Y, Ti C, Quan X, Wang S, Wei W, Yan X (2016) Dissimilatory nitrate reduction processes in typical Chinese paddy soils: rates, relative contributions and influencing factors. Environ Sci Technol 50:9972–9980
Shan J, Yang P, Shang X et al (2018) Anaerobic ammonium oxidation and denitrification in a paddy soil as affected by temperature, pH, organic carbon, and substrates. Biol Fertil Soils 54:341–348. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00374-018-1263-z
Shen LD, Liu S, Huang Q, Lian X, He ZF, Geng S, Jin RC, He YF, Lou LP, Xu XY, Zheng P, Hu BL (2014) Evidence for the co-occurrence of nitrite dependent anaerobic ammonium and methane oxidation processes in a flooded paddy field. Appl Environ Microbiol 80:7611–7619. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.02379-14
Sheng R, Meng DL, Wu MN, Di HJ, Qin HL, Wei WX (2013) Effect of agricultural land use change on community composition of bacteria and ammonia oxidizers. J Soils Sediments 13:1246–1256. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-013-0713-3
Smith CJ, Nedwell DB, Dong LF, Osborn AM (2007) Diversity and abundance of nitrate reductase genes (narG and napA), nitrite reductase genes (nirS and nrfA), and their transcripts in estuarine sediments. App Environ Microbiol 73:3612–3622
Smolders E, Brans K, Coppens F, Merckx R (2001) Potential nitrification rate as a tool for screening toxicity in metal-contaminated soils. Environ Toxicol Chem 20(12):2469–2474
Subbarao GV, Ito O, Sahrawat KL, Berry WL, Nakahara K, Ishikawa T, Watanabe T, Suenaga K, Rondon M, Rao IM (2006) Scope and strategies for regulation of nitrification in agricultural systems-challenges and opportunities. Crit Rev Plant Sci 25(4):303–335
Timilsina A, Bizimana F, Pandey B, Yadav R, Dong W, Hu C (2020) Nitrous oxide emissions from paddies: understanding the role of rice plants. Plants (Basel, Switzerland) 9(2):180. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants9020180
Tomlinson DL, Wilson JG, Harris CR, Jeffrey DW (1980) Problems in the assessment of heavy-metal levels in estuaries and the formation of a pollution index. Helgolander Meeresunters 33:566–575. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02414780
van Kessel M, Speth DR, Albertsen M, Nielsen PH, den Camp HJO, Kartal B, Jetten MSM, Lücker S (2015) Complete nitrification by a single microorganism. Nature 528:555–559
Wackett LP (2015) Nitrogen fixation in microbial biotechnology. Microb Biotechnol 8:896–897. https://doi.org/10.1111/1751-7915.12313
Wang H, Li X, Li X, Li X, Wang J, Zhang H (2017) Changes of microbial population and N cycling function genes with depth in three Chinese paddy soils. PLoS ONE 12(12):e0189506. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0189506
Wang Z, Cao Y, Zhu-Barker X, Nicol GW, Wright AL, Jia Z, Jiang X (2019) Comammox Nitrospira clade B contributes to nitrification in soil. Soil Biol Biochem 135:392–395
Welsh A, Chee-Sanford JC, Connor LM, Löffler FE, Sanford RA (2014) Refined nrfA phylogeny improves PCR-based nrfA gene detection. Appl Environ Microbiol 80:2110–2119. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.03443-13
Wu Y, Lu L, Wang B, Lin X, Zhu J, Cai Z, Yan X, Jia Z (2011) Long-term field fertilization significantly alters community structure of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria rather than archaea in a paddy soil. Soil Sci Soc Am J 75:1431–1439. https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj2010.0434
Yang XR, Li H, Nie SA, Su JQ, Weng BS, Zhu GB, Yao HY, Gilbert JA, Zhu YG (2015) Potential contribution of anammox to nitrogen loss from paddy soils in Southern China. Appl Environ Microbiol 81:938–947. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.02664-14
Zabaloy MC, Allegrini M, Tebbe DA, Schuster K, Gomez EDV (2017) Nitrifying bacteria and archaea withstanding glyphosate in fertilized soil microcosms. Appl Soil Ecol 117–118:88–95
Zhu GB, Wang SY, Wang Y, Wang CX, Risgaard-Petersen N, Jetten MSM, Yin CQ (2011) Anaerobic ammonia oxidation in a fertilized paddy soil. ISME J 5:1905–1912
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to Dr. Patti Fisher, Professional Editor, World LLC for checking the paper’s English and grammatical errors. The authors thank the University Grant Commission (UGC) Bangladesh and Islamic University, Kushtia-7003 (141/Edu/IU-2019/331) and the Ministry of Science and Technology, Bangladesh (390000000090602419/ES-373) for partial funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rahman, M.M., Khanom, A. & Biswas, S.K. Effect of Pesticides and Chemical Fertilizers on the Nitrogen Cycle and Functional Microbial Communities in Paddy Soils: Bangladesh Perspective. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 106, 243–249 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-020-03092-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-020-03092-5