Abstract
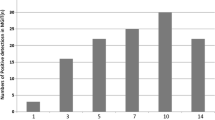
Loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) is a highly sensitive, rapid, cost-effective nucleic acid amplification method. Tuberculosis (TB) is widely popular in the world and it is difficult to cure. The fundamental treatment is to clear the types of TB pathogens such as Mycobacterium bovis (M. bovis), Mycobacterium tuberculosis (M. tuberculosis). In order to detect and diagnose TB early, we constructed the differential diagnostic method of TB. In this study, we used LAMP for detection of M. bovis, based on amplification of the mpb70 gene which is a unique gene in M. bovis strain. The LAMP assay was able to detect only seven copies of the gene per reaction, whereas for the conventional PCR, it was 70 copies. The LAMP was evaluated for its specificity using six strains of five Mycobacterium species and 18 related non-Mycobacterium microorganism strains as controls. The target three Mycobacterium strains were all amplified, and no cross-reaction was found with 18 non-Mycobacterium microorganism strains. TB was detected by two methods, LAMP and conventional PCR (based on mpb70 gene); the positive rates of the two methods were 9.55 and 7.01 %, respectively. Our results indicate that the LAMP method should be a potential tool with high convenience, rapidity, sensitivity and specificity for the diagnosis of TB caused by M. bovis. Most importance is that the use of LAMP as diagnostic method in association with diagnostic tests based on mpb70 gene would allow the differentiation between M. bovis and other Mycobacterium in humans or animals. The LAMP method is actually in order to detect human TB, and it can be used for differential diagnosis in this paper.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brisson-Noel A, Gicquel B, Lecossier D, Levy-Frebault V, Nassif X, Hance AJ (1989) Rapid diagnosis of tuberculosis by amplification of mycobacterial DNA in clinical samples. Lancet 2:1069–1071
Caipang CM, Hirono I, Aoki T (2003) Development of a real-time PCR assay for the detection and quantification of red seabream iridovirus (RSIV). Fish Pathol (Japan) 38(1):1–7. doi:10.3147/jsfp.38.1
Caws M et al (2007) PCR-restriction fragment length polymorphism for rapid, low-cost identification of isoniazid-resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J Clin Microbiol 45:1789–1793. doi:10.1128/JCM.01960-06
Gonzalo-Asensio J et al (2014) Evolutionary history of tuberculosis shaped by conserved mutations in the PhoPR virulence regulator. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 111:11491–11496. doi:10.1073/pnas.1406693111
Harboe M, Nagai S (1984) MPB70, a unique antigen of Mycobacterium bovis BCG. Am Rev Respir Dis 129:444–452
Jayawardena S et al (2007) Loop-mediated isothermal amplification for influenza A (H5N1) virus. Emerg Infect Dis 13:899
Mikhailovich VM et al (2001) Detection of rifampicin-resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis strains by hybridization and polymerase chain reaction on a specialized TB-microchip. Bull Exp Biol Med 131:94–98
Mori Y, Nagamine K, Tomita N, Notomi T (2001) Detection of loop-mediated isothermal amplification reaction by turbidity derived from magnesium pyrophosphate formation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 289:150–154
Nagai S, Matsumoto J, Nagasuga T (1981) Specific skin-reactive protein from culture filtrate of Mycobacterium bovis BCG. Infect Immun 31:1152–1160
Nagamine K, Hase T, Notomi T (2002) Accelerated reaction by loop-mediated isothermal amplification using loop primers. Mol Cell Probes 16:223–229
Netto EM, Dye C, Raviglione MC (1999) Progress in global tuberculosis control 1995-1996, with emphasis on 22 high-incidence countries. Global Monitoring and Surveillance Project. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis 3:310–320
Notomi T et al (2000) Loop-mediated isothermal amplification of DNA. Nucleic Acids Res 28:e63
Organization WH (1997) The current global situation of the HIV/AIDS pandemic. Organization 48:359–360
Osawa R et al (2007) Rapid detection of Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans using a loop-mediated isothermal amplification method. Oral Microbiol Immunol 22:252–259
Palmer MV, Waters WR (2006) Advances in bovine tuberculosis diagnosis and pathogenesis: what policy makers need to know. Vet Microbiol 112:181–190
Palmer M, Waters W, Thacker T, Greenwald R, Esfandiari J, Lyashchenko K (2006) Effects of different tuberculin skin-testing regimens on gamma interferon and antibody responses in cattle experimentally infected with Mycobacterium bovis. Clin Vaccine Immunol 13:387–394
Poon LL et al (2006) Sensitive and inexpensive molecular test for falciparum malaria: detecting Plasmodium falciparum DNA directly from heat-treated blood by loop-mediated isothermal amplification. Clin Chem 52:303–306. doi:10.1373/clinchem.2005.057901
Song L, Li J, Hou S, Li X, Chen S (2012) Establishment of loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) for rapid detection of Brucella spp. and application to milk and blood samples. J Microbiol Methods 90:292–297. doi:10.1016/j.mimet.2012.05.024
Stefan B, Smith NH (2014) Why doesn’t bovine tuberculosis transmit between humans? Trends Microbiol 22:552–553
Takahashi T, Nakayama T (2006) Novel technique of quantitative nested real-time PCR assay for Mycobacterium tuberculosis DNA. J Clin Microbiol 44:1029–1039. doi:10.1128/JCM.44.3.1029-1039.2006
Takahashi T et al (2008) Novel wide-range quantitative nested real-time PCR assay for Mycobacterium tuberculosis DNA: development and methodology. J Clin Microbiol 46:1708–1715. doi:10.1128/JCM.01200-07
Thekisoe OM et al (2007) Species-specific loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) for diagnosis of trypanosomosis. Acta Trop 102:182–189
Thierry D, Brisson-Noel A, Vincent-Levy-Frebault V, Nguyen S, Guesdon JL, Gicquel B (1990) Characterization of a Mycobacterium tuberculosis insertion sequence, IS6110, and its application in diagnosis. J Clin Microbiol 28:2668–2673
Troesch A et al (1999) Mycobacterium species identification and rifampin resistance testing with high-density DNA probe arrays. J Clin Microbiol 37:49–55
van der Vliet GM, Schukkink RA, van Gemen B, Schepers P, Klatser PR (1993) Nucleic acid sequence-based amplification (NASBA) for the identification of mycobacteria. J Gen Microbiol 139:2423–2429
Warner DF, Koch A, Mizrahi V (2015) Diversity and disease pathogenesis in Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Trends Microbiol 23:14–21. doi:10.1016/j.tim.2014.10.005
WHO (2010) Global tuberculosis control report. Cent Eur J Public Health 18:237
Zhang F et al (2009) Sensitive and rapid detection of Karenia mikimotoi (Dinophyceae) by loop-mediated isothermal amplification. Harmful Algae 8:839–842
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Grants from the International Science and Technology Cooperation Project of China (2015DFR31110 and 2013DFA32380), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31460650, 31360610, 31572491), and the University Key Research Project of Henan Province (16A230013).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Communicated by Michael Berney.
Hui Zhang and Zhen Wang have contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, H., Wang, Z., Cao, X. et al. Loop-mediated isothermal amplification assay targeting the mpb70 gene for rapid differential detection of Mycobacterium bovis . Arch Microbiol 198, 905–911 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-016-1232-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-016-1232-6