Abstract
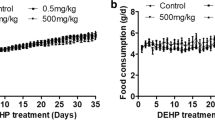
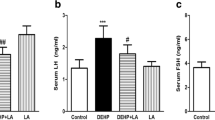
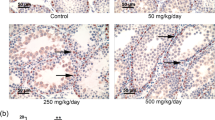
This study was conducted to determine the functional role of phospholipase D (PLD) involved in testicular Leydig cell damage caused by di (2-ethylhexyl) phthalate (DEHP) in Sprague–Dawley rats. DEHP (500 mg/kg/day) was administered orally to prepubertal rats for 1, 7, 14, 21 or 28 days. After 7 days of exposure, DEHP produced morphological changes in the testis, including alterations in seminiferous tubule diameters and loss of spermatogenic cells. Immunohistochemistry (IHC) analyses revealed that DEHP increased Leydig cell number in the testes as well as significantly increased the expression of PLD1/2 in Leydig cells after 7 days of exposure. Furthermore, the protein levels of phosphorylated extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 (pERK1/2) increased in a similar manner to the PLD1/2 expression patterns. DEHP significantly reduced the expression of sperm-associated antigen 4 (Spag4) and lactate dehydrogenase A (LDHA) mRNA. In contrast, there was a significant increase in the expression of steroidogenic acute regulatory (StAR) mRNA against DEHP in a time-dependent manner, but serum testosterone concentration was decreased. These findings demonstrate that DEHP induces PLD expression in the testicular Leydig cells; this plays a key role in hyperplasia of Leydig cells and steroidogenic pathway via pERK1/2 activation.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akingbemi BT, Ge R, Klinefelter GR, Zirkin BR, Hardy MP (2004) Phthalate-induced Leydig cell hyperplasia is associated with multiple endocrine disturbances. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:775–780
Albro PW, Chapin RE, Corbett JT, Schroeder J, Phelps JL (1989) Mono-2-ethylhexyl phthalate, a metabolite of di-(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate, causally linked to testicular atrophy in rats. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 100:193–200
Ali RB, Klouz A, Boubaker S, Lakhal M, Belkahia C (2009) An animal model of testicular toxicity by cyclosporine: evaluation and protection. Fundam Clin Pharmacol 23:241–246
Benitez-Rajal J, Lorite MJ, Burt AD, Day CP, Thompson MG (2006) Phospholipase D and extracellular signal-regulated kinase in hepatic stellate cells: effects of platelet-derived growth factor and extracellular nucleotides. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 291:977–986
Exton JH (2002) Regulation of phospholipase D. FEBS Lett 531:58–61
Foster DA, Xu L (2003) Phospholipase D in cell proliferation and cancer. Mol Cancer Res 1:789–800
Ge RS, Chen GR, Tanrikut C, Hardy MP (2007) Phthalate ester toxicity in Leydig cells: developmental timing and dosage considerations. Reprod Toxicol 23:366–373
Green R, Hauser R, Calafat AM, Weuve J, Schettler T, Ringer S, Huttner K, Hu H (2005) Use of di(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate-containing medical products and urinary levels of mono(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate in neonatal intensive care unit infants. Environ Health Perspect 113:1222–1225
Hanahan DJ, Chaikoff IL (1948) On the nature of the phosphorus-containing lipides of cabbage leaves and their relation to a phospholipide-splitting enzyme contained in these leaves. J Biol Chem 172:191–198
Heller M (1978) Phospholipase D. Adv Lipid Res 16:267–326
Hong JH, Oh SO, Lee M, Kim YR, Kim DU, Hur GM, Lee JH, Lim K, Hwang BD, Park SK (2001) Enhancement of lysophosphatidic acid-induced ERK phosphorylation by phospholipase D1 via the formation of phosphatidic acid. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 281:1337–1342
Kang DW, Park MH, Lee YJ, Kim HS, Kwon TK, Park WS, Min DS (2008) Phorbol ester up-regulates phospholipase D1 but not phospholipase D2 expression through a PKC/Ras/ERK/NFkappaB-dependent pathway and enhances matrix metalloproteinase-9 secretion in colon cancer cells. J Biol Chem 283:4094–4104
Kasahara E, Sato EF, Miyoshi M, Konaka R, Hiramoto K, Sasaki J, Tokuda M, Nakano Y, Inoue M (2002) Role of oxidative stress in germ cell apoptosis induced by di(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate. Biochem J 365:849–856
Kim HS, Saito K, Ishizuka M, Kazusaka A, Fujita S (2003) Short period exposure to di(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate regulates testosterone metabolism in testis of prepubertal rats. Arch Toxicol 77:446–451
Kim S, Kim H, Lee Y, Hyun JW, Lee YH, Shin MK, Min DS, Shin T (2007a) The expression and cellular localization of phospholipase D isozymes in the developing mouse testis. J Vet Sci 8:209–212
Kim H, Lee J, Kim S, Shin MK, Min DS, Shin T (2007b) Differential expression of phospholipases D1 and D2 in mouse tissues. Cell Biol Int 31:148–155
Lahousse SA, Wallace DG, Liu D, Gaido KW, Johnson KJ (2006) Testicular gene expression profiling following prepubertal rat mono-(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate exposure suggests a common initial genetic response at fetal and prepubertal ages. Toxicol Sci 93:369–381
Lauritzen L, Hansen HS (1995) Differential phospholipid-labeling suggests two subtypes of phospholipase D in rat Leydig cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 217:747–754
Lee J, Richburg JH, Younkin SC, Boekelheide K (1997) The Fas system is a key regulator of germ cell apoptosis in the testis. Endocrinology 138:2081–2088
Leung PC, Steele GL (1992) Intracellular signaling in the gonads. Endocr Rev 13:476–498
Lovekamp-Swan T, Jetten AM, Davis BJ (2003) Dual activation of PPARalpha and PPARgamma by mono-(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate in rat ovarian granulose cells. Mol Cell Endocrinol 201:133–141
Mahood IK, Hallmark N, McKinnell C, Walker M, Fisher JS, Sharpe RM (2005) Abnormal Leydig cell aggregation in the fetal testis of rats exposed to di (n-butyl) phthalate and its possible role in testicular dysgenesis. Endocrinology 146:613–623
Manna PR, Jo Y, Stocco DM (2007) Regulation of Leydig cell steroidogenesis by extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2: role of protein kinase A and protein kinase C signaling. J Endocrinol 193:53–63
Morris AJ, Engebrecht J, Frohman MA (1996) Structure and regulation of phospholipase D. Trends Pharmacol Sci 17:182–185
Oishi S (1986) Testicular atrophy induced by di(2-ethylhexyl)phthalate: changes in histology, cell specific enzyme activities and zinc concentrations in rat testis. Arch Toxicol 59:290–295
Rizzo MA, Shome K, Vasudevan C, Stolz DB, Sung TC, Frohman MA, Watkins SC, Romero G (1999) Phospholipase D and its product, phosphatidic aid, mediate agonist-dependent raf-1 translocation to the plasma membrane and the activation of the mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway. J Biol Chem 274:1131–1139
Rommerts FF, Brinkman AO (1981) Modulation of steroidogenic activities in testis Leydig cells. Mol Cell Endocrinol 21:15–28
Ryu JY, Whang J, Park H, Im JY, Kim J, Ahn MY, Lee J, Kim HS, Lee BM, Yoo SD, Kwack SJ, Oh JH, Park KL, Han SY, Kim SH (2007) Di(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate induces apoptosis through peroxisome proliferators-activated receptor-gamma and ERK 1/2 activation in testis of Sprague-Dawley rats. J Toxicol Environ Health PartA 70:1296–1303
Sathyanarayana S (2008) Phthalates and children’s health. Curr Probl Pediatr Adolesc Health Care 38:34–49
Strand AM, Lauritzen L, Vinggaard AM, Hansen HS (1999) The subcellular localization of phospholipase D activities in rat Leydig cells. Mol Cell Endocrinol 152:99–110
Varadharaj S, Steinhour E, Hunter MG, Watkins T, Baran CP, Magalang U, Kuppusamy P, Zweier JL, Marsh CB, Natarajan V, Parinandi NL (2006) Vitamin C-induced activation of phospholipase D in lung microvascular endothelial cells: regulation by MAP kinases. Cell Signal 18:1396–1407
Vinggaard AM, Hansen HS (1991) Phorbol ester and vasopressin activate phospholipase D in Leydig cells. Mol Cell Endocrinol 79:157–165
Wilson VS, Lambright C, Furr J, Ostby J, Wood C, Held G, Gray LE Jr (2004) Phthalate ester-induced gubernacular lesions are associated with reduced insl3 gene expression in the fetal rat testis. Toxicol Lett 146:207–215
Acknowledgments
We thank Prof. Byung Mu Lee for discussion that inspired us to perform this study. We also thank Hae Young Chung and Jee H. Jung for helpful comments on the manuscript. Lee Y.J. and Ahn M.Y. were supported by grants from the Brain Korea 21 project. We thank Aging Tissue Bank for providing research resources.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, Y.J., Ahn, M.Y., Kim, H.S. et al. Role of phospholipase D in regulation of testicular Leydig cell hyperplasia in Sprague–Dawley rats treated with di(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate. Arch Toxicol 85, 975–985 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-010-0618-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-010-0618-5