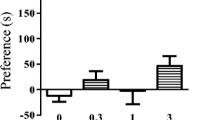
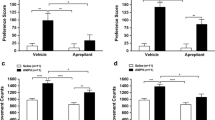
Abstract
Rationale
N-Methyl-d-aspartate (NMDA) receptors have an important role in different forms of behavioral and neural plasticity. Evidence suggests that these receptors may also be involved in plasticity arising from long-term treatment with different drugs of abuse, including tolerance, sensitization, and physical dependence. There is abundant evidence demonstrating that NMDA receptors are involved in tolerance to opiate-induced antinociception; however, the role of these receptors in sensitization to the locomotor effects of opiates is more controversial.
Objective
The ability of NMDA receptor antagonists to modify the development of sensitization to the locomotor stimulant effect of three different opiates was examined. In selected studies, the ability of the antagonists to modify tolerance to the antinociceptive effects of the opiates was also examined.
Materials and methods
Adult male Sprague–Dawley rats were used to assess the effects of NMDA receptor antagonists (MK-801, memantine or LY235959) on tolerance and sensitization to three opiates: morphine, methadone, or buprenorphine. It was predicted that low, selective doses of the antagonists would inhibit the development of opiate tolerance and sensitization.
Results
Consistent with our predictions, the noncompetitive NMDA receptor antagonists MK-801 and memantine and the competitive NMDA receptor antagonist LY235959 inhibited the development of sensitization to the locomotor stimulant effect of morphine. Additionally, MK-801 inhibited the development of tolerance and sensitization to methadone and buprenorphine in a similar manner.
Conclusions
The results, together with previous research, suggest that NMDA receptors are broadly involved in opiate-induced plasticity, including the development of opiate tolerance and sensitization.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen RM, Dykstra LA (1999) The competitive NMDA receptor antagonist LY235959 modulates the progression of morphine tolerance in rats. Psychopharmacology 142:209–214
Allen RM, Dykstra LA (2000a) Attenuation of mu-opioid tolerance and cross-tolerance by the competitive N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor antagonist LY235959 is related to tolerance and cross-tolerance magnitude. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 295:1012–1021
Allen RM, Dykstra LA (2000b) Role of morphine maintenance dose in the development of tolerance and its attenuation by an NMDA receptor antagonist. Psychopharmacology 148:59–65
Atalla A, Kuschinsky K (2006) Effects of blockade of glutamate NMDA receptors or of NO synthase on the development or the expression of associative or non-associative sensitization to locomotor activation by morphine. J Neural Transm V113:1–10
Bell RF, Dahl JB, Moore RA, Kalso E (2005) Peri-operative ketamine for acute post-operative pain: a quantitative and qualitative systematic review (Cochrane review). Acta Anaesthesiol Scand 49:1405–1428
Belozertseva IV, Bespalov A (1998) Effects of NMDA receptor channel blockers, dizocilpine and memantine, on the development of opiate analgesic tolerance induced by repeated morphine exposures or social defeats in mice. Naunyn-Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 358:270–274
Ben-Eliyahu S, Marek P, Vaccarino AL, Mogil JS, Sternberg WF, Liebeskind JC (1992) The NMDA receptor antagonist MK-801 prevents long-lasting non-associative morphine tolerance in the rat. Brain Res 575:304–308
Bilsky EJ, Inturrisi CE, Sadee W, Hruby VJ, Porreca F (1996) Competitive and non-competitive NMDA antagonists block the development of antinociceptive tolerance to morphine, but not to selective μ or ∂ opioid agonists in mice. Pain 68:229–237
Bisaga A, Popik P (2000) In search of a new pharmacological treatment for drug and alcohol addiction: N-methyl-d-aspartate (NMDA) antagonists. Drug Alcohol Depend 59:1–15
Bubser M, Keseberg U, Notz PK, Schmidt WJ (1992) Differential behavioral and neurochemical effects of competitive and non-competitive NMDA receptor antagonists in rats. Eur J Pharmacol 229:75–82
Carlezon WA Jr, Mendrek A, Wise RA (1995) MK-801 disrupts the expression but not the development of bromocriptine sensitization: a state-dependency interpretation. Synapse 20:1–9
Carlezon WA Jr, Kosten TA, Nestler EJ (2000) Behavioral interactions caused by combined administration of morphine and MK-801 in rats. Psychopharmacology 151:261–272
Carter AJ (1994) Many agents that antagonize the NMDA receptor–channel complex in vivo also cause disturbances of motor coordination. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 269:573–580
Danysz W, Parsons CG (1998) Glycine and N-methyl-d-aspartate receptors: physiological significance and possible therapeutic applications. Pharmacol Rev 50:597–664
Danysz W, Essman U, Bresink I, Wilke R (1994) Glutamate antagonists have different effects on spontaneous locomotor activity in rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 48:111–118
Geter-Douglass B, Witkin JM (1997) Dizocilpine-like discriminative stimulus effects of competitive NMDA receptor antagonists in mice. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 133:43–50
Geter-Douglass B, Witkin JM (1999) Behavioral effects and anticonvulsant efficacies of low-affinity, uncompetitive NMDA antagonists in mice. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 146:280–289
Gutstein HB, Trujillo KA (1993) MK-801 inhibits the development of morphine tolerance at spinal sites. Brain Res 626:332–334
Herman BH, Vocci F, Bridge P (1995) The effects of NMDA receptor antagonists and nitric oxide synthase inhibitors on opioid tolerance and withdrawal. Medication development issues for opiate addiction. Neuropsychopharmacology 13:269–293
Iijima Y, Asami T, Kuribara H (1996) Modification by MK-801(dizocilpine), a noncompetitive NMDA receptor antagonist, of morphine sensitization: evaluation by ambulation in mice. Japanese Journal of Psychopharmacology 16:11–18
Inturrisi CE (1997) Preclinical evidence for a role of glutamatergic systems in opioid tolerance and dependence. Semin Neurosci 9:110–119
Jeziorski M, White FJ, Wolf ME (1994) MK-801 prevents the development of behavioral sensitization during repeated morphine administration. Synapse 16:137–147
Kosten TA, Bombace JC (2000) Prior and delayed applications of dizocilpine or ethanol alter locomotor sensitization to morphine. Brain Res 878:20–31
Li Y, Wolf ME (1999) Can the “ state-dependency” hypothesis explain prevention of amphetamine sensitization in rats by NMDA receptor antagonists? Psychopharmacology (Berl) 141:351–61
Lodge D, Danysz W, Parsons CG (2002) Ionotropic glutamate receptors as therapeutic targets. F.P. Graham, Johnson City, TN
Mao J (1999) NMDA and opioid receptors: their interactions in antinociception, tolerance and neuroplasticity. Brain Res Rev 30:289–304
Mao J, Price DD, Lu J, Mayer DJ (1998) Antinociceptive tolerance to the mu-opioid agonist DAMGO is dose-dependently reduced by MK-801 in rats. Neurosci Lett 250:193–196
Marek P, Ben-Eliyahu S, Vaccarino AL, Liebeskind JC (1991) Delayed application of MK-801 attenuates development of morphine tolerance in rats. Brain Res 558:163–165
Mayer DJ, Mao J (1999) Mechanisms of opioid tolerance: a current view of cellular mechanisms. Pain Forum 8:14–18
Mayer DJ, Mao J, Holt J, Price DD (1999) Cellular mechanisms of neuropathic pain, morphine tolerance, and their interactions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 96:7731–7736
Miyamoto Y, Yamada K, Nagai T, Mori H, Mishina M, Furukawa H, Noda Y, Nabeshima T (2004) Behavioural adaptations to addictive drugs in mice lacking the NMDA receptor epsilon1 subunit. Eur J Neurosci 19:151–158
Parsons CG, Danysz W, Quack G (1999) Memantine is a clinically well-tolerated N-methyl-d-aspartate (NMDA) receptor antagonists—a review of preclinical data. Neuropharmacology 38:735–767
Peterson DJ (2003) The effects of memantine on opiate tolerance, sensitization and physical dependence department of psychology. California State University, San Marcos
Peterson DJ, Mendez IA, Lewellen RM, Trujillo KA (2002) NMDA receptor antagonists prevent and slowly reverse opiate-induced behavioral and neural plasticity. In International Narcotics Research Conference, Asilomar, CA
Popik P, Kozela E (1999) Clinically available NMDA antagonist, memantine, attenuates tolerance to analgesic effects of morphine in a mouse tail flick test. Pol J Pharmacol 51:223–231
Popik P, Kozela E, Danysz W (2000) Clinically available NMDA receptor antagonists memantine and dextromethorphan reverse existing tolerance to the antinociceptive effects of morphine in mice. Naunyn-Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 361:425–432
Ranaldi R, Munn E, Neklesa T, Wise RA (2000) Morphine and amphetamine sensitization in rats demonstrated under moderate- and high-dose NMDA receptor blockade with MK-801 (dizocilpine). Psychopharmacology 151:192–201
Redwine KE, Trujillo KA (2003) Effects of NMDA receptor antagonists on acute mu opioid analgesia in the rat. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 76:361–372
Shimoyama N, Shimoyama M, Davis AM, Monaghan DT, Inturrisi CE (2005) An antisense oligonucleotide to the N-methyl-d-aspartate (NMDA) Subunit NMDAR1 Attenuates NMDA-induced nociception, hyperalgesia, and morphine tolerance. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 312:834–840
Subramaniam K, Subramaniam B, Steinbrook RA (2004) Ketamine as adjuvant analgesic to opioids: a quantitative and qualitative systematic review. Anesth Analg 99:482–495
Swadley-Lewellen RM, Trujillo KA (1998) Are NMDA receptors involved in tolerance and sensitization to the locomotor effects of morphine? Society for Neuroscience Abstracts 24:1968
Tiseo PJ, Inturrisi CE (1993) Attenuation and reversal of morphine tolerance by the competitive N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor antagonist LY274614. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 264:1090–1096
Trujillo KA (1995) Effects of non-competitive N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor antagonists on opiate tolerance and physical dependence. Neuropsychopharmacology 13:301–307
Trujillo KA (2000) Are NMDA receptors involved in opiate-induced neural and behavioral plasticity? A review of preclinical findings. Psychopharmacology 151:121–141
Trujillo KA (2002) The neurobiology of opiate tolerance, dependence and sensitization: Mechanisms of NMDA receptor-dependent synaptic plasticity. Neurotox Res 4:373–391
Trujillo KA, Akil H (1991) Inhibition of morphine tolerance and dependence by the NMDA receptor antagonist MK-801. Science 251:85–87
Trujillo KA, Akil H (1994) Inhibition of opiate tolerance by non-competitive N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor antagonists. Brain Res 633:178–188
Trujillo KA, Akil H (1995) Excitatory amino acids and drugs of abuse: a role for N-methyl-d-aspartate receptors in drug tolerance, sensitization and physical dependence. Drug Alcohol Depend 38:139–154
Trujillo KA, Warmoth KP, Peterson DJ, Albertson DN, Swadley-Lewellen RM (2000) Potential role for NMDA receptors in acute locomotor effects of opiates. Society for Neuroscience Abstracts 26:272
Trujillo KA, Warmoth KP, Mendez IA, Watorski K, Peterson DJ, Albertson DN, Swadley-Lewellen RM (2001a) Contrasting effects of NMDA receptor antagonists on opiate analgesia and locomotion. Drug Alcohol Depend 63(Suppl 1):S159–S160
Trujillo KA, Warmoth KP, Peterson DJ, Albertson DN, Watorski K, Swadley-Lewellen RM (2001b) NMDA receptor antagonists inhibit the development of tolerance and sensitization to the locomotor effects of opiates. Society for Neuroscience Abstracts 27, Abstract #224.11
Tzschentke TM, Schmidt WJ (1996) Procedural examination of behavioral sensitisation to morphine: lack of blockade by MK-801, occurrence of sensitised sniffing, and evidence for cross-sensitisation between morphine and MK-801. Behav Pharmacol 7:169–184
Tzschentke TM, Schmidt WJ (1998) Does the non-competitive NMDA receptor antagonist dizocilpine (MK-801) really block behavioral sensitization associated with repeated drug administration? Trends Pharmacol Sci 19:447–451
Tzschentke TM, Schmidt WJ (2000) Effects of the non-competitive NMDA-receptor antagonist memantine on morphine- and cocaine-induced potentiation of lateral hypothalamic brain stimulation reward. Psychopharmacology 149:225–234
Vanderschuren LJ, Kalivas PW (2000) Alterations in dopaminergic and glutamatergic transmission in the induction and expression of behavioral sensitization: a critical review of preclinical studies. Psychopharmacology 151:99–120
Vanderschuren LJ, Schoffelmeer AN, De Vries TJ (1997) Does dizocilpine (MK-801) inhibit the development of morphine-induced behavioral sensitization in rats? Life Sci 61:427–433
Wolf ME (1998) The role of excitatory amino acids in behavioral sensitization to psychomotor stimulants. Prog Neurobiol 54:679–720
Wolf ME, Jeziorski M (1993) Coadministration of MK-801 with amphetamine, cocaine or morphine prevents rather than transiently masks the development of behavioral sensitization. Brain Res 613:291–294
Acknowledgment
This research was supported by the National Institute on Drug Abuse (DA 19859), the National Institute of General Medical Sciences (GM 59833), and the Office for Biomedical Research and Training at California State University San Marcos. Ian Mendez was supported by the National Institute of General Medical Sciences (GM 64783). We would like to thank Kathleen Warmoth for the expert technical assistance and Jon Athancio for the help with the graphing.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mendez, I.A., Trujillo, K.A. NMDA receptor antagonists inhibit opiate antinociceptive tolerance and locomotor sensitization in rats. Psychopharmacology 196, 497–509 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-007-0984-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-007-0984-8