Abstract
Rationale
Decision making is thought to play a key role in psychostimulant relapse, but very few studies have addressed the issue of how to counteract decision-making deficits in addicted individuals. According to the somatic marker framework, pervasive decision-making problems in addicted individuals may relate to abnormalities in the processing of emotional signals that work to anticipate the prospective outcomes of potential decisions.
Objective
The present study was conducted to test whether the induction of different emotional states (positive, negative, or drug-related) could either normalize or further impair decision-making performance in male cocaine polysubstance-using individuals (CPSI), as indexed by the Iowa gambling task (IGT).
Methods
Forty-two CPSI and 65 healthy control individuals (all males) were randomly allocated in four affective conditions using a parallel-group design. Participants in the different conditions performed the IGT during exposure to neutral, positive, negative, or drug-related sets of affective images.
Results
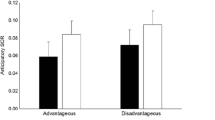
The results showed that the CPSI exposed to the negative affective context showed a preference for the risk-averse safe choices of the IGT and had a net performance indistinguishable from that of controls. On the other hand, CPSI exposed to positive, drug-related, and neutral contexts showed the typical pattern of disadvantageous performance in the IGT and performed significantly poorer than controls. The impact of the negative mood induction could not be explained in terms of baseline differences in decision-making skills, personality traits related to sensitivity to reward/punishment, or trait positive/negative affect.
Conclusions
We conclude that negative mood induction can normalize decision-making performance in male CPSI, which may have important implications for the treatment of cocaine use-related disorders.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aguilar de Arcos F, Verdejo-García A, Peralta-Ramírez MI, Sánchez-Barrera M, Pérez-García M (2005) Experience of emotions in substance abusers exposed to images containing neutral, positive, and negative affective stimuli. Drug Alcohol Depend 78:159–167
Aguilar de Arcos F, Verdejo-García A, Ceverino A, Montañez-Pareja M, López-Juárez E, Sánchez-Barrera M, López-Jiménez A, Pérez-García M (2008) Dysregulation of emotional response in current and abstinent heroin users: negative heightening and positive blunting. Psychopharmacology 198:159–166
Bechara A (2004) A neural view of the regulation of complex cognitive functions by emotion. In: Philippot P, Feldman RS (eds) The regulation of emotion. Lawrence Erlbaum, New Jersey, pp 3–32
Bechara A, Damasio H (2002) Decision-making and addiction (part I): impaired activation of somatic states in substance dependent individuals when pondering decisions with negative future consequences. Neuropsychologia 40:1675–1689
Bechara A, Damasio AR (2005) The somatic marker hypothesis: a neural theory of economic decision. Games Econ Behav 52:336–372
Bechara A, Damasio H, Damasio AR (2000) Emotion, decision-making and the orbitofrontal cortex. Cereb Cortex 10:295–307
Bechara A, Dolan S, Hindes A (2002) Decision-making and addiction (part II): myopia for the future of hypersensitivity to reward? Neuropsychologia 40:1690–1705
Bechara A, Damasio H, Tranel D, Damasio AR (2005) The Iowa gambling task and the somatic marker hypothesis: some questions and answers. Trends Cogn Sci 9:159–162
Bowden-Jones H, McPhillips M, Rogers R, Hutton S, Joyce E (2005) Risk taking on tests sensitive to ventromedial prefrontal cortex dysfunction predicts early relapse in alcohol dependency: a pilot study. J Neuropsychiatry Clin Neurosci 17:417–420
Bower GH (1981) Mood and memory. Am Psychol 36:129–148
Bradley MM, Cuthbert BN, Lang PJ (1996) Picture media and emotion: effects of a sustained affective context. Psychophysiology 33:662–670
Caseras X, Ávila C, Torrubia R (2003) The measurement of individual differences in behavioural inhibition and behavioral activation systems: a comparison of personality scales. Pers Individ Differ 34:999–1013
Chapin TM, Hong K, Fox HC, Siedlarz KM, Bergquist K, Sinha R (2010) Behavioral arousal in response to stress and drug cue in alcohol and cocaine addicted individuals versus healthy controls. Hum Psychopharmacol 25:368–376
Damasio AR (1994) Descartes’ error: emotion, reason, and the human brain. Grosset, New York
de Visser L, van der Knaap LJ, van de Loo AJ, van der Weerd CM, Ohl F, van den Bos R (2010) Trait anxiety affects decision-making differently in healthy men and women: towards gender-specific endophenotypes of anxiety. Neuropsychologia 48:1598–1606
Epstein DH, Willner-Reid J, Vahabzadeh M, Mezghanni M, Lin JL, Preston KL (2009) Real-time electronic diary reports of cue exposure and mood in the hours before cocaine and heroin craving and use. Arch Gen Psychiatry 66:88–94
Fellows LK (2007) The role of orbitofrontal cortex in decision making. A component process account. Ann NY Acad Sci 1121:421–430
Fishbein DH, Eldreth DL, Hyde C, Matochik JA, London ED, Contoreggi C et al (2005) Risky decision-making and the anterior cingulate cortex in abstinent drug abusers and nonusers. Cogn Brain Res 23:119–136
Goldstein RZ, Volkow ND (2002) Drug addiction and its underlying neurobiological basis: neuroimaging evidence for the involvement of the frontal cortex. Am J Psychiatry 159:1642–1652
Hamilton M (1959) The assessment of anxiety states by rating. Br J Med Psychol 32:50–55
Hamilton M (1960) A rating scale for depression. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 23:56–62
Heilman RM, Criçan LG, Houser D, Miclea M, Miu AD (2010) Emotion regulation and decision making under risk and uncertainty. Emotion 10:257–265
Knutson B, Greer SM (2008) Anticipatory affect: neural correlates and consequences for choice. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 363:3771–3786
Koob GF, Le Moal M (2001) Drug addiction, dysregulation of reward, and allostasis. Neuropsychopharmacology 24:97–129
Lang PJ, Greenwald MK, Bradley MM, Hamm AO (1993) Looking at picture: affective, facial, visceral, and behavioral reactions. Psychophysiology 30:261–273
Lang PJ, Bradley MM, Cuthbert BN (2001) International affective picture system (IAPS); Instruction manual and effective ratings. Technical Report A-5, The Center for Research in Psychophysiology, University of Florida
Li CS, Sinha R (2008) Inhibitory control and emotional stress regulation: neuroimaging evidence for frontal-limbic dysfunction in psycho-stimulant addiction. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 32:581–597
Li CS, Kosten TR, Sinha R (2005) Sex differences in brain activation during stress imagery in abstinent cocaine users: a functional magnetic resonance imaging study. Biol Psychiatry 57:487–494
Li CS, Zhang S, Duann JR, Yan P, Sinha R, Mazure CM (2009) Gender differences in cognitive control: an extended investigation of the stop signal task. Brain Imaging Behav 3:262–276
Lobo A, Chamorro L, Luque A, Dal-Ré R, Badia X, Baro E (2002) Validación de las versiones en español de la Montgomery–Asberg Depression Rating Scale y la Hamilton Anxiety Rating Scale para la evaluación de la depresión y de la ansiedad. Med Clin (Barc) 118:493–499
Loewenstein G, Weber EU, Hsee CK, Welch N (2001) Risk as feelings. Psychol Bull 127:267–286
Lubman DI, Yücel M, Kettle JWL, Scaffidi A, MacKenzie T, Simmons JG et al (2009) Responsiveness to drug cues and natural rewards in opiate addiction. Arch Gen Psychiatry 66:205–212
Miu AC, Heilman RM, Houser D (2008) Anxiety impair decision-making: psychophysiological evidence from an Iowa gambling task. Biol Psychol 77:353–358
Nieuwenhuis S, Holroyd CB, Mol N, Coles MG (2004) Reinforcement-related brain potentials from medial frontal cortex: origins and functional significance. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 28:441–448
Overman W, Graham L, Redmond A, Eubank R, Boettcher L, Samplawski O, Walsh K (2006) Contemplation of moral dilemmas eliminates sex differences on the Iowa gambling task. Behav Neurosci 120:817–825
Passetti F, Clark L, Mehta MA, Joyce E, King M (2008) Neuropsychological predictors of clinical outcome in opiate addiction. Drug Alcohol Depend 94:82–91
Paulus MP, Tapert SF, Schuckit MA (2005) Neural activation patterns of methamphetamine-dependent subjects during decision-making predicts relapse. Arch Gen Psychiatry 62:761–768
Ramos-Brieva JA, Cordero A, Yánez R (1994) Nuevos datos sobre la validez y fiabilidad de la versión castellana de la escala de Hamilton para la depresión. An Psiquiatr 10:146–151
Redish AD, Jensen S, Johnson A (2008) A unified framework for addiction: vulnerabilities in the decision process. Behav Brain Sci 31:415–487
Sandín B, Chorot P, Lostao L, Joiner TE, Santed MA, Valiente RM (1999) Escalas PANAS de afecto positivo y negativo: validación factorial y convergencia transcultural. Psicothema 11:37–51
Sinha R, Garcia M, Paliwal P, Kreek MJ, Rounsaville BJ (2006) Stress-induced cocaine craving and hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal responses are predictive of cocaine relapse outcomes. Arch Gen Psychiatry 63:324–331
Smoski MJ, Lynch TR, Rosenthal MZ, Cheavens JS, Chapman AL, Krishnan RR (2008) Decision-making and risk aversion among depressive adults. J Behav Ther Exp Psychiatry 39:567–576
Starcke K, Wofl OT, Markowitsch HJ, Brand M (2008) Anticipatory stress influences decision making under explicit risk conditions. Behav Neurosci 122:1352–1360
Torrubia R, Ávila C, Moltó J, Caseras X (2001) The Sensitivity to Punishment and Sensitivity to Reward Questionnaire (SPSRQ) as a measure of Gray’s anxiety and impulsivity dimensions. Pers Individ Differ 31:837–862
Verdejo-García AJ, López-Torrecillas F, Aguilar de Arcos F, Pérez-García M (2005) Differential effects of MDMA, cocaine, and cannabis use severity on distinctive components of the executive functions in polysubstance users: a multiple regression analysis. Addict Behav 30:89–101
Verdejo-García A, Pérez-García M, Bechara A (2006) Emotion, decision-making and substance dependence: a somatic-marker model of addiction. Curr Neuropharmacol 4:17–31
Verdejo-García A, Lawrence AJ, Clark L (2008) Impulsivity as a vulnerability marker for substance-use disorders: review of findings from high-risk research, problem gamblers and genetic association studies. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 32:777–810
Verdejo-García A, López-Torrecillas F, Pita Calandre E, Delgado-Rodríguez A, Bechara A (2009) Executive function and decision-making in women with fibromyalgia. Arch Clin Neuropsychol 24:113–122
Walitzer KS, Dearing RL (2006) Gender differences in alcohol and substance use relapse. Clin Psychol Rev 26:128–148
Watson D, Clark LA (1994) The PANAS-X: manual for the positive and negative affect schedule-expanded form. University of Iowa, Iowa
Watson D, Clark LA, Tellegen A (1988) Development and validation of brief measures of positive and negative affect: the PANAS Scales. J Pers Soc Psychol 54:1063–1070
Weiss R, Griffin M, Hufford C (1995) Craving in hospitalized cocaine abusers as a predictor of outcome. Am J Drug Alcohol Abuse 21:289–301
Weiss RD, Griffin ML, Hufford C, Muenz LR, Najavits LM, Jansson SB et al (1997) Early prediction of initiation of abstinence from cocaine. Am J Addict 6:224–231
Weiss R, Griffin ML, Mazurik C, Berkman B, Gastfriend DR, Frank A et al (2003) The relationship between cocaine craving, psychosocial treatment and subsequent cocaine use. Am J Psych 160:1320–1325
Werner NS, Duschek S, Schandry R (2009) Relationships between affective states and decision-making. Int J Psychophysiol 74:259–265
Wiswede D, Münte TF, Goschke T, Rüsseler J (2009) Modulation of the error-related negativity by induction of short-term negative affect. Neuropsychologia 47:83–90
Acknowledgment
This work was funded by the Spanish Ministry of Education under the FPU national plan (grant reference AP 2005-1411) and grant SEJ 2006-8278 by the Junta de Andalucía through the grant P07.HUM 03089 and by the Plan Nacional sobre Drogas (2009), COPERNICO grant.
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fernández-Serrano, M.J., Moreno-López, L., Pérez-García, M. et al. Negative mood induction normalizes decision making in male cocaine dependent individuals. Psychopharmacology 217, 331–339 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-011-2288-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-011-2288-2