Abstract
Rationale
There are evidences indicating the role of kinins in pathophysiology of traumatic brain injury, but little is known about their action on memory deficits.
Objectives
Our aim was to establish the role of bradykinin receptors B1 (B1R) and B2 (B2R) on the behavioral, biochemical, and histologic features elicited by moderate lateral fluid percussion injury (mLFPI) in mice.
Methods
The role of kinin B1 and B2 receptors in brain damage, neuromotor, and cognitive deficits induced by mLFPI, was evaluated by means of subcutaneous injection of B2R antagonist (HOE-140; 1 or 10 nmol/kg) or B1R antagonist (des-Arg9-[Leu8]-bradykinin (DAL-Bk; 1 or 10 nmol/kg) 30 min and 24 h after brain injury. Brain damage was evaluated in the cortex, being considered as lesion volume, inflammatory, and oxidative damage. The open field and elevated plus maze tests were performed to exclude the nonspecific effects on object recognition memory test.
Results
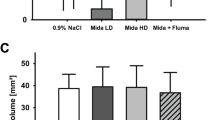
Our data revealed that HOE-140 (10 nmol/kg) protected against memory impairment. This treatment attenuated the brain edema, interleukin-1β, tumor necrosis factor-α, and nitric oxide metabolites content elicited by mLFPI. Accordingly, HOE-140 administration protected against the increase of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate oxidase activity, thiobarbituric-acid-reactive species, protein carbonylation generation, and Na+ K+ ATPase inhibition induced by trauma. Histologic analysis showed that HOE-140 reduced lesion volume when analyzed 7 days after brain injury.
Conclusions
This study suggests the involvement of the B2 receptor in memory deficits and brain damage caused by mLFPI in mice.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aiguo W, Zhe Y, Gomez-Pinilla F (2010) Vitamin E protects against oxidative damage and learning disability after mild traumatic brain injury in rats. Neurorehabil Neural Repair 24:290–298. doi:10.1177/1545968309348318
Albert-Weissenberger C, Stetter C, Meuth SG, Gobel K, Bader M, Siren AL, Kleinschnitz C (2012) Blocking of bradykinin receptor B1 protects from focal closed head injury in mice by reducing axonal damage and astroglia activation. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 32:1747–1756. doi:10.1038/jcbfm.2012.62
Ates O, Cayli S, Altinoz E, Gurses I, Yucel N, Sener M, Kocak A, Yologlu S (2007) Neuroprotection by resveratrol against traumatic brain injury in rats. Mol Cell Biochem 294:137–144. doi:10.1007/s11010-006-9253-0
Austinat M, Braeuninger S, Pesquero JB, Brede M, Bader M, Stoll G, Renne T, Kleinschnitz C (2009) Blockade of bradykinin receptor B1 but not bradykinin receptor B2 provides protection from cerebral infarction and brain edema. Stroke 40:285–293. doi:10.1161/STROKEAHA.108.526673
Ayer R, Jadhav V, Sugawara T, Zhang JH (2011) The neuroprotective effects of cyclooxygenase-2 inhibition in a mouse model of aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. Acta Neurochir Suppl 111:145–149. doi:10.1007/978-3-7091-0693-8_24
Baratz R, Tweedie D, Rubovitch V, Luo W, Yoon JS, Hoffer BJ, Greig NH, Pick CG (2011) Tumor necrosis factor-alpha synthesis inhibitor, 3,6′-dithiothalidomide, reverses behavioral impairments induced by minimal traumatic brain injury in mice. J Neurochem 118:1032–1042. doi:10.1111/j.1471-4159.2011.07377.x
Bay E, Covassin T (2012) Chronic stress, somatic and depressive symptoms following mild to moderate traumatic brain injury. Arch Psychiatr Nurs 26:477–486. doi:10.1016/j.apnu.2012.06.002
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Carbonell WS, Maris DO, McCall T, Grady MS (1998) Adaptation of the fluid percussion injury model to the mouse. J Neurotrauma 15:217–229
Chao J, Woodley C, Chao L, Margolius HS (1983) Identification of tissue kallikrein in brain and in the cell-free translation product encoded by brain mRNA. J Biol Chem 258:15173–15178
Clausen F, Lundqvist H, Ekmark S, Lewen A, Ebendal T, Hillered L (2004) Oxygen free radical-dependent activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase mediates apoptosis-like cell death after traumatic brain injury. J Neurotrauma 21:1168–1182. doi:10.1089/neu.2004.21.1168
Clausen F, Hanell A, Bjork M, Hillered L, Mir AK, Gram H, Marklund N (2009) Neutralization of interleukin-1beta modifies the inflammatory response and improves histological and cognitive outcome following traumatic brain injury in mice. Eur J Neurosci 30:385–396. doi:10.1111/j.1460-9568.2009.06820.x
Correa FM, Innis RB, Uhl GR, Snyder SH (1979) Bradykinin-like immunoreactive neuronal systems localized histochemically in rat brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 76:1489–1493
Donkin JJ, Vink R (2010) Mechanisms of cerebral edema in traumatic brain injury: therapeutic developments. Curr Opin Neurol 23:293–299. doi:10.1097/WCO.0b013e328337f451
Gahm C, Holmin S, Wiklund PN, Brundin L, Mathiesen T (2006) Neuroprotection by selective inhibition of inducible nitric oxide synthase after experimental brain contusion. J Neurotrauma 23:1343–1354. doi:10.1089/neu.2006.23.1343
Gilgun-Sherki Y, Rosenbaum Z, Melamed E, Offen D (2002) Antioxidant therapy in acute central nervous system injury: current state. Pharmacol Rev 54:271–284
Gorlach C, Hortobagyi T, Hortobagyi S, Benyo Z, Relton J, Whalley ET, Wahl M (2001) Bradykinin B2, but not B1, receptor antagonism has a neuroprotective effect after brain injury. J Neurotrauma 18:833–838. doi:10.1089/089771501316919193
Groger M, Lebesgue D, Pruneau D, Relton J, Kim SW, Nussberger J, Plesnila N (2005) Release of bradykinin and expression of kinin B2 receptors in the brain: role for cell death and brain edema formation after focal cerebral ischemia in mice. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 25:978–989. doi:10.1038/sj.jcbfm.9600096
Hall JM (1992) Bradykinin receptors: pharmacological properties and biological roles. Pharmacol Ther 56:131–190
Hellal F, Pruneau D, Palmier B, Faye P, Croci N, Plotkine M, Marchand-Verrecchia C (2003) Detrimental role of bradykinin B2 receptor in a murine model of diffuse brain injury. J Neurotrauma 20:841–851. doi:10.1089/089771503322385773
Hsieh HL, Wang HH, Wu CY, Yang CM (2010) Reactive oxygen species-dependent c-Fos/activator protein 1 induction upregulates heme oxygenase-1 expression by bradykinin in brain astrocytes. Antioxid Redox Signal 13:1829–1844. doi:10.1089/ars.2009.2957
Ivashkova Y, Svetnitsky A, Mayzler O, Pruneau D, Benifla M, Fuxman Y, Cohen A, Artru AA, Shapira Y (2006) Bradykinin B2 receptor antagonism with LF 18-1505T reduces brain edema and improves neurological outcome after closed head trauma in rats. J Trauma 61:879–885. doi:10.1097/01.ta.0000234722.98537.01
Jamme I, Petit E, Divoux D, Gerbi A, Maixent JM, Nouvelot A (1995) Modulation of mouse cerebral Na+, K(+)-ATPase activity by oxygen free radicals. Neuroreport 7:333–337
Kaplanski J, Pruneau D, Asa I, Artru AA, Azez A, Ivashkova Y, Rudich Z, Shapira Y (2002) LF 16-0687 Ms, a bradykinin B2 receptor antagonist, reduces brain edema and improves long-term neurological function recovery after closed head trauma in rats. J Neurotrauma 19:953–964. doi:10.1089/089771502320317104
Kaplanski J, Asa I, Artru AA, Azez A, Ivashkova Y, Rudich Z, Pruneau D, Shapira Y (2003) LF 16-0687 Ms, a new bradykinin B2 receptor antagonist, decreases ex vivo brain tissue prostaglandin E2 synthesis after closed head trauma in rats. Resuscitation 56:207–213
Klasner B, Lumenta DB, Pruneau D, Zausinger S, Plesnila N (2006) Therapeutic window of bradykinin B2 receptor inhibition after focal cerebral ischemia in rats. Neurochem Int 49:442–447. doi:10.1016/j.neuint.2006.02.010
Komada M, Takao K, Miyakawa T (2008) Elevated plus maze for mice. J Vis Exp. doi:10.3791/1088
Lee YJ, Zachrisson O, Tonge DA, McNaughton PA (2002) Upregulation of bradykinin B2 receptor expression by neurotrophic factors and nerve injury in mouse sensory neurons. Mol Cell Neurosci 19:186–200. doi:10.1006/mcne.2001.1073
Levine RL, Garland D, Oliver CN, Amici A, Climent I, Lenz AG, Ahn BW, Shaltiel S, Stadtman ER (1990) Determination of carbonyl content in oxidatively modified proteins. Methods Enzymol 186:464–478
Lima FD, Souza MA, Furian AF, Rambo LM, Ribeiro LR, Martignoni FV, Hoffmann MS, Fighera MR, Royes LF, Oliveira MS, de Mello CF (2008) Na+, K+-ATPase activity impairment after experimental traumatic brain injury: relationship to spatial learning deficits and oxidative stress. Behav Brain Res 193:306–310. doi:10.1016/j.bbr.2008.05.013
Lima FD, Oliveira MS, Furian AF, Souza MA, Rambo LM, Ribeiro LR, Silva LF, Retamoso LT, Hoffmann MS, Magni DV, Pereira L, Fighera MR, Mello CF, Royes LF (2009) Adaptation to oxidative challenge induced by chronic physical exercise prevents Na+, K+-ATPase activity inhibition after traumatic brain injury. Brain Res 1279:147–155. doi:10.1016/j.brainres.2009.04.052
Lin CC, Hsieh HL, Shih RH, Chi PL, Cheng SE, Chen JC, Yang CM (2012) NADPH oxidase 2-derived reactive oxygen species signal contributes to bradykinin-induced matrix metalloproteinase-9 expression and cell migration in brain astrocytes. Cell Commun Signal 10:35. doi:10.1186/1478-811X-10-35
Liu HT, Akita T, Shimizu T, Sabirov RZ, Okada Y (2009) Bradykinin-induced astrocyte-neuron signalling: glutamate release is mediated by ROS-activated volume-sensitive outwardly rectifying anion channels. J Physiol 587:2197–2209. doi:10.1113/jphysiol.2008.165084
Lu J, Moochhala S, Shirhan M, Ng KC, Teo AL, Tan MH, Moore XL, Wong MC, Ling EA (2003) Neuroprotection by aminoguanidine after lateral fluid-percussive brain injury in rats: a combined magnetic resonance imaging, histopathologic and functional study. Neuropharmacology 44:253–263
Marceau F, Regoli D (2004) Bradykinin receptor ligands: therapeutic perspectives. Nat Rev Drug Discov 3:845–852. doi:10.1038/nrd1522
Miranda KM, Espey MG, Wink DA (2001) A rapid, simple spectrophotometric method for simultaneous detection of nitrate and nitrite. Nitric Oxide 5:62–71. doi:10.1006/niox.2000.0319
Moreau ME, Garbacki N, Molinaro G, Brown NJ, Marceau F, Adam A (2005) The kallikrein–kinin system: current and future pharmacological targets. J Pharmacol Sci 99:6–38
Noda M, Kariura Y, Amano T, Manago Y, Nishikawa K, Aoki S, Wada K (2003) Expression and function of bradykinin receptors in microglia. Life Sci 72:1573–1581
Noda M, Kariura Y, Pannasch U, Nishikawa K, Wang L, Seike T, Ifuku M, Kosai Y, Wang B, Nolte C, Aoki S, Kettenmann H, Wada K (2007) Neuroprotective role of bradykinin because of the attenuation of pro-inflammatory cytokine release from activated microglia. J Neurochem 101:397–410. doi:10.1111/j.1471-4159.2006.04339.x
Ohkawa H, Ohishi N, Yagi K (1979) Assay for lipid peroxides in animal tissues by thiobarbituric acid reaction. Anal Biochem 95:351–358
Plesnila N, Schulz J, Stoffel M, Eriskat J, Pruneau D, Baethmann A (2001) Role of bradykinin B2 receptors in the formation of vasogenic brain edema in rats. J Neurotrauma 18:1049–1058. doi:10.1089/08977150152693746
Potts MB, Koh SE, Whetstone WD, Walker BA, Yoneyama T, Claus CP, Manvelyan HM, Noble-Haeusslein LJ (2006) Traumatic injury to the immature brain: inflammation, oxidative injury, and iron-mediated damage as potential therapeutic targets. NeuroRx 3:143–153. doi:10.1016/j.nurx.2006.01.006
Pun PB, Lu J, Moochhala S (2009) Involvement of ROS in BBB dysfunction. Free Radic Res 43:348-364. doi:10.1080/10715760902751902
Raghupathi R, Fernandez SC, Murai H, Trusko SP, Scott RW, Nishioka WK, McIntosh TK (1998) BCL-2 overexpression attenuates cortical cell loss after traumatic brain injury in transgenic mice. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 18:1259–1269. doi:10.1097/00004647-199811000-00013
Raidoo DM, Bhoola KD (1998) Pathophysiology of the kallikrein–kinin system in mammalian nervous tissue. Pharmacol Ther 79:105–127
Raslan F, Schwarz T, Meuth SG, Austinat M, Bader M, Renne T, Roosen K, Stoll G, Siren AL, Kleinschnitz C (2010) Inhibition of bradykinin receptor B1 protects mice from focal brain injury by reducing blood–brain barrier leakage and inflammation. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 30:1477–1486. doi:10.1038/jcbfm.2010.28
Schneider Oliveira M, Flavia Furian A, Freire Royes LF, Rechia Fighera M, de Carvalho Myskiw J, Gindri Fiorenza N, Mello CF (2004) Ascorbate modulates pentylenetetrazol-induced convulsions biphasically. Neuroscience 128:721–728. doi:10.1016/j.neuroscience.2004.07.012
Silva LF, Hoffmann MS, Rambo LM, Ribeiro LR, Lima FD, Furian AF, Oliveira MS, Fighera MR, Royes LF (2011) The involvement of Na+, K+-ATPase activity and free radical generation in the susceptibility to pentylenetetrazol-induced seizures after experimental traumatic brain injury. J Neurol Sci 308:35–40. doi:10.1016/j.jns.2011.06.030
Silva LF, Hoffmann MS, Gerbatin R, Fiorin F, Dobrachinski F, Mota BC, Wouters AT, Soares FA, Pavarini SP, Fighera MR, Royes LF (2013) Treadmill exercise protects against pentylenetetrazol-induced seizures and oxidative stress after traumatic brain injury. J Neurotrauma. doi:10.1089/neu.2012.2577
Singleton RH, Yan HQ, Fellows-Mayle W, Dixon CE (2010) Resveratrol attenuates behavioral impairments and reduces cortical and hippocampal loss in a rat controlled cortical impact model of traumatic brain injury. J Neurotrauma 27:1091–1099. doi:10.1089/neu.2010.1291
Sosin DM, Sniezek JE, Waxweiler RJ (1995) Trends in death associated with traumatic brain injury, 1979 through 1992. Success and failure. JAMA 273:1778–1780
Souza MA, Oliveira MS, Furian AF, Rambo LM, Ribeiro LR, Lima FD, Dalla Corte LC, Silva LF, Retamoso LT, Dalla Corte CL, Puntel GO, de Avila DS, Soares FA, Fighera MR, de Mello CF, Royes LF (2009) Swimming training prevents pentylenetetrazol-induced inhibition of Na+, K+-ATPase activity, seizures, and oxidative stress. Epilepsia 50:811–823. doi:10.1111/j.1528-1167.2008.01908.x
Stokely ME, Orr EL (2008) Acute effects of calvarial damage on dural mast cells, pial vascular permeability, and cerebral cortical histamine levels in rats and mice. J Neurotrauma 25:52–61. doi:10.1089/neu.2007.0397
Stover JF, Dohse NK, Unterberg AW (2000) Significant reduction in brain swelling by administration of nonpeptide kinin B2 receptor antagonist LF 16-0687Ms after controlled cortical impact injury in rats. J Neurosurg 92:853–859. doi:10.3171/jns.2000.92.5.0853
Su J, Cui M, Tang Y, Zhou H, Liu L, Dong Q (2009) Blockade of bradykinin B2 receptor more effectively reduces postischemic blood-brain barrier disruption and cytokines release than B1 receptor inhibition. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 388:205–211. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2009.07.135
Thannickal VJ, Fanburg BL (1995) Activation of an H2O2-generating NADH oxidase in human lung fibroblasts by transforming growth factor beta 1. J Biol Chem 270:30334–30338
Theodoros DG, Shrapnel N, Murdoch BE (1998) Motor speech impairment following traumatic brain injury in childhood: a physiological and perceptual analysis of one case. Pediatr Rehabil 2:107–122
Trabold R, Eros C, Zweckberger K, Relton J, Beck H, Nussberger J, Muller-Esterl W, Bader M, Whalley E, Plesnila N (2010) The role of bradykinin B(1) and B(2) receptors for secondary brain damage after traumatic brain injury in mice. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 30:130–139. doi:10.1038/jcbfm.2009.196
Unterberg AW, Stover J, Kress B, Kiening KL (2004) Edema and brain trauma. Neuroscience 129:1021–1029. doi:10.1016/j.neuroscience.2004.06.046
Wada K, Chatzipanteli K, Busto R, Dietrich WD (1998a) Role of nitric oxide in traumatic brain injury in the rat. J Neurosurg 89:807–818. doi:10.3171/jns.1998.89.5.0807
Wada K, Chatzipanteli K, Kraydieh S, Busto R, Dietrich WD (1998b) Inducible nitric oxide synthase expression after traumatic brain injury and neuroprotection with aminoguanidine treatment in rats. Neurosurgery 43:1427–1436
Wada K, Chatzipanteli K, Busto R, Dietrich WD (1999) Effects of L-NAME and 7-NI on NOS catalytic activity and behavioral outcome after traumatic brain injury in the rat. J Neurotrauma 16:203–212
Walker K, Perkins M, Dray A (1995) Kinins and kinin receptors in the nervous system. Neurochem Int 26:1–16; discussion 17–26
Werner C, Engelhard K (2007) Pathophysiology of traumatic brain injury. Br J Anaesth 99:4–9. doi:10.1093/bja/aem131
Writer BW, Schillerstrom JE (2009) Psychopharmacological treatment for cognitive impairment in survivors of traumatic brain injury: a critical review. J Neuropsychiatry Clin Neurosci 21:362–370. doi:10.1176/appi.neuropsych.21.4.362
Yan LJ, Traber MG, Packer L (1995) Spectrophotometric method for determination of carbonyls in oxidatively modified apolipoprotein B of human low-density lipoproteins. Anal Biochem 228:349–351. doi:10.1006/abio.1995.1362
Yang CM, Hsieh HL, Lin CC, Shih RH, Chi PL, Cheng SE, Hsiao LD (2013) Multiple factors from bradykinin-challenged astrocytes contribute to the neuronal apoptosis: involvement of astroglial ROS, MMP-9, and HO-1/CO system. Mol Neurobiol 47:1020–1033. doi:10.1007/s12035-013-8402-1
Zhan H, Tada T, Nakazato F, Tanaka Y, Hongo K (2004) Spatial learning transiently disturbed by intraventricular administration of ouabain. Neurol Res 26:35–40. doi:10.1179/016164104773026507
Ziebell JM, Bye N, Semple BD, Kossmann T, Morganti-Kossmann MC (2011) Attenuated neurological deficit, cell death and lesion volume in Fas-mutant mice is associated with altered neuroinflammation following traumatic brain injury. Brain Res 1414:94–105. doi:10.1016/j.brainres.2011.07.056
Zink BJ (2001) Traumatic brain injury outcome: concepts for emergency care. Ann Emerg Med 37:318–332. doi:10.1067/mem.2001.113505
Zweckberger K, Eros C, Zimmermann R, Kim SW, Engel D, Plesnila N (2006) Effect of early and delayed decompressive craniectomy on secondary brain damage after controlled cortical impact in mice. J Neurotrauma 23:1083–1093. doi:10.1089/neu.2006.23.1083
Acknowledgments
The presente study was supported by Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico (CNPq) and by Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Ensino Superior (CAPES; Brazil). Ferreira J is the recipient of CNPq fellowships, grant numbers 301552/2007-0. Royes L.F.F is recipient of CNPq/FAPERGS fellowships, grant numbers 11/2082-4. The funding sources had no involvement in study design, in the collection, analysis, interpretation of data, and in the writing of the report. We also attest that all the experimentswere performed in compliance with Brazilian (law no. 6638 of 1979—Standards for the Practice Teaching-scientific Animal use) law currently in force, and that experiments were previously approved by the Committee on the Use and Care of Laboratory Animals of the Federal University of the Santa Maria (process number: 113/2010).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ferreira, A.P.O., Rodrigues, F.S., Della-Pace, I.D. et al. HOE-140, an antagonist of B2 receptor, protects against memory deficits and brain damage induced by moderate lateral fluid percussion injury in mice. Psychopharmacology 231, 1935–1948 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-013-3336-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-013-3336-x