Abstract
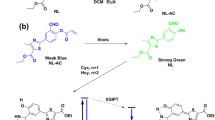
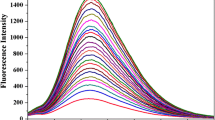
A novel fluorescent probe IPY-MAL for thiols was developed based on imidazo[1,5-α]pyridine derivative, which was decorated with a maleimide group. The probe IPY-MAL showed a rapid response (30 s), high sensitivity and selectivity for thiols with a large Stokes shift (140 nm), which was triggered by the Michael addition reaction of thiols toward the C=C double bond of the maleimide group. Moreover, this probe IPY-MAL could quantitatively detect the concentrations of thiols ranging from 0 to 50 μM, and the detection limit was found to be as low as 28 nM. Cell imaging results indicated that the probe IPY-MAL could detect and visualize thiols in the living cells.

A novel imidazo[1,5-α]pyridine-based fluorescent probe was developed for sensitively monitoring and imaging thiols in living A549 cells with a large Stokes shift.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ma T, Ding H, Xu HJ, Lv YL, Liu H, Wang HD, et al. Dual-functional probes for sequential thiol and redox homeostasis sensing in live cells. Analyst. 2015;140:322–9.
Chu PY, Liu MY. Amino acid cystine induces senescence and decelerates cell growth in melanoma. J Funct Foods. 2015;18:455–62.
Townsend DM, Tew KD, Tapiero H. The importance of glutathione in human disease. Biomed Pharmacother. 2003;57:145–55.
Reddie KG, Carroll KS. Expanding the functional diversity of proteins through cysteine oxidation. Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2008;12:746–54.
Zhang X, Lu J, Ren X, Du Y, Zheng Y, Ioannou PV, et al. Oxidation of structural cysteine residues in thioredoxin 1 by aromaticarsenicals enhances cancer cell cytotoxicity caused by the inhibition of thioredoxin reductase 1. Free Radic Biol Med. 2015;89:192–200.
Weerapana E, Wang C, Simon GM, Richter F, Khare S, Dillon MBD, et al. Quantitative reactivity profiling predicts functional cysteines in proteomes. Nature. 2010;468:790–5.
Kong F, Liu R, Chu R, Wang X, Xu K, Tang B. A highly sensitive near-infrared fluorescent probe for cysteine and homocysteine in living cells. Chem Commun. 2013;49:9176–8.
Niu LY, Guan YS, Chen YZ, Wu LZ, Tung CH, Yang QZ. BODIPY-based ratiometric fluorescent sensor for highly selective detection of glutathione over cysteine and homocysteine. J Am Chem Soc. 2012;134:18928–31.
Janáky R, Varga V, Hermann A, Saransaari P, Oja SS. Mechanisms of L-cysteine neurotoxicity. Neurochem Res. 2000;25:1397–405.
Dorszewska J, Prendecki M, Oczkowska A, Dezor M, Kozubski W. Molecular basis of familial and sporadic Alzheimer’s disease. Curr Alzheimer Res. 2016;13:952–63.
Nekrassova O, Lawrence NS, Compton RG. Analytical determination of homocysteine: a review. Talanta. 2003;6:1085–95.
Seshadri S, Beiser A, Selhub J, Jacques PF, Rosenberg IH, D'Agostino RB, et al. Plasma homocysteine as a risk factor for dementia and Alzheimer’s disease. N Engl J Med. 2002;346:476–83.
Forman HJ, Zhang HQ, Rinna A. Glutathione: overview of its protective roles, measurement, and biosynthesis. Mol Asp Med. 2009;30:1–12.
Atkuri KR, Mantovani JJ, Herzenberg LA, Herzenberg LA. N-acetyl-cysteine a safe antidote for cysteine/glutathione deficiency. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2007;7:355–9.
Wu C, Fan D, Zhou C, Liu Y, Wang E. Colorimetric strategy for highly sensitive and selective simultaneous detection of histidine and cysteine based on G-quadruplex-Cu(II) metalloenzyme. Anal Chem. 2016;88:2899–903.
Yan Z, Guang S, Xu H, Liu X. An effective real-time colorimeteric sensor for sensitive and selective detection of cysteine under physiological conditions. Analyst. 2011;136:1916–21.
Ivanov AV, Virus ED, Luzyanin BP, Kubatiev AA. Capillary electrophoresis coupled with 1,1′-thiocarbonyldiimidazole derivatization for the rapid detection of total homocysteine and cysteine in human plasma. J Chromatogr B. 2015;1004:30–6.
Liu LP, Yin ZJ, Yang ZS. A L-cysteine sensor based on Pt nanoparticles/poly(o-aminophenol) film on glassy carbon electrode. Bioelectrochemistry. 2010;79:84–9.
Wang W, Li L, Liu S, Ma C, Zhang S. Determination of physiological thiols by electrochemical detection with piazselenole and its application in rat breast cancer cells 4T-1. J Am Chem Soc. 2008;130:10846–7.
Borowczyk K, Wyszczelska-Rokiel M, Kubalczyk P, Glowacki P. Simultaneous determination of albumin and low-molecular-mass thiols in plasma by HPLC with UV detection. J Chromatogr B. 2015;981:57–64.
Childs S, Haroune N, Williams L. Determination of cellular glutathione: glutathione disulfide ratio in prostate cancer cells by high performance liquid chromatography with electrochemical detection. J Chromatogr A. 2016;1437:67–73.
Jin XL, Wu SP, She MY, Jia YF, Hao LK, Yin B, et al. Novel fluorescein-based fluorescent probe for detecting H2S and its real applications in blood plasma and biological imaging. Anal Chem. 2016;88(22):11253–60.
Cheng D, Pan Y, Wang L, Zeng Z, Yuan L, Zhang X, et al. Selective visualization of the endogenous peroxynitrite in an inflamed mouse model by a mitochondria-targetable two-photon ratiometric fluorescent probe. J Am Chem Soc. 2017;139:285–92.
Xu W, Zeng Z, Jiang JH, Chang YT, Yuan L. Discerning the chemistry in individual organelles with small-molecule fluorescent probes. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2016;55:13658–99.
Li HM, Wang CL, She MY, Zhu YL, Zhang JD, Yang Z, et al. Two rhodamine lactam modulated lysosome-targetable fluorescence probes for sensitively and selectively monitoring subcellular organelle pH change. Anal Chim Acta. 2015;900:97–102.
Wei M, Yin P, Shen Y, Zhang L, Deng J, Xue S, et al. A new turn-on fluorescent probe for selective detection of glutathione and cysteine in living cells. Chem Commun. 2013;49(41):4640–2.
Chen S, Hou P, Zhou B, Song X, Wu J, Zhang H, et al. A colorimetric and ratiometric fluorescent probe for Cu2+ with a large red shift and its imaging in living cells. RSC Adv. 2013;3:11543–6.
Liu XJ, Gao L, Yang L, Zou LF, Chen WQ, Song XZ. A phthalimide-based fluorescent probe for thiol detection with a large Stokes shift. RSC Adv. 2015;5:18177–82.
Yang Z, Zhao N, Sun Y, Miao F, Liu Y, Liu X, et al. Highly selective red- and green-emitting two-photon fluorescent probes for cysteine detection and their bio-imaging in living cells. Chem Commun. 2012;48(28):3442–4.
Ma Y, Liu S, Yang H, Wu Y, Yang C, Liu X, et al. Water-soluble phosphorescent iridium(III) complexes as multicolor probes for imaging of homocysteine and cysteine in living cells. J Mater Chem. 2011;21:18974–82.
Mei J, Wang YJ, Tong JQ, Wang J, Qin AJ, Sun JZ, et al. Discriminatory detection of cysteine and homocysteine based on dialdehyde-functionalized aggregation-induced emission fluorophores. Chem Eur J. 2013;19(2):612–9.
Das P, Mandal AK, Chandar NB, Baidya M, Bhatt HB, Ganguly B, et al. New chemodosimetric reagents as ratiometric probes for cysteine and homocysteine and possible detection in living cells and in blood plasma. Chem Eur J. 2012;18:15382–93.
Chen H, Li X, Wu Y, Gao W, Bai R. A ruthenium(II) complex with environment-responsive dual emission and its application in the detection of cysteine/homocysteine. Dalton Trans. 2012;41:13292–7.
Wang J, Li B, Zhao W, Zhang X, Luo X, Corkins ME, et al. Two-photon near infrared fluorescent turn-on probe toward cysteine and its imaging applications. ACS Sensors. 2016;1:882–7.
Zhu B, Guo B, Zhao Y, Zhang B, Du B. A highly sensitive ratiometric fluorescent probe with a large emission shift for imaging endogenous cysteine in living cells. Biosens Bioelectron. 2014;55:72–5.
Zhang J, Wang J, Liu J, Ning L, Zhu X, Yu B, et al. Near-infrared and naked-eye fluorescence probe for direct and highly selective detection of cysteine and its application in living cells. Anal Chem. 2015;87:4856–63.
Xie H, Li X, Zhao L, Han L, Zhao W, Chen X. Electrochemiluminescence performance of nitroolefin-based fluorescein in different solutions and its application for the detection of cysteine. Sensors Actuators B Chem. 2016;222:226–31.
Yue Y, Yin C, Huo F, Chao J, Zhang Y. Thiol-chromene click chemistry: a turn-on fluorescent probe for specific detection of cysteine and its application in bioimaging. Sensors Actuators B Chem. 2016;223:496–500.
Zhang C, Zhang G, Feng L, Li J. A ratiometric fluorescent probe for sensitive and selective detection of hydrogen sulfide and its application for bioimaging. Sensors Actuators B Chem. 2015;216:412–7.
Pires MM, Chmielewski J. Fluorescence imaging of cellular gluathiane using a latent rhodamine. Org Lett. 2008;10:837–40.
Zhu B, Zhang X, Li Y, Wang P, Zhang H, Zhuang X. A colorimetric and ratiometric fluorescent probe for thiols and its bioimaging applications. Chem Commun. 2010;46:5710–2.
Tang B, Yin L, Wang X, Chen Z, Tong L, Xu K. The barrier to enantiomerization and dynamic resolution of N-Boc-2-lithiopiperidine and the effect of TMEDA. Chem Commun. 2009;35:5293–5.
Wang H, Zhou G, Chen X. An iminofluorescein-Cu2+ ensemble probe for selective detection of thiols. Sensors Actuators B Chem. 2013;176:698–703.
Zhang YL, Shao XM, Wang Y, Pan FC, Kang RX, Peng FF, et al. Dual emission channels for sensitive discrimination of Cys/Hcy and GSH in plasma and cells. Chem Commun. 2015;51:4245–8.
Chen S, Li HM, Hou P. A novel imidazo[1,5-α]pyridine-based fluorescent probe with a large stokes shift for imaging hydrogen sulfide. Sensors Actuators B Chem. 2018;256:1086–92.
Chen S, Li HM, Hou P. Imidazo[1,5-α]pyridine-derived fluorescent turn-on probe for cell imaging with a large Stokes shift. Tetrahedron Lett. 2017;58:2654–7.
Chen S, Li HM, Hou P. A large Stokes shift fluorescent probe for sensing of thiophenols based on imidazo[1,5-α]pyridine in both aqueous medium and living cells. Anal Chim Acta. 2017;993:63–70.
Rao B, Simpson C, Lin H, Liang LY, Gu BH. Determination of thiol functional groups on bacteria and natural organic matter in environmental systems. Talanta. 2014;119:240–7.
Qu LJ, Yin CX, Huo FJ, Li JF, Chao JB, Zhang YB. A maleimide-based thiol fluorescent probe and its application for bioimaging. Sensors Actuators B Chem. 2014;195:246–51.
Acknowledgments
The research was supported by University Nursing Program for Young Scholars with Creative Talents in Heilongjiang Province (No. UNPYSCT-2017167), China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 1207 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, S., Hou, P., Wang, J. et al. A highly sensitive fluorescent probe based on the Michael addition mechanism with a large Stokes shift for cellular thiols imaging. Anal Bioanal Chem 410, 4323–4330 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-018-1082-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-018-1082-y