Abstract
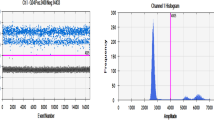
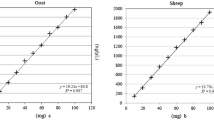
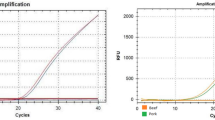
The performance of quantitative PCR-methods for the determination of beef and pork fraction in sausage was tested in an interlaboratory trial. Twelve different laboratories analysed four sausages of different composition of beef and pork by using four sausages of known fraction of meat as calibrators. Although different PCR-methods were applied, the precision of all results was better than 16% and the trueness better than 25%. The main reason for the good performance is the use of common calibrators emphasizing the importance of the quality of calibrators for molecular analysis. Thus, we conclude, that PCR-based detection methods are suitable for quantitative control of meat fractions in sausages.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Schweizerische Verordnung über Lebensmittel tierischer Herkunft vom 23.November 2005 (SR 817.022.108) Art. 8 Abs. 5
Binke R, Spiegel K, Schwägele F (2005) Vergleichende Untersuchung von mitochondrialen und nukleären Gensequenzen zur Identifizierung von tierischen Bestandteilen in Fleischerzeugnissen mittels PCR. Mitteilungsblatt der Fleischforschung Kulmbach 44(169):201–210
Lopez-Andreo M, Lugo L, Garrido-Pertierra A, Prieto MI, Puyet A (2005) Identification and quantitation of species in complex DNA mixtures by real-time polymerase chain reaction. Anal Biochem 339:73–82
Hird H, Chisholm J, Brown J (2005) The detection of commercial duck species in food using a single probe-multiple species-specific primer real time PCR assay. Eur Food Res Technol 221:559–563
Rodriguez MA, Garcia T, Gonzales I, Asensio L, Hernandez PE, Martin R (2004) Quantiation of mule duck in goose foie gras using TaqMan real-time polymerase chain reaction. J Agric Food Chem 52:1478–1483
Laube I, Spiegelberg A, Butschke A, Zagon J, Schauzu M, Kroh L, Broll H (2003) Methods for the detection of beef and pork in foods using real-time polymerase chain reaction. Int J Food Sci Technol 38:111–118
Calvo JH, Osta R, Zaragoza P (2002) Quantitative PCR detection of pork in raw and heated ground beef and pâté. J Agric Food Chem 50:5265–5267
Meyer R, Candrian U, Lüthy J (1994) Detection of pork in heated meat products by the polymerase chain reaction. J AOAC Int 77(3):617–622
Laube I, Butschke A, Zagon J, Spiegelberg A, Schauzu M, Bögl K-W, Kroh LW, Broll H (2001) Nachweisverfahren für Rindfleisch in Lebensmitteln unter Anwendung der TaqManTM-Technologie. Bundesgesundheitsbl 44:326–330
Brodmann P, Moor D (2003) Sensitive and semi-quantitative TaqManTM real-time polymerase chain reaction systems for the detection of beef (Bos taurus) and the detection of the family Mammalia in food and feed. Meat Sci 65:599–607
Sawyer J, Wood C, Shanahan D, Gout S, McDowell D (2003) Real-time PCR for quantitative meat species testing. Food Control 14:579–583
Swiss Food Manual (SLMB) Chapter 11 Meat and Meat Products (1999); 4.3.2. Beurteilungskriterien
Hubner P, Waiblinger Hu, Pietsch K, Brodmann P (2001) Validation of PCR methods for quantitation of genetically modified plants in food. J AOAC Int 84(6):1855–1864
Acknowledgments
We thank all participating laboratories: Coop-Labor, Service de la consommation du canton Neuchâtel, Chemisches und Veterinäruntersuchungsamt Freiburg, Bundesinstitut für Risikobewertung Berlin, Chemisches und Veterinäruntersuchungsamt Dresden, Thüringer Landesamt für Lebensmittelsicherheit undVerbraucherschutz Jena. Special thank goes to the butchery Hoesli Geb. AG for the production of Sample D and to SQTS for the quality control of reference sausages.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Eugster, A., Ruf, J., Rentsch, J. et al. Quantification of beef and pork fraction in sausages by real-time PCR analysis: results of an interlaboratory trial. Eur Food Res Technol 227, 17–20 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00217-007-0686-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00217-007-0686-9