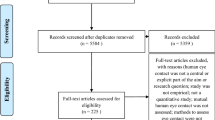
Abstract
The parasympathetic nervous system (PNS) has been implicated in the development of visually induced motion sickness. The objective of this study was to perform a systematic review and meta-analysis of the effect of visually induced motion sickness on validated parameters of PNS tone. Methods followed PRISMA recommendations. Controlled trials reporting validated measures of PNS tone in visually induced motion sickness in healthy adults were included. One reviewer performed the screening of articles and data extraction, and two reviewers independently performed methodological evaluation. Data were synthesised using standardised mean differences (SMDs) for all relevant outcomes using a random-effects model. Publication bias was assessed via funnel plots and Egger’s test. The search strategy identified seven citations comprising 237 healthy individuals. The mean quality score was 4/10 (range 3–7). There was no difference between baseline PNS tone between individuals who developed visually induced motion sickness and those that did not. Visually induced motion sickness (VIMS)-sensitive individuals had a reduction in PNS tone, following exposure to the stimulus (mean weighted SMD = −0.45, 95 % confidence interval −0.64 to −0.27, Z = −4.8, p < 0.0001). There was no evidence of heterogeneity or publication bias. These data suggest that baseline PNS parameters do not provide a useful measure of predicting the probability of developing visually induced motion sickness. However, a fall in PNS tone, as indicated by cardiac activity, is characteristic in sensitive individuals. Further work is needed to characterise these responses in clinical populations, in conjunction with improvements and standardisation in study design.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
(1996) Heart rate variability: standards of measurement, physiological interpretation and clinical use. Task force of the European Society of Cardiology and the North American Society of Pacing and Electrophysiology. Circulation 93:1043–1065
Borenstein M (2009) Introduction to meta-analysis. Wiley, Oxford
Cowings PS, Toscano WB (2000) Autogenic-feedback training exercise is superior to promethazine for control of motion sickness symptoms. J Clin Pharmacol 40:1154–1165
Edwards CM, Carmichael J, Baylis PH, Harris AL (1989) Arginine vasopressin—a mediator of chemotherapy induced emesis? Br J Cancer 59:467–470
Egger M, Davey Smith G, Schneider M, Minder C (1997) Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test. BMJ 315:629–634
Farmer AD, Coen SJ, Kano M et al (2013) Psychophysiological responses to pain identify reproducible human clusters. Pain 154:2266–2276. doi:10.1016/j.pain.2013.05.016
Feldman M, Samson WK, O'Dorisio TM (1988) Apomorphine-induced nausea in humans: release of vasopressin and pancreatic polypeptide. Gastroenterology 95:721–726
Fernandez-Ortega P, Caloto MT, Chirveches E et al (2012) Chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting in clinical practice: impact on patients’ quality of life. Support Care Cancer 20:3141–3148. doi:10.1007/s00520-012-1448-1
Fisher RD, Rentschler RE, Nelson JC, Godfrey TE, Wilbur DW (1982) Elevation of plasma antidiuretic hormones (ADH) associated with chemotherapy-induced emesis in man. Cancer Treat Rep 66:25–29
Gianaros PJ, Muth ER, Mordkoff JT, Levine ME, Stern RM (2001) A questionnaire for the assessment of the multiple dimensions of motion sickness. Aviat Space Environ Med 72:115–119
Gianaros PJ, Quigley KS, Muth ER, Levine ME, Vasko RC, Jr., Stern RM (2003) Relationship between temporal changes in cardiac parasympathetic activity and motion sickness severity. Psychophysiology 40:39–44
Golding JF (2006) Motion sickness susceptibility. Auton Neurosci 129:67–76. doi:10.1016/j.autneu.2006.07.019
Grunberg SM, Deuson RR, Mavros P et al (2004) Incidence of chemotherapy-induced nausea and emesis after modern antiemetics. Cancer 100:2261–2268. doi:10.1002/cncr.20230
Hall SM, Brannick MT (2002) Comparison of two random-effects methods of meta-analysis. J Appl Psychol 87:377–389
Hasler WL, Kim MS, Chey WD, Stevenson V, Stein B, Owyang C (1995) Central cholinergic and alpha-adrenergic mediation of gastric slow wave dysrhythmias evoked during motion sickness. Am J Physiol 268:G539–G547
Himi N, Koga T, Nakamura E, Kobashi M, Yamane M, Tsujioka K (2004) Differences in autonomic responses between subjects with and without nausea while watching an irregularly oscillating video. Auton Neurosci 116:46–53. doi:10.1016/j.autneu.2004.08.008
Holmes AM, Rudd JA, Tattersall FD, Aziz Q, Andrews PL (2009) Opportunities for the replacement of animals in the study of nausea and vomiting. Br J Pharmacol 157:865–880. doi:10.1111/j.1476-5381.2009.00176.x
Horn CC (2008) Why is the neurobiology of nausea and vomiting so important? Appetite 50:430–434. doi:10.1016/j.appet.2007.09.015
Hu S, Grant WF, Stern RM, Koch KL (1991) Motion sickness severity and physiological correlates during repeated exposures to a rotating optokinetic drum. Aviat Space Environ Med 62:308–314
Jadad AR, Moore RA, Carroll D, Jenkinson C, Reynolds DJ, Gavaghan DJ, McQuay HJ (1996) Assessing the quality of reports of randomized clinical trials: is blinding necessary? Control Clin Trials 17:1–12
Kamath MV, Fallen EL (1993) Power spectral analysis of heart rate variability: a noninvasive signature of cardiac autonomic function. Crit Rev Biomed Eng 21:245–311
Kim J, Napadow V, Kuo B, Barbieri R (2011) A combined HRV-fMRI approach to assess cortical control of cardiovagal modulation by motion sickness. Conf Proc IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc 2011:2825–2828 doi:10.1109/IEMBS.2011.6090781
Klosterhalfen S, Pan F, Kellermann S, Enck P (2006) Gender and race as determinants of nausea induced by circular vection. Gend Med 3:236–242
Koch KL, Stern RM, Vasey MW, Seaton JF, Demers LM, Harrison TS (1990) Neuroendocrine and gastric myoelectrical responses to illusory self-motion in humans. Am J Physiol 258:E304–E310
Lacount L, Napadow V, Kuo B, Park K, Kim J, Brown E, Barbieri R (2009) Dynamic cardiovagal response to motion sickness: a point-process heart rate variability study. Comput Cardiol 36:49–52
Lane RD, Waldstein SR, Critchley HD et al (2009) The rebirth of neuroscience in psychosomatic medicine, part II: clinical applications and implications for research. Psychosom Med 71:135–151. doi:10.1097/PSY.0b013e318198a11f
Liberati A, Altman DG, Tetzlaff J et al (2009) The PRISMA statement for reporting systematic reviews and meta-analyses of studies that evaluate healthcare interventions: explanation and elaboration. BMJ 339:b2700. doi:10.1136/bmj.b2700
Little CJ, Julu PO, Hansen S, Reid SW (1999) Real-time measurement of cardiac vagal tone in conscious dogs. Am J Physiol 276:H758–H765
Matchock RL, Levine ME, Gianaros PJ, Stern RM (2008) Susceptibility to nausea and motion sickness as a function of the menstrual cycle. Womens Health Issues 18:328–335. doi:10.1016/j.whi.2008.01.006
Miaskiewicz SL, Stricker EM, Verbalis JG (1989) Neurohypophyseal secretion in response to cholecystokinin but not meal-induced gastric distention in humans. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 68:837–843. doi:10.1210/jcem-68-4-837
Murray PG, Hamilton RM, Macfarlane PW (2001) Reproducibility of a non-invasive real-time measure of cardiac parasympathetic activity. Physiol Meas 22:661–672
Muth ER, Koch KL, Stern RM, Thayer JF (1999) Effect of autonomic nervous system manipulations on gastric myoelectrical activity and emotional responses in healthy human subjects. Psychosom Med 61:297–303
Ng KS, Chua YC, Gresty MA, et al (2010) Identification of Psychophysiological biomarkers of nausea using a novel visual induction method. Gastroenterology 138:S-467
Nussey SS, Hawthorn J, Page SR, Ang VT, Jenkins JS (1988) Responses of plasma oxytocin and arginine vasopressin to nausea induced by apomorphine and ipecacuanha. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 28:297–304
Parkinson J, Muthas D, Clark M, Boyer S, Valentin JP, Ewart L (2012) Application of data mining and visualization techniques for the prediction of drug-induced nausea in man. Toxicol Sci 126:275–284. doi:10.1093/toxsci/kfr334
Percie du Sert N, Holmes AM, Wallis R, Andrews PL (2012) Predicting the emetic liability of novel chemical entities: a comparative study. Br J Pharmacol 165:1848–1867. doi:10.1111/j.1476-5381.2011.01669.x
Redmond M, Glass P (2005) Opiate-induced nausea and vomiting: what is the challenge? Anesth Analg 101:1341–1342. doi:10.1213/01.ANE.0000181329.07214.D8
Rottenberg J (2007) Cardiac vagal control in depression: a critical analysis. Biol Psychol 74:200–211. doi:10.1016/j.biopsycho.2005.08.010
Rowe JW, Shelton RL, Helderman JH, Vestal RE, Robertson GL (1979) Influence of the emetic reflex on vasopressin release in man. Kidney Int 16:729–735
Sanger GJ, Broad J, Andrews PL (2013) The relationship between gastric motility and nausea: gastric prokinetic agents as treatments. Eur J Pharmacol 715:10–14. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2013.06.031
Stern RM, Hu S, LeBlanc R, Koch KL (1993) Chinese hyper-susceptibility to vection-induced motion sickness. Aviat Space Environ Med 64:827–830
Stern RM, Koch KL, Andrews PLR (2011) Nausea: mechanisms and management. Oxford University Press, New York
Tak LM, Riese H, de Bock GH, Manoharan A, Kok IC, Rosmalen JG (2009) As good as it gets? A meta-analysis and systematic review of methodological quality of heart rate variability studies in functional somatic disorders. Biol Psychol 82:101–110. doi:10.1016/j.biopsycho.2009.05.002
Thayer JF, Sternberg E (2006) Beyond heart rate variability: vagal regulation of allostatic systems. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1088:361–372. doi:10.1196/annals.1366.014
Thayer JF, Hall M, Sollers JJ 3rd, Fischer JE (2006) Alcohol use, urinary cortisol, and heart rate variability in apparently healthy men: evidence for impaired inhibitory control of the HPA axis in heavy drinkers. Int J Psychophysiol 59:244–250. doi:10.1016/j.ijpsycho.2005.10.013
van Eekelen AP, Houtveen JH, Kerkhof GA (2004) Circadian variation in base rate measures of cardiac autonomic activity. Eur J Appl Physiol 93:39–46. doi:10.1007/s00421-004-1158-6
Xu LH, Koch KL, Summy-Long J et al (1993) Hypothalamic and gastric myoelectrical responses during vection-induced nausea in healthy Chinese subjects. Am J Physiol 265:E578–E584
Yen M, Lo LH (2002) Examining test–retest reliability: an intra-class correlation approach. Nurs Res 51:59–62
Yen Pik Sang FD, Golding JF, Gresty MA (2003) Suppression of sickness by controlled breathing during mildly nauseogenic motion. Aviat Space Environ Med 74:998–1002
Yokota Y, Aoki M, Mizuta K, Ito Y, Isu N (2005) Motion sickness susceptibility associated with visually induced postural instability and cardiac autonomic responses in healthy subjects. Acta Otolaryngol 125:280–285
Zabara J (1988) Neuroinhibition of xylazine induced emesis. Pharmacol Toxicol 63:70–74
Zabara J (1992) Inhibition of experimental seizures in canines by repetitive vagal stimulation. Epilepsia 33:1005–1012
Zabara J, Chaffee RB Jr, Tansy MF (1972) Neuroinhibition in the regulation of emesis. Space Life Sci 3:282–292
Zautra AJ, Fasman R, Davis MC, Craig AD (2010) The effects of slow breathing on affective responses to pain stimuli: an experimental study. Pain 149:12–18. doi:10.1016/j.pain.2009.10.001
Zuzewicz K, Saulewicz A, Konarska M, Kaczorowski Z (2011) Heart rate variability and motion sickness during forklift simulator driving. Int J Occup Saf Ergon 17:403–410
Acknowledgments
A.D.F. was funded by the Whitechapel Society for the Advancement of Gastroenterology, which had no input on the study design, data interpretation or drafting of the manuscript.
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflict of interests to declare.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Farmer, A.D., Al Omran, Y., Aziz, Q. et al. The role of the parasympathetic nervous system in visually induced motion sickness: systematic review and meta-analysis. Exp Brain Res 232, 2665–2673 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-014-3964-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-014-3964-3