Abstract
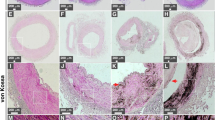
Vascular calcification, albeit heterogeneous in terms of biological and physicochemical properties, has been associated with ageing, lifestyle, diabetes, and chronic kidney disease (CKD). It is unknown whether or not moderately impaired renal function (CKD stages 2–4) affects the physiochemical composition and/or the formation of magnesium-containing tricalcium phosphate ([Ca,Mg]3[PO4]2, whitlockite) in arterial microcalcification. Therefore, a high-resolution scanning X-ray diffraction analysis (European Synchrotron Radiation Facility, Grenoble, France) utilizing histological sections of paraffin-embedded arterial specimens derived from atherosclerotic patients with normal renal function (n = 15) and CKD (stages 2–4, n = 13) was performed. This approach allowed us to spatially assess the contribution of calcium phosphate (apatite) and whitlockite to arterial microcalcification. Per group, the number of samples (13 vs. 12) with sufficient signal intensity and total lengths of regions (201 vs. 232 μm) giving rise to diffractograms (“informative regions”) were comparable. Summarizing all informative regions per group into one composite sample revealed calcium phosphate/apatite as the leading mineral phase in CKD patients, whereas in patients with normal renal function the relative contribution of whitlockite and calcium phosphate/apatite was on the same order of magnitude (CKD, calcium phosphate/apatite 157 μm, whitlockite 38.7 μm; non-CKD, calcium phosphate/apatite 79.0 μm, whitlockite 94.1 μm; each p < 0.05). Our results, although based on a limited number of samples, indicate that chronic impairment of renal function affects local magnesium homeostasis and thus contributes to the physicochemical composition of microcalcification in atherosclerotic patients.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rennenberg RJ, Kessels AG, Schurgers LJ, van Engelshoven JM, de Leeuw PW, Kroon AA (2009) Vascular calcifications as a marker of increased cardiovascular risk: a meta-analysis. Vasc Health Risk Manag 5:185–197
Persy V, D’Haese P (2009) Vascular calcification and bone disease: the calcification paradox. Trends Mol Med 15:405–416
Atkinson J (2008) Age-related medial elastocalcinosis in arteries: mechanisms, animal models, and physiological consequences. J Appl Physiol 105:1643–1651
Abedin M, Tintut Y, Demer LL (2004) Vascular calcification: mechanisms and clinical ramifications. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 24:1161–1170
Dellegrottaglie S, Sanz J, Rajagopalan S (2006) Molecular determinants of vascular calcification: a bench to bedside view. Curr Mol Med 6:515–524
O’Neill WC, Lomashvili KA (2010) Recent progress in the treatment of vascular calcification. Kidney Int 78:1232–1239
Demer LL, Tintut Y (2008) Vascular calcification: pathobiology of a multifaceted disease. Circulation 117:2938–2948
Speer MY, Giachelli CM (2004) Regulation of cardiovascular calcification. Cardiovasc Pathol 13:63–70
Shao JS, Cai J, Towler DA (2006) Molecular mechanisms of vascular calcification: lessons learned from the aorta. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 26:1423–1430
Shao JS, Cheng SL, Sadhu J, Towler DA (2010) Inflammation and the osteogenic regulation of vascular calcification: a review and perspective. Hypertension 55:579–592
Voigt M, Fischer DC, Rimpau M, Schareck W, Haffner D (2010) Fibroblast growth factor (FGF)-23 and fetuin-A in calcified carotid atheroma. Histopathology 56:775–788
Bobryshev YV (2005) Transdifferentiation of smooth muscle cells into chondrocytes in atherosclerotic arteries in situ: implications for diffuse intimal calcification. J Pathol 205:641–650
Neven E, Dauwe S, De Broe ME, D’Haese PC, Persy V (2007) Endochondral bone formation is involved in media calcification in rats and in men. Kidney Int 72:574–581
Jahnen-Dechent W, Heiss A, Schäfer C, Ketteler M (2011) Fetuin-a regulation of calcified matrix metabolism. Circ Res 108:1494–1509
Vattikuti R, Towler DA (2004) Osteogenic regulation of vascular calcification: an early perspective. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 286:E686–E696
Toussaint ND (2011) Extracellular matrix calcification in chronic kidney disease. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens 20:360–368
Wuthier RE, Lipscomb GF (2011) Matrix vesicles: structure, composition, formation and function in calcification. Front Biosci 17:2812–2902
Verberckmoes SC, Persy V, Behets GJ, Neven E, Hufkens A, Zebger-Gong H, Muller D, Haffner D, Querfeld U, Bohic S, De Broe ME, D’Haese PC (2007) Uremia-related vascular calcification: more than apatite deposition. Kidney Int 71:298–303
LeGeros RZ, Contiguglia SR, Alfrey AC (1973) Pathological calcifications associated with uremia: two types of calcium phosphate deposits. Calcif Tissue Res 13:173–185
Lagier R, Baud CA (2003) Magnesium whitlockite, a calcium phosphate crystal of special interest in pathology. Pathol Res Pract 199:329–335
Schlieper G, Aretz A, Verberckmoes SC, Krüger T, Behets GJ, Ghadimi R, Weirich TE, Rohrmann D, Langer S, Tordoir JH, Amann K, Westenfeld R, Brandenburg VM, D’Haese PC, Mayer J, Ketteler M, McKee MD, Floege J (2010) Ultrastructural analysis of vascular calcifications in uremia. J Am Soc Nephrol 21:689–696
Levey AS, Bosch JP, Lewis JB, Greene T, Rogers N, Roth D (1999) A more accurate method to estimate glomerular filtration rate from serum creatinine: a new prediction equation. Modification of diet in Renal Disease Study Group. Ann Intern Med 130:461–470
Haffner D, Hocher B, Muller D, Simon K, Konig K, Richter CM, Eggert B, Schwarz J, Godes M, Nissel R, Querfeld U (2005) Systemic cardiovascular disease in uremic rats induced by 1,25(OH)2D3. J Hypertens 23:1067–1075
Hammersley AP, Svensson SO, Hanfland M, Fitch AN, Hausermann D (1996) Two-dimensional detector software: from real detector to idealised image or two-theta scan. High Press Res 14:235
Murshed M, McKee MD (2010) Molecular determinants of extracellular matrix mineralization in bone and blood vessels. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens 19:359–365
Reid JD, Andersen ME (1993) Medial calcification (whitlockite) in the aorta. Atherosclerosis 101:213–224
O’Neill WC (2007) Vascular calcification: not so crystal clear. Kidney Int 71:282–283
Zittermann A, Schleithoff SS, Koerfer R (2007) Vitamin D and vascular calcification. Curr Opin Lipidol 18:41–46
Shroff R, Knott C, Rees L (2010) The virtues of vitamin D–but how much is too much? Pediatr Nephrol 25:1607–1620
Razzaque MS (2011) The dualistic role of vitamin D in vascular calcifications. Kidney Int 79:708–714
de Boer IH, Kestenbaum B, Shoben AB, Michos ED, Sarnak MJ, Siscovick DS (2009) 25-Hydroxyvitamin D levels inversely associate with risk for developing coronary artery calcification. J Am Soc Nephrol 20:1805–1812
Lopez I, Mendoza FJ, Aguilera-Tejero E, Perez J, Guerrero F, Martin D, Rodriguez M (2008) The effect of calcitriol, paricalcitol, and a calcimimetic on extraosseous calcifications in uremic rats. Kidney Int 73:300–307
Arsenault AL, Ottensmeyer FP, Heath IB (1988) An electron microscopic and spectroscopic study of murine epiphyseal cartilage: analysis of fine structure and matrix vesicles preserved by slam freezing and freeze substitution. J Ultrastruct Mol Struct Res 98:32–47
Acknowledgments
The outstanding technical assistance of Birgit Salewski and Anja Rahn is highly appreciated. We acknowledge the European Synchrotron Radiation Facility for provision of synchrotron radiation facilities and for assistance in using beamline ID 13. The study was funded by a grant (FORUN-program, 88 90 47) from the Medical Faculty, University of Rostock.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The authors have stated that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fischer, DC., Behets, G.J., Hakenberg, O.W. et al. Arterial Microcalcification in Atherosclerotic Patients with and Without Chronic Kidney Disease: A Comparative High-Resolution Scanning X-Ray Diffraction Analysis. Calcif Tissue Int 90, 465–472 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00223-012-9594-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00223-012-9594-5