Abstract
Purpose
Delirium is reported in over 50% of critically ill ICU patients, and is associated with increased mortality and long-term cognitive consequences. Prevention and early management of delirium are essential components of ICU care. However, pharmacological interventions have not been effective in delirium prevention. This study investigated the effect of aripiprazole in the prevention of delirium in a neurosurgical intensive care unit.
Methods
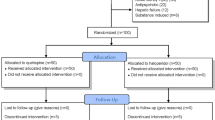
In this prospective, randomized placebo-controlled small clinical trial, 53 patients, 18 to 80 years old, were randomized to receive enteric aripiprazole (15 mg) or placebo for up to 7 days. Delirium, detected by the Confusion Assessment Method-ICU, ICU events, laboratory studies, aripiprazole safety, time to delirium onset, delirium-free days, delirium prevalence during follow-up and ICU length of stay were recorded.
Results
Forty patients with similar baseline characteristics, including age, sex, neurosurgery types and APACHE II scores, completed the study. Delirium incidence and the mean days to its onset were 20% vs. 55% (p = 0.022) and 2.17 ± 0.41 vs. 2.09 ± 0.30 (p = 0.076) in the aripiprazole and placebo groups, respectively. The mean number of delirium-free days were: 5.6 (95%CI, 4.6-6.5) and 4.3 (95%CI, 3.2-5.4), in aripiprazole and placebo groups, respectively (p = 0.111). The prevalence of delirium during the follow-up was significantly lower in the aripiprazole group (p = 0.018). Serious aripiprazole adverse reactions were not observed.
Conclusions
Aripiprazole can reduce the incidence of delirium in the neurosurgical ICU. Studies with larger sample size in diverse ICU settings and longer follow-up are needed to confirm our findings.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ICU:
-
Intensive care unit
- CAM-ICU:
-
Confusion Assessment Method for the ICU
- EPS:
-
Extrapyramidal syndrome
- TBI:
-
Traumatic brain injury
- SAH:
-
Subarachnoid hemorrhage
- IQCODE:
-
Informant Questionnaire on Cognitive Decline in the Elderly
- RASS:
-
Richmond Agitation–Sedation Scale
- APACHE-II:
-
Acute Physiology and Chronic Health Evaluation II
References
Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (2013) Fifth edn. American Psychiatric Association
Ely EW, Inouye SK, Bernard GR, Gordon S, Francis J, May L, Truman B, Speroff T, Gautam S, Margolin R, Hart RP, Dittus R (2001) Delirium in mechanically ventilated patients: validity and reliability of the confusion assessment method for the intensive care unit (CAM-ICU). JAMA 286(21):2703–2710
Ely EW, Margolin R, Francis J, May L, Truman B, Dittus R, Speroff T, Gautam S, Bernard GR, Inouye SK (2001) Evaluation of delirium in critically ill patients: validation of the confusion assessment method for the intensive care unit (CAM-ICU). Crit Care Med 29(7):1370–1379
Gilchrist NA, Asoh I, Greenberg B (2012) Atypical antipsychotics for the treatment of ICU delirium. J Intensive Care Med 27(6):354–361. https://doi.org/10.1177/0885066611403110
van Eijk MM, van Marum RJ, Klijn IA, de Wit N, Kesecioglu J, Slooter AJ (2009) Comparison of delirium assessment tools in a mixed intensive care unit. Crit Care Med 37(6):1881–1885. https://doi.org/10.1097/CCM.0b013e3181a00118
Medicare & Medicaid statistical supplement (2013). United State Department of Health and Human Services, Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services
Inouye SK (1998) Delirium in hospitalized older patients. Clin Geriatr Med 14(4):745–764
Pandharipande PP, Ely EW, Arora RC, Balas MC, Boustani MA, La Calle GH, Cunningham C, Devlin JW, Elefante J, Han JH, MacLullich AM, Maldonado JR, Morandi A, Needham DM, Page VJ, Rose L, Salluh JIF, Sharshar T, Shehabi Y, Skrobik Y, Slooter AJC, Smith HAB (2017) The intensive care delirium research agenda: a multinational, interprofessional perspective. Intensive Care Med 43(9):1329–1339. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00134-017-4860-7
Han CS, Kim YK (2004) A double-blind trial of risperidone and haloperidol for the treatment of delirium. Psychosomatics 45(4):297–301. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0033-3182(04)70170-X
Lee KU, Won WY, Lee HK, Kweon YS, Lee CT, Pae CU, Bahk WM (2005) Amisulpride versus quetiapine for the treatment of delirium: a randomized, open prospective study. Int Clin Psychopharmacol 20(6):311–314
Maneeton B, Maneeton N, Srisurapanont M (2007) An open-label study of quetiapine for delirium. J Med Assoc Thail 90(10):2158–2163
Pae CU, Lee SJ, Lee CU, Lee C, Paik IH (2004) A pilot trial of quetiapine for the treatment of patients with delirium. Hum Psychopharmacol 19(2):125–127. https://doi.org/10.1002/hup.559
Skrobik YK, Bergeron N, Dumont M, Gottfried SB (2004) Olanzapine vs haloperidol: treating delirium in a critical care setting. Intensive Care Med 30(3):444–449. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00134-003-2117-0
Devlin JW, Roberts RJ, Fong JJ, Skrobik Y, Riker RR, Hill NS, Robbins T, Garpestad E (2010) Efficacy and safety of quetiapine in critically ill patients with delirium: a prospective, multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled pilot study. Crit Care Med 38(2):419–427. https://doi.org/10.1097/CCM.0b013e3181b9e302
Girard TD, Pandharipande PP, Carson SS, Schmidt GA, Wright PE, Canonico AE, Pun BT, Thompson JL, Shintani AK, Meltzer HY, Bernard GR, Dittus RS, Ely EW, Investigators MT (2010) Feasibility, efficacy, and safety of antipsychotics for intensive care unit delirium: the MIND randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Crit Care Med 38(2):428–437
Neufeld KJ, Yue J, Robinson TN, Inouye SK, Needham DM (2016) Antipsychotic medication for prevention and treatment of delirium in hospitalized adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Am Geriatr Soc 64(4):705–714. https://doi.org/10.1111/jgs.14076
Boettger S, Breitbart W (2011) An open trial of aripiprazole for the treatment of delirium in hospitalized cancer patients. Palliat Support Care 9(4):351–357. https://doi.org/10.1017/s1478951511000368
Al-Qadheeb NS, Skrobik Y, Schumaker G, Pacheco MN, Roberts RJ, Ruthazer RR, Devlin JW (2016) Preventing ICU subsyndromal delirium conversion to delirium with low-dose IV haloperidol: a double-blind, placebo-controlled pilot study. Crit Care Med 44(3):583–591. https://doi.org/10.1097/CCM.0000000000001411
Wang W, Li HL, Wang DX, Zhu X, Li SL, Yao GQ, Chen KS, Gu XE, Zhu SN (2012) Haloperidol prophylaxis decreases delirium incidence in elderly patients after noncardiac surgery: a randomized controlled trial*. Crit Care Med 40(3):731–739. https://doi.org/10.1097/CCM.0b013e3182376e4f
Prakanrattana U, Prapaitrakool S (2007) Efficacy of risperidone for prevention of postoperative delirium in cardiac surgery. Anaesth Intensive Care 35(5):714–719
Brummel NE, Girard TD (2013) Preventing delirium in the intensive care unit. Crit Care Clin 29(1):51–65. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccc.2012.10.007
Stahl SM (2001) Dopamine system stabilizers, aripiprazole, and the next generation of antipsychotics, part 2: illustrating their mechanism of action. J Clin Psychiatry 62(12):923–924
Potkin SG, Saha AR, Kujawa MJ, Carson WH, Ali M, Stock E, Stringfellow J, Ingenito G, Marder SR (2003) Aripiprazole, an antipsychotic with a novel mechanism of action, and risperidone vs placebo in patients with schizophrenia and schizoaffective disorder. Arch Gen Psychiatry 60(7):681–690. https://doi.org/10.1001/archpsyc.60.7.681
Shapiro DA, Renock S, Arrington E, Chiodo LA, Liu LX, Sibley DR, Roth BL, Mailman R (2003) Aripiprazole, a novel atypical antipsychotic drug with a unique and robust pharmacology. Neuropsychopharmacology 28(8):1400–1411. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.npp.1300203
Fanoe S, Pehrson S, Bundgaard H, Fink-Jensen A, Kristensen D, Jensen HK, Toft E, Nielsen J, Videbech P (2014) Risk of arrhythmia induced by psychotropic medications: a proposal for clinical management. Eur Heart J 35(20):1306–1315. https://doi.org/10.1093/eurheartj/ehu100
Boettger S, Friedlander M, Breitbart W, Passik S (2011) Aripiprazole and haloperidol in the treatment of delirium. Aust N Z J Psychiatry 45(6):477–482. https://doi.org/10.3109/00048674.2011.543411
Jorm AF, Jacomb PA (1989) The informant questionnaire on cognitive decline in the elderly (IQCODE): socio-demographic correlates, reliability, validity and some norms. Psychol Med 19(4):1015–1022
Ely EW, Truman B, Shintani A, Thomason JW, Wheeler AP, Gordon S, Francis J, Speroff T, Gautam S, Margolin R, Sessler CN, Dittus RS, Bernard GR (2003) Monitoring sedation status over time in ICU patients: reliability and validity of the Richmond agitation-sedation scale (RASS). JAMA 289(22):2983–2991. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.289.22.2983
Monette J, Galbaud du Fort G, Fung SH, Massoud F, Moride Y, Arsenault L, Afilalo M (2001) Evaluation of the confusion assessment method (CAM) as a screening tool for delirium in the emergency room. Gen Hosp Psychiatry 23(1):20–25
Barr J, Fraser GL, Puntillo K, Ely EW, Gelinas C, Dasta JF, Davidson JE, Devlin JW, Kress JP, Joffe AM, Coursin DB, Herr DL, Tung A, Robinson BR, Fontaine DK, Ramsay MA, Riker RR, Sessler CN, Pun B, Skrobik Y, Jaeschke R, American College of Critical Care M (2013) Clinical practice guidelines for the management of pain, agitation, and delirium in adult patients in the intensive care unit. Crit Care Med 41(1):263–306. https://doi.org/10.1097/CCM.0b013e3182783b72
Knaus WA, Draper EA, Wagner DP, Zimmerman JE (1985) APACHE II: a severity of disease classification system. Crit Care Med 13(10):818–829
Twisk JW, Smidt N, de Vente W (2005) Applied analysis of recurrent events: a practical overview. J Epidemiol Community Health 59(8):706–710. https://doi.org/10.1136/jech.2004.030759
Stuart R, Lipsitz NML, Harrington DP (1991) Generalized estimating equations for correlated binary data: using the odds ratio as a measure of association. Biometrika 78(1):153–160
Schreiber MP, Colantuoni E, Bienvenu OJ, Neufeld KJ, Chen KF, Shanholtz C, Mendez-Tellez PA, Needham DM (2014) Corticosteroids and transition to delirium in patients with acute lung injury. Crit Care Med 42(6):1480–1486. https://doi.org/10.1097/CCM.0000000000000247
Han L, McCusker J, Cole M, Abrahamowicz M, Primeau F, Elie M (2001) Use of medications with anticholinergic effect predicts clinical severity of delirium symptoms in older medical inpatients. Arch Intern Med 161(8):1099–1105
Riviere J, van der Mast RC, Vandenberghe J, Van Den Eede F (2019) Efficacy and tolerability of atypical antipsychotics in the treatment of delirium: a systematic review of the literature. Psychosomatics 60(1):18–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psym.2018.05.011
Devlin JW, Zaal IJ, Slooter AJ (2014) Clarifying the confusion surrounding drug-associated delirium in the ICU. Crit Care Med 42(6):1565–1566. https://doi.org/10.1097/CCM.0000000000000293
Zaal IJ, Devlin JW, Peelen LM, Slooter AJ (2015) A systematic review of risk factors for delirium in the ICU. Crit Care Med 43(1):40–47. https://doi.org/10.1097/CCM.0000000000000625
Sauer AM, Slooter AJ, Veldhuijzen DS, van Eijk MM, Devlin JW, van Dijk D (2014) Intraoperative dexamethasone and delirium after cardiac surgery: a randomized clinical trial. Anesth Analg 119(5):1046–1052. https://doi.org/10.1213/ANE.0000000000000248
Marder SR, McQuade RD, Stock E, Kaplita S, Marcus R, Safferman AZ, Saha A, Ali M, Iwamoto T (2003) Aripiprazole in the treatment of schizophrenia: safety and tolerability in short-term, placebo-controlled trials. Schizophr Res 61(2-3):123–136
Gury C, Canceil O, Iaria P (2000) Antipsychotic drugs and cardiovascular safety: current studies of prolonged QT interval and risk of ventricular arrhythmia. Encephale 26(6):62–72
Lacro JP FS, Endow-Eyer RA (2012) Schizophrenia. In: Koda-Kimble (ed) Applied therapeutics, the clinical use of drugs. 10 edn
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MM and MS created the concept. Literature review and drafting of the proposal were done by MF and MJ. MG, SMRH, MN, NG, and GM performed the search and gathered clinical data. MY analyzed the data. All authors reviewed and helped to finalize the article for publication.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This study was performed at Firoozgar Hospital, Iran University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mokhtari, M., Farasatinasab, M., Jafarpour Machian, M. et al. Aripiprazole for prevention of delirium in the neurosurgical intensive care unit: a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled study. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 76, 491–499 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00228-019-02802-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00228-019-02802-1