Abstract
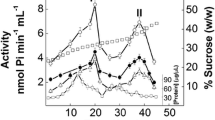
We characterize the kinetic properties of a gill (Na+, K+)-ATPase from the pelagic marine seabob Xiphopenaeus kroyeri. Sucrose density gradient centrifugation revealed membrane fractions distributed mainly into a heavy fraction showing considerable (Na+, K+)-ATPase activity, but also containing mitochondrial F0F1- and Na+- and V-ATPases. Western blot analysis identified a single immunoreactive band against the (Na+, K+)-ATPase α-subunit with an Mr of ≈110 kDa. The α-subunit was immunolocalized to the intralamellar septum of the gill lamellae. The (Na+, K+)-ATPase hydrolyzed ATP obeying Michaelis–Menten kinetics with VM = 109.5 ± 3.2 nmol Pi min−1 mg−1 and KM = 0.03 ± 0.003 mmol L−1. Mg2+ (VM = 109.8 ± 2.1 nmol Pi min−1 mg−1, K0.5 = 0.60 ± 0.03 mmol L−1), Na+ (VM = 117.6 ± 3.5 nmol Pi min−1 mg−1, K0.5 = 5.36 ± 0.14 mmol L−1), K+ (VM = 112.9 ± 1.4 nmol Pi min−1 mg−1, K0.5 = 1.32 ± 0.08 mmol L−1), and NH4 + (VM = 200.8 ± 7.1 nmol Pi min−1 mg−1, K0.5 = 2.70 ± 0.04 mmol L−1) stimulated (Na+, K+)-ATPase activity following site–site interactions. K+ plus NH4 + does not synergistically stimulate (Na+, K+)-ATPase activity, although each ion modulates affinity of the other. The enzyme exhibits a single site for K+ binding that can be occupied by NH4 +, stimulating the enzyme. Ouabain (KI = 84.0 ± 2.1 µmol L−1) and orthovanadate (KI = 0.157 ± 0.001 µmol L−1) inhibited total ATPase activity by ≈50 and ≈44 %, respectively. Ouabain inhibition increases ≈80 % in the presence of NH4 + with a threefold lower KI, suggesting that NH4 + is likely transported as a K+ congener.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Armstrong DA, Strange K, Crowe J, Knight A, Simmons M (1981) High salinity acclimation by the prawn Macrobrachium rosenbergii—uptake of exogenous ammonia and changes in endogenous nitrogen compounds. Biol Bull 160:349–365
Belli NM, Faleiros RO, Firmino KCS, Masui DC, Leone FA, McNamara JC, Furriel RPM (2009) Na, K-ATPase activity and epithelial interfaces in gills of the freshwater shrimp Macrobrachium amazonicum (Decapoda, Palaemonidae). Comp Biochem Physiol 152A:431–439
Blanco G, Mercer RW (1998) Isozymes of the Na-K-ATPase: heterogeneity in structure, diversity in function. Am J Physiol 275:F633–F650
Blanco G, Wagoner K, Sanchez G, Enders GC (2005) Ontogeny of the Na, K-ATPase alpha 4 isoform during rat male germ cell development. FASEB J 19:A1153–A1173
Boudour-Boucheker N, Boulo V, Charmantier-Daures M, Grousset E, Anger K, Charmantier G, Lorin-Nebel C (2014) Differential distribution of V-type H(+)-ATPase and Na, K-ATPase in the brachial chamber of the palaemonidae shrimp Macrobrachium amazonicum. Cell Tissue Res 357:195–206
Bowman EJ, Siebers A, Altendorf K (1988) Bafilomycins: a class of inhibitors of membrane ATPase from microorganisms, animal cells, and plant cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 85:7972–7976
Cameron JN, Batterton CV (1978) Antennal gland function in the freshwater crab Callinectes sapidus: water, electrolyte acid-base and ammonia excretion. J Comp Physiol 123B:143–148
Corotto FS, Holliday CW (1996) Branchial Na, K-ATPase and osmoregulation in the purple shore crab Hemigrapsus nudus (Dana). Comp Biochem Physiol 113A:361–368
Costa RC, Fransozo A, Melo GAS, Freire FAM (2003) An illustrated key for Dendrobranchiata shrimps from the northern coast of São Paulo State, Brazil. Biota Neotrop 3:1–12
Crambert G, Hasler U, Beggah AT, Yu CL, Modyanov NN, Horisberger JD, Lelievre L, Geering K (2000) Transport and pharmacological properties of nine different human isozymes. J Biol Chem 275:1976–1986
Crambert G, Schaner D, Roy S, Geering K (2004) New molecular determinants controling the accessibility of ouabain to its binding site in human Na,K-ATPase alpha isoforms. Mol Pharmacol 65:335–341
D’Orazio SE, Holliday CW (1985) Gill Na+, K+-ATPase and osmoregulation in the sand fiddler crab, Uca pugilator. Physiol Zool 58:364–373
Dall W, Hill BJ, Rothlisberg PC, Sharples DJ (1990) The biology of the Penaeidae. In: Blaxter JHS, Southward AJ (eds) Advances in marine biology, vol 27. Academic Press, San Diego, pp 1–489
Donnet C, Arystarkhova E, Sweadner KJ (2001) Thermal denaturation of the Na, K-ATPase provides evidence for alpha-alpha oligomeric interaction and γ subunit association with the C-terminal domain. J Biol Chem 276:7357–7365
Faleiros RO, Goldman MHS, Furriel RPM, McNamara JC (2010) Differential adjustment in gill Na+/K+- and V-ATPase activities and transporter mRNA expression during osmoregulatory acclimation in the cinnamon shrimp Macrobrachium amazonicum (Decapoda, Palaemonidae). J Exp Biol 15:3894–3905
Fedosova NU, Cornelius F, Klodos I (1998) E2P phosphoforms of Na, K-ATPase. I Comparison of phosphointermediates formed from ATP and Pi by their reactivity toward hydroxylamine and vanadate. Biochemistry 37:13634–13642
Firmino KCS, Faleiros RO, Masui DC, McNamara JC, Furriel RPM (2011) Short- and long-term salinity-induced modulation of V-ATPase activity in the posterior gills of the true freshwater crab, Dilocarcinus pagei (Brachyura, Trichodactylidae). Comp Biochem Physiol 160B:24–31
França JL, Pinto MR, Lucena MN, Garçon DP, Valenti WC, McNamara JC, Leone FA (2013) Subcellular localization and kinetic characterization of a gill (Na+, K+)-ATPase from the giant freshwater prawn Macrobrachium rosenbergii. J Memb Biol 246:529–543
Freire CA, McNamara JC (1995) Fine structure of the gills of the fresh-water shrimp Macrobrachium olfersii (Decapoda): effect of acclimation to high salinity medium and evidence for involvement of the lamellar septum in ion uptake. J Crustacean Biol 15:103–116
Freire CA, Onken H, McNamara JC (2008) A structure-function analysis of ion transport in crustacean gills and excretory organs. Comp Biochem Physiol 151A:272–304
Furriel RPM, McNamara JC, Leone FA (2000) Characterization of (Na+, K+)-ATPase in gill microsomes of the freshwater shrimp Macrobrachium olfersii. Comp Biochem Physiol 126B:303–315
Furriel RPM, Masui DC, McNamara JC, Leone FA (2004) Modulation of gill (Na+, K+)-ATPase activity by ammonium ions: putative coupling of nitrogen excretion and ion uptake in the freshwater shrimp Macrobrachium olfersii. J Exp Zool 301A:63–74
Furriel RPM, Firmino KCS, Masui DC, Faleiros RO, Torres AH, McNamara JC (2010) Structural and biochemical correlates of Na+, K+-ATPase driven ion uptake across the posterior epithelium of the true freshwater crab Dilocarcinus pagei (Brachyura, Trichodactylidae). J Exp Zool 313A:508–523
Gache C, Rossi B, Lazdunski M (1976) (Na+, K+)-Activated adenosinetriphosphatase of axonal membranes: cooperativity and control. Eur J Biochem 65:293–306
Garçon DP, Masui DC, Mantelatto FLM, McNamara JC, Furriel RPM, Leone FA (2007) K+ and NH4 + modulate gill (Na+ K+)-ATPase activity in the blue crab Callinectes ornatus: fine tuning of ammonia excretion. Comp Biochem Physiol 147A:145–155
Garçon DP, Masui DC, Mantelatto FLM, McNamara JC, Furriel RPM, Leone FA (2009) Hemolymph ionic regulation and adjustments in gill (Na+, K+)-ATPase activity during salinity acclimation in the swimming crab Callinectes ornatus (Decapoda Brachyura). Comp Biochem Physiol 154A:44–55
Garty H, Karlish SJD (2006) Role of FXYD proteins in ion transport. Ann Rev Physiol 68:431–459
Geering K (2008) Functional roles of NaK-ATPase subunits. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens 17:526–532
Glynn IM (1985) The (Na+, K+)-transporting adenosine triphosphatase. In: Martonosi AN (ed) The enzymes of biological membranes, vol 10. Plenum Press, New York, pp 35–114
Gonçalves RR, Masui DC, McNamara JC, Mantelatto FLM, Garçon DP, Furriel RPM, Leone FA (2006) A kinetic study of the gill (Na+ K+)-ATPase and its role in ammonia excretion in the intertidal hermit crab Clibanarius vittatus. Comp Biochem Physiol 145A:346–356
Gordon JA (1991) Use of vanadate as protein-phosphotyrosine phosphatase inhibitor. Methods Enzymol 201:477–482
Heckler GS, Costa RC, Fransozo A, Rosso R, Shimizu RM (2014) Long-term patterns of spatial and temporal distribution in the seabob shrimp Xiphopenaeus kroyeri (Decapoda: Penaeidae) population in Southeastern Brazil. J Crustacean Biol 34:326–333
Heller C (1862) Beiträge zur näheren Kenntnis der Macrouren. Sitzundberichten Math-Phys. Kl. K. Bayer. Akad. Wiss. Muench 45:389–425
Holliday CW (1985) Salinity-induced changes in gill Na, K ATPase activity in the mud fiddler crab Uca pugnax. J Exp Zool 233:199–208
Horisberger JD (2004) Recent insights into the structure and mechanism of the sodium pump. Physiology 19:377–387
Jorgensen PL, Hakansson KO, Karlish SJD (2003) Structure and mechanism of Na, K-ATPase: functional sites and their interactions. Ann Rev Physiol 65:817–849
Kaplan JH (2002) Biochemistry of Na, K-ATPase. Ann Rev Biochem 71:511–535
Karlish SJ (2003) Investigating the energy transduction mechanism of P-type ATPases with Fe2+-catalyzed oxidative cleavage. Ann NY Acad Sci 986:39–49
Kirschner LB (2004) The mechanism of sodium chloride uptake in hyperregulating aquatic animals. J Exp Biol 207:1439–1452
Koroleff F (1983) Methods of seawater analysis. In: Grasshoff K, Ehrhart M, Kremling K (eds) Determination of ammonia. Verlag Chemie, Weinheim, pp 150–151
Laemmli UK (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature (Lond) 227:680–685
Lee CE, Kiergaard M, Gelembiuk GW, Eads BD, Posavi M (2011) Pumping ions: rapid parallel evolution of ionic regulation following habitat invasions. Evolution 65:2229–2244
Leone FA, Baranauskas JA, Furriel RPM, Borin IA (2005) SigrafW: an easy-to-use program for fitting enzyme kinetic data. Biochem Mol Biol Ed 33:399–403
Leone FA, Masui DC, Bezerra TMS, Garçon DP, Valenti VC, Augusto AS, McNamara JC (2012) Kinetic analysis of gill (Na+, K+)-ATPase activity in selected ontogenetic stages of the Amazon River shrimp Macrobrachium amazonicum (Decapoda Palaemonidae): interactions at ATP- and cation-binding sites. J Memb Biol 245:201–215
Leone FA, Bezerra TMS, Garçon DP, Lucena MN, Pinto MR, Fontes CFL, McNamara JC (2014) Modulation by K+ and NH4 + of microsomal (Na+, K+)-ATPase activity in selected ontogenetic stages of the diadromous river shrimp Macrobrachium amazonicum (Decapoda, Palaemonidae). PLoS One 9(2):e8925. doi:10.1371/journalpone008925
Lovett DL, Watts SA (1995) Changes in polyamine levels in response to acclimation salinity in gills of the blue crab Callinectes sapidus Rathbun. Comp Biochem Physiol 110B:115–119
Lucena MN, Garçon DP, Mantelatto FLM, Pinto MR, McNamara JC, Leone FA (2012) Hemolymph ion regulation and kinetic characteristics of the gill (Na+K+)-ATPase in the hermit crab Clibanarius vittatus (Decapoda, Anomura) acclimated to high salinity. Comp Biochem Physiol 161B:380–391
Lucena MN, Pinto MR, Garçon DP, McNamara JC, Leone FA (2015) A kinetic characterization of the gill V(H+)-ATPase in juvenile and adult Macrobrachium amazonicum, a diadromous palaemonid shrimp. Comp Biochem Physiol 181B:15–25
Lucu C (1990) Ionic regulatory mechanisms in crustacean gill epithelia. Comp Biochem Physiol 97A:297–306
Lucu C, Flik G (1999) Na+ K+-ATPase and Na+/Ca2+ exchange activities in gills of hyperregulating Carcinus maenas. Am J Physiol 276:R490–R499
Lucu C, Towle DW (2003) Na+ K+-ATPase in gills of aquatic crustacean. Comp Biochem Physiol 135A:195–214
Lucu C, Devescovi M, Siebers D (1989) Do amiloride and ouabain affect ammonia fluxes in perfused Carcinus gill epithelia. J Exp Zool 249:1–5
Lucu C, Devescovi M, Skaramuca M, Kozul V (2000) Gill Na, K-ATPase in the spiny lobster Palinurus elephas and other marine osmoconformers adaptiveness of enzymes from osmoconformity to hyperregulation. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 246:163–178
Mangum CP, Towle DW (1977) Physiological adaptation to unstable environments. Am Sci 65:67–75
Mantelatto FL, Avelar WEP, Silva DML, Tomazelli AC, Lopez JLC, Shuhama T (1999) Heavy metals in the shrimp Xiphopenaeus kroyeri (Heller, 1862) (Crustacea, Penaeidae) from Ubatuba Bay, São Paulo, Brazil. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 62:152–159
Marks MJ, Seeds NW (1978) A heterogeneous ouabain-ATPase interaction in mouse brain. Life Sci 23:2735–2744
Masui DC, Furriel RPM, McNamara JC, Mantelatto FLM, Leone FA (2002) Modulation by ammonium ions of gill microsomal (Na+, K+)-ATPase in the swimming crab Callinectes danae: a possible mechanism for the regulation of ammonia excretion. Comp Biochem Physiol 132C:471–482
Masui DC, Furriel RPM, Silva ECC, Mantelatto FLM, McNamara JC, Barrabin HM, Scofano HM, Fontes CFL, Leone FA (2005) Gill microsomal (Na+, K+)-ATPase from the blue crab Callinectes danae: interactions at cationic sites. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 37:2521–2535
Masui DC, Mantelatto FLM, McNamara JC, Furriel RPM, Leone FA (2009) (Na+, K+)-ATPase activity in gill microsomes from the blue crab, Callinectes danae, acclimated to low salinity: novel perspectives on ammonia excretion. Comp Biochem Physiol 153A:141–148
McNamara JC, Faria SC (2012) Evolution of osmoregulatory patterns and gill ion transport mechanisms in the decapod Crustacea: a review. J Comp Physiol 182B:997–1014
McNamara JC, Lima AG (1997) The route of ion and water movements across the gill epithelium of the freshwater shrimp Macrobrachium olfersii (Decapoda, Palaemonidae): evidence from ultrastructural changes induced by acclimation to saline media. Biol Bull 192:321–331
Moretti R, Martin M, Proverbio T, Proverbio F, Martin T (1991) Ouabain-insensitive Na-ATPase activity in homogenates from different animal tissues. Comp Biochem Physiol 98:623–626
Morris S (2001) Neuroendocrine regulation of osmoregulation and the evolution of air-breathing in decapod crustaceans. J Exp Biol 204:979–989
Morth JP, Pedersen BP, Toustrup-Jensen MS, Sorensen TLM, Petersen J, Andersen JP, Vilsen B, Nissen P (2007) Crystal structure of the sodium-potassium pump. Nature 450:1043–1050
Nesher M, Spolansky U, Rosen H, Lichtstein D (2007) The endogenous digitalis- like compounds—A new family of steroid hormones. Life Sci 80:2093–2107
Onken H, Tresguerres M, Luquet CM (2003) Active NaCl absorption across posterior gills of hyperosmoregulating Chasmagnathus granulatus. J Exp Biol 206:1017–1023
Palmgren MG, Nissen P (2011) P-Type ATPases. Annu Rev Biophys 40:243–266
Pedemonte CH, Beaugé L (1983) Inhibition of (Na+, K+)-ATPase by magnesium-ions and inorganic-phosphate and release of these ligands in the cycles of ATP hydrolysis. Biochim Biophys Acta 748:245–253
Péqueux A (1995) Osmotic regulation in crustaceans. J Crust Biol 15:1–60
Pick U (1982) The interaction of vanadate ions with the Ca-ATPase from sarcoplasmic reticulum. J Biol Chem 257:6111–6119
Piller SC, Henry RP, Doeller JE, Kraus DW (1995) A comparison of the gill physiology of two euryhaline crab species, Callinectes Sapidus and Callinectes similis: energy production, transport-related enzymes and osmorregulation as a function of acclimation salinity. J Exp Biol 198:349–358
Pires AMS (1992) Structure and dynamics of benthic megafauna on the continental shelf offshore of Ubatuba, southeastern Brazil. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 86:63–76
Poulsen H, Morth P, Egebjerg J, Nissen P (2010) Phosphorylation of the Na+K+-ATPase and the H+K+-ATPase. FEBS Lett 584:2589–2595
Proverbio T, Zanders IP, Marin R, Rodrigues JM, Proverbio F (1990) Effects of Na+ and/or K+ on the Mg2+-dependent ATPase activities in shrimp (Macrobrachium amazonicum) gill homogenates. Comp Biochem Physiol 97B:383–390
Ratheal IM, Virgin GK, Yu H, Roux B, Gatto C, Artigas P (2010) Selectivity of externally facing ion-binding sites in the Na/K pump to alkali metals and organic cations. PNAS 107:18718–18723
Read SM, Northcote DH (1981) Minimization of variation in the response to different proteins of the Coomassie blue G dye-binding assay for protein. Analyt Biochem 116:53–64
Robinson JD (1970) Interactions between monovalent cations and the (Na+ + K+)- dependent adenosine triphosphatase. Arch Biochem Biophys 139:17–27
Robinson JD (1982) Tryptic digestion of the (Na + K)-ATPase is both sensitive to and modifies K+ interactions with the enzyme. J Bioenerg Biomemb 14:319–333
Rudolph FB, Baugher BW, Beissner RS (1979) Techniques in coupled enzyme assays. Methods Enzymol 63:22–42
Sáez AG, Lozano E, Zaldívar-Riverón A (2009) Evolutionary history of Na, K-ATPases and their osmoregulatory role. Genetica 136:479–490
Santos LCF, Belli NM, Augusto A, Masui DC, Leone FA, McNamara JC, Furriel RPM (2007) Gill (Na+, K+)-ATPase in diadromous freshwater palaemonid shrimps: species specific kinetic characteristics and α-subunit expression. Comp Biochem Physiol 148A:178–188
Shindo Y, Morishita K, Kotake E, Miura H, Carninci P, Kawai J, Hayashizaki Y, Hino A, Kanda T, Kusakabe Y (2011) FXYD6: a Na, K-ATPase regulator is expressed in type II taste cells. Biosci Biotech Biochem 75:1061–1066
Silva ECC, Masui DC, Furriel RP, McNamara JC, Barrabin H, Scofano HM, Perales J, Teixeira-Ferreira A, Leone FA, Fontes CFL (2012) Identification of a crab gill FXYD2 protein and regulation of crab microsomal Na K-ATPase activity by mammalian FXYD2 peptide. Biochim Biophys Acta 1818:2588–2597
Skou JC, Esmann M (1992) The (Na+, K+)-ATPase. J Bioenerg Biomemb 24:249–261
Takeyasu K, Tamkun M, Renaud KJ, Fambrough DM (1988) Ouabain-sensitive (Na+- K+)-ATPase activity expressed in mouse L cells by transfection with DNA encoding the a-subunit of an avian sodium pump. J Biol Chem 263:4347–4354
Taylor HH, Taylor EW (1992) Gills and lungs: the exchange of gases and ions. In: Harrison FW, Humes AG (eds) Microscopic anatomy of invertebrates, decapod Crustacea, vol 10. Wiley-Liss, New York, pp 203–293
Towbin H, Staehelin T, Gordon J (1979) Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 76:4350–4354
Towle DW, Kays WT (1986) Basolateral localization of Na+ + K+-ATPase in gill epithelium of two osmoregulating crabs, Callinectes-sapidus and Carcinus maenas. J Exp Zool 239:311–318
Towle DW, Weihrauch D (2001) Osmoregulation by gills of euryhaline crabs: molecular analysis of transporters. Am Zool 41:770–780
Wall SM (1996) Ammonium transport and the role of the Na, K-ATPase Miner. Electrol Metab 22:311–317
Ward DG, Cavieres JD (1998) Affinity labeling of two nucleotide sites on Na, K-ATPase using 2′(3′)-O-(2,4,6-trinitrophenyl) 8-azidoadenosine 5′-[alpha-P-32] diphosphate (TNP-8N(3)-[alpha-P-32]ADP) as a photoactivatable probe. Label incorporation before and after blocking the high affinity ATP site with fluorescein isothiocyanate. J Biol Chem 273:33759–33765
Weihrauch D, Towle DW (2000) Na+/H+-exchanger and Na+/K+/2Cl–cotransporter are expressed in gills of the euryhaline Chinese crab Eriocheir sinensis. Comp Biochem Physiol 126:S158–S198
Weihrauch D, Becker W, Postel U, Riestenpatt S, Siebers D (1998) Active excretion of ammonia across the gills of the shore crab Carcinus maenas and its relation to osmoregulatory ion uptake. J Comp Physiol 168B:364–376
Weihrauch D, Becker W, Postel U, Luck-Kopp S, Siebers D (1999) Potential of active excretion of ammonia in three different haline species of crabs. J Comp Physiol 169B:25–37
Weihrauch D, Morris S, Towle DW (2004) Ammonia excretion in aquatic and terrestrial crabs. J Exp Biol 207:4491–4504
Wheatly MG, Henry RP (1987) Branchial and antennal gland Na+, K+-dependent ATPase and carbonic anhydrase activity during salinity acclimation of the euryhaline crayfish Pacifastacus leniusculus. J Exp Biol 133:73–86
Wilder MN, Huong DTT, Atmomarsono M, Tran TTH, Phu TQ, Yang WJ (2000) Characterization of Na/K-ATPase in Macrobrachium rosenbergii and the effects of changing salinity on enzymatic activity. Comp Biochem Physiol 125A:377–388
Williams AB (1984) Shrimps, lobsters and crabs of the Atlantic Coast of the Eastern United State, Maine to Florida. Smithsonian Institute Press, Washington
Yoda A, Yoda S (1982) Interaction between ouabain and the phosphorylated intermediate of (Na+, K+)-ATPase. Mol Pharmacol 22:700–705
Acknowledgments
This work constitutes part of a Ph D thesis by LAR. We thank the Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de São Paulo (FAPESP 2010/17534-0; 2002/08178-/9; 2010/50188-8), the Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq 470830/2011-5), and Instituto Nacional de Ciência e Tecnologia (INCT) Adapta/Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado do Amazonas (FAPEAM- 573976/2008-2) for financial support received. FAL (302776/2011-7), JCM (300662/2009-2) and FLM (302748/2010-5) received research scholarships from CNPq. DPG (2010/06395-9) and MNL (2010/16115-3) received Ph D scholarships from FAPESP. MRP received post-doctoral scholarships from CNPq (560501/2010-2). We thank Nilton Rosa Alves for technical assistance. This laboratory (FAL) is integrated with the Amazon Shrimp Network (Rede de Camarão da Amazônia) and with ADAPTA (Centro de Estudos de Adaptações da Biota Aquática da Amazônia).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Leone, F.A., Lucena, M.N., Rezende, L.A. et al. A Kinetic Characterization of (Na+, K+)-ATPase Activity in the Gills of the Pelagic Seabob Shrimp Xiphopenaeus kroyeri (Decapoda, Penaeidae). J Membrane Biol 248, 257–272 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00232-014-9765-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00232-014-9765-6