Abstract
Purpose
Prediction of the rupture risk is critical for the identification of unruptured cerebral aneurysms (UCAs) eligible for invasive treatments. The size ratio (SR) is a strong morphological predictor for rupture. We investigated the relationship between the inflow hemodynamics evaluated on four-dimensional (4D) flow magnetic resonance (MR) imaging and the SR to identify specific characteristics related to UCA rupture.
Methods
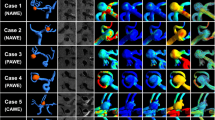
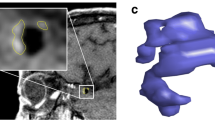
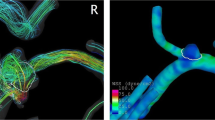
We evaluated the inflow jet patterns and inflow hemodynamic parameters of 70 UCAs on 4D flow MR imaging and compared them among 23 aneurysms with an SR ≧2.1 and 47 aneurysms with an SR ≦2.0. Based on the shape of inflow streamline bundles with a velocity ≧75% of the maximum flow velocity in the parent artery, the inflow jet patterns were classified as concentrated (C), diffuse (D), neck-limited (N), and unvisualized (U).
Results
The incidence of patterns C and N was significantly higher in aneurysms with an SR ≧2.1. The rate of pattern U was significantly higher in aneurysms with an SR ≦2.0. The maximum inflow rate and the inflow rate ratio were significantly higher in aneurysms with an SR ≧2.1.
Conclusions
The SR affected the inflow jet pattern, the maximum inflow rate, and the inflow rate ratio of UCAs. In conjunction with the SR, inflow hemodynamic analysis using 4D flow MR imaging may contribute to the risk stratification for aneurysmal rupture.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ICA:
-
Internal carotid artery
- MR:
-
Magnetic resonance
- SR:
-
Size ratio
- TOF:
-
Time-of-flight
- UCA:
-
Unruptured cerebral aneurysm
- 3D:
-
Three-dimensional
- 4D:
-
Four-dimensional
References
Orz Y, Kobayashi S, Osawa M, Tanaka Y (1997) Aneurysm size: a prospective factor for rupture. Br J Neurosurg 11:144–149
Ujiie H, Tachibana H, Hiramatsu O, Hazel AL, Matsumoto T, Ogasawara Y, Nakajima H, Hori T, Takakura K, Kajiya F (1999) Effects of size and shape (aspect ratio) on the hemodynamics of saccular aneurysms: a possible index for surgical treatment of intracranial aneurysms. Neurosurgery 45:119–130
Wiebers DO, Whisnant JP, Huston JIII, Meissner I, Brown RD Jr, Piepgras DG, Forbes GS, Thielen K, Nichols D, O’Fallon WM, Peacock J, Jaeger L, Kassell NF, Kongable-Beckman GL, Torner JC (2003) International study of unruptured intracranial aneurysms investigators. Unruptured intracranial aneurysms: natural history, clinical outcome, and risks of surgical and endovascular treatment. Lancet 362:103–110
Raghavan ML, Ma B, Harbaugh RE (2005) Quantified aneurysm shape and rupture risk. J Neurosurg 102:355–362
Dhar S, Tremmel M, Mocco J, Kim M, Yamamoto J, Siddiqui AH, Hopkins LN, Meng H (2008) Morphological parameter for intracranial aneurysm rupture risk assessment. Neurosurgery 63:185–197
Baharoglu MI, Schirmer CM, Hoit DA, Gao BL, Malek AM (2010) Aneurysm inflow-angle as a discriminant for rupture in sidewall cerebral aneurysms: morphometric and computational fluid dynamic analysis. Stroke 41:1423–1430
The UCAS Japan Investigators (2012) The natural course of unruptured cerebral aneurysms in a Japanese cohort. N Engl J Med 366:2474–2482
Cai W, Shi D, Gong J, Chen G, Qiao F, Dou X, Li H, Lu K, Yuan S, Sun C, Lan Q (2015) Are morphologic parameters actually correlated with the rupture status of anterior communicating artery aneurysms? World Neurosurg 84:1278–1283
Kang H, Ji W, Qian Z, Li Y, Jiang C, Wu Z, Wen X, Xu W, Liu A (2015) Aneurysm characteristics associated with the rupture risk of intracranial aneurysms: a self-controlled study. PLoS One 10:e0142330
Xiang J, Natarajan SK, Tremmel M, Ma D, Mocco J, Hopkins LN, Siddiqui AH, Levy EI, Meng H (2011) Hemodynamic-morphologic discriminants for intracranial aneurysm rupture. Stroke 42:144–152
Li M, Jiang Z, Yu H, Hong T (2013) Size ratio: a morphological factor predictive of the rupture of cerebral aneurysm? Can J Neurol Sci 40:366–371
Farnoush A, Avolio A, Qian Y (2014) A growth model of saccular aneurysms based on hemodynamic and morphologic discriminant parameters for risk of rupture. J Clin Neurosci 21:1514–1519
Castro MA, Putman CM, Sheridan MJ, Cebral JR (2009) Hemodynamic patterns of anterior communicating artery aneurysms: a possible association with rupture. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 30:297–302
Cebral JR, Mut F, Weir J, Putman CM (2011) Association of hemodynamic characteristics and cerebral aneurysm rupture. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 32:264–270
Qian Y, Takao H, Umezu M, Murayama Y (2011) Risk analysis of unruptured aneurysms using computational fluid dynamics technology: preliminary results. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 32:1948–1955
Tremmel M, Dhar S, Levy EI, Mocco J, Meng H (2009) Influence of intracranial aneurysm-to-parent vessel size ratio on hemodynamics and implication for rupture: results from virtual experimental study. Neurosurgery 64:622–630
Cebral JR, Castro MA, Burgess JE, Pergolizzi RS, Sheridan MJ, Putman CM (2005) Characterization of cerebral aneurysms for assessing risk of rupture by using patient-specific computational hemodynamics models. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:2550–2559
Cebral JR, Mut F, Weir J, Putman C (2011) Quantitative caharacterization of the hemodynamic environment in ruptured and unruptured brain aneurysms. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 32:145–151
Gasteiger R, Lehmann DJ, van Pelt R, Janiga G, Beuing O, Vilanova A, Theisel H, Preim B (2012) Automatic detection and visualization of qualitative hemodynamic characteristics in cerebral aneurysms. IEEE Trans Vis Comput Graph 18:2178–2187
Neugebauer M, Gasteiger R, Janiga G, Beuing O, Preim B (2013) Effective visual exploration of hemodynamics in cerebral aneurysms. In: Hege HC, Vilanova A (eds) Eurographics 2013 - Dirk Bartz Prize. Proceeding of the conference of the European association for computer graphics. The Eurographics Association, Geona, Spain, May pp 6–10. doi:10.2312/conf/EG2013/med/005-008
Boussel L, Rayz V, Martin A, Acevedo-Bolton G, Lawton MT, Higashida R, Smith WS, Young WL, Saloner D (2009) Phase-contrast magnetic resonance imaging measurements in intracranial aneurysms in vivo of flow patterns, velocity fields, and wall shear stress: comparisons with computational fluid dynamics. Magn Reson Med 61:409–417
Meckel S, Stalder AF, Santini F, Radü EW, Rüfenacht DA, Markl M, Wetzel SG (2008) In vivo visualization and analysis of 3-D hemodynamics in cerebral aneurysms with flow-sensitized 4-D MR imaging at 3 T. Neuroradiology 50:473–484
Isoda H, Ohkura Y, Kosugi T, Hirano M, Alley MT, Bammer R, Pelc NJ, Namba H, Sakahara H (2010) Comparison of hemodynamics of intracranial aneurysms between MR fluid dynamics using 3D cine phase contrast MRI and MR-based computational fluid dynamics. Neuroradiology 52:913–920
Naito T, Miyachi S, Matsubara N, Isoda H, Izumi T, Haraguchi K, Takahashi I, Ishii K, Wakabayashi T (2012) Magnetic resonance fluid dynamics for intracranial aneurysms: comparison with computed fluid dynamics. Acta Neurochir 154:993–1001
Futami K, Sano H, Kitabayashi T, Misaki K, Nakada M, Uchiyama N, Ueda F (2015) Parent artery curvature influences inflow zone location of unruptured sidewall cerebral aneurysms. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 36:342–348
Futami K, Kitabayashi T, Sano H, Misaki K, Uchiyama N, Ueda F, Nakada M (2016) Inflow jet patterns of unruptured cerebral aneurysms based on the flow velocity in the parent artery: evaluation using 4D flow MRI. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 37:1318–1323
Lorensen WE, Cline HE (1987) Marching cubes: a high resolution 3D surface construction algorithm. ACM Siggraph Computer Graphics 21:163–169
Shimai H, Yokota H, Nakamura S, Himeno R (2005) Extraction from biological volume data of a region of interest with nonuniform intensity. In: Proceedings of the Society of Photo-Optical Instrumentation Engineers 6051. RIKEN, Japan, 6 December 2005. doi:10.1117/12.648945
Schneiders JJ, Marquering HA, Antiga L, van den Berg R, VanBavel E, Majoie CB (2013) Intracranial aneurysm neck size overestimation with 3D rotational angiography: the impact on intra-aneurysmal hemodynamics simulated with computational fluid dynamics. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 34:121–128
Jansen IGH, Schneiders JJ, Potters WV, van Ooij P, van den Berg R, van Bavel E, Marquering HA, Majoie CBLM (2014) Generalized versus patient-specific inflow boundary conditions in computational fluid dynamics simulations of cerebral aneurysmal hemodynamics. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 35:1543–1548
Szikora I, Paal G, Ugron A, Nasztanovics F, Marosfoi M, Berentei Z, Kulcsar Z, Lee W, Bojtar I, Nyary I (2008) Impact of aneurysmal geometry on intraaneurysmal flow: a computerized flow simulation study. Neuroradiology 50:411–421
Tang C, Blatter CC, Paker DL (1993) Accuracy of phase-contrast flow measurements in the presence of partial-volume effects. J Magn Reson Imaging 3:377–385
Hollnagel DI, Summers PE, Poulikakos D, Kollias SS (2009) Comparative velocity investigations in cerebral arteries and aneurysms: 3D phase-contrast MR angiography, laser Doppler velocimetry and computational fluid dynamics. NMR Biomed 22:795–808
Lauric A, Baharoglu MI, Gao B, Malek AM (2012) Incremental contribution of size ratio as a discriminant for rupture status in cerebral aneurysms: comparison with size, height, and vessel diameter. Neurosurgery 70:944–952
Lin N, Ho A, Gross BA, Pieper S, Frerichs KU, Day AL, Du R (2012) Differences in simple morphological variables in ruptured and unruptured middle cerebral artery aneurysms. J Neurosurg 117:913–919
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
No funding was received for this study.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Futami, K., Nambu, I., Kitabayashi, T. et al. Inflow hemodynamics evaluated by using four-dimensional flow magnetic resonance imaging and the size ratio of unruptured cerebral aneurysms. Neuroradiology 59, 411–418 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-017-1801-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-017-1801-7