Abstract
Purpose
Single ventricle heart disease (SVHD) patients show injury in brain sites that regulate autonomic, mood, and cognitive functions. However, the nature (acute or chronic changes) and extent of brain injury in SVHD are unclear. Our aim was to examine regional brain tissue damage in SVHD over controls using DTI-based mean diffusivity (MD), axial diffusivity (AD), radial diffusivity (RD), and fractional anisotropy (FA) procedures.
Methods
We collected two DTI series (3.0-T MRI), mood and cognitive data, from 27 SVHD and 35 control adolescents. Whole-brain MD, AD, RD, and FA maps were calculated from each series, realigned and averaged, normalized to a common space, smoothed, and compared between groups using ANCOVA (covariates, age and sex; false discovery rate, p < 0.05). Region-of-interest analyses were performed to calculate MD, AD, RD, and FA values for magnitude assessment between groups.
Results
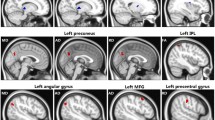
SVHD patients showed impaired mood and cognitive functions over healthy adolescents. Multiple brain sites in SVHD showed increased MD values, including the insula, caudate, cingulate, hypothalamus, thalamus, medial prefrontal and frontal cortices, parahippocampal gyrus, hippocampus, precentral gyrus, amygdala, cerebellum, corpus callosum, basal forebrain, mammillary bodies, internal capsule, midbrain, fornix, and occipital, parietal, and temporal cortices, indicating chronic tissue changes. Similar areas showed either increased AD or RD values, with RD changes more enhanced over AD in SVHD compared to controls. Few brain regions emerged with increased or decreased FA values in SVHD patients over controls.
Conclusion
SVHD adolescents, more than a decade from their last surgical procedure, show widespread brain abnormalities in autonomic, mood, and cognitive regulatory areas. These findings indicate that brain injury is in a chronic stage in SVHD with predominantly myelin changes that may result from previous hypoxia/ischemia- or developmental-induced processes.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mulkey SB, Ou X, Ramakrishnaiah RH, Glasier CM, Swearingen CJ, Melguizo MS, Yap VL, Schmitz ML, Bhutta AT (2014) White matter injury in newborns with congenital heart disease: a diffusion tensor imaging study. Pediatr Neurol 51(3):377–383
Rollins CK, Watson CG, Asaro LA, Wypij D, Vajapeyam S, Bellinger DC, DeMaso DR, Robertson RL Jr, Newburger JW, Rivkin MJ (2014) White matter microstructure and cognition in adolescents with congenital heart disease. J Pediatr 165(5):936–944 e931-932
Rivkin MJ, Watson CG, Scoppettuolo LA, Wypij D, Vajapeyam S, Bellinger DC, DeMaso DR, Robertson RL, Newburger JW (2013) Adolescents with D-transposition of the great arteries repaired in early infancy demonstrate reduced white matter microstructure associated with clinical risk factors. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 146(3):543–U593
Nath K, Saraswat VA, Krishna YR, Thomas MA, Rathore RKS, Pandey CM, Gupta RK (2008) Quantification of cerebral edema on diffusion tensor imaging in acute-on-chronic liver failure. NMR Biomed 21(7):713–722
Newcombe V, Chatfield D, Outtrim J, Vowler S, Manktelow A, Cross J, Scoffings D, Coleman M, Hutchinson P, Coles J, Carpenter TA, Pickard J, Williams G, Menon D (2011) Mapping traumatic axonal injury using diffusion tensor imaging: correlations with functional outcome. PLoS One 6(5):e19214
Basser PJ, Pierpaoli C (1996) Microstructural and physiological features of tissues elucidated by quantitative-diffusion-tensor MRI. J Magn Reson Ser B 111(3):209–219
Woo MA, Palomares JA, Macey PM, Fonarow GC, Harper RM, Kumar R (2015) Global and regional brain mean diffusivity changes in patients with heart failure. J Neurosci Res 93(4):678–685
Kumar R, Chavez AS, Macey PM, Woo MA, Yan-Go FL, Harper RM (2012) Altered global and regional brain mean diffusivity in patients with obstructive sleep apnea. J Neurosci Res 90(10):2043–2052
Song SK, Sun SW, Ju WK, Lin SJ, Cross AH, Neufeld AH (2003) Diffusion tensor imaging detects and differentiates axon and myelin degeneration in mouse optic nerve after retinal ischemia. NeuroImage 20(3):1714–1722
Ontaneda D, Sakaie K, Lin J, Wang XF, Lowe MJ, Phillips MD, Fox RJ (2017) Measuring brain tissue integrity during 4 years using diffusion tensor imaging. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 38(1):31–38
Stebbins GT, Murphy CM (2009) Diffusion tensor imaging in Alzheimer’s disease and mild cognitive impairment. Behav Neurol 21(1):39–49
Hashim E, Caverzasi E, Papinutto N, Lewis CE, Jing RW, Charles O, Zhang SD, Lin A, Graham SJ, Schweizer TA, Bharatha A, Cusimano MD (2017) Investigating microstructural abnormalities and neurocognition in sub-acute and chronic traumatic brain injury patients with normal-appearing white matter: a preliminary diffusion tensor imaging study. Front Neurol 8:97
Kumar R, Pham TT, Macey PM, Woo MA, Yan-Go FL, Harper RM (2014) Abnormal myelin and axonal integrity in recently diagnosed patients with obstructive sleep apnea. Sleep 37(4):723–732
Kumar R, Woo MA, Macey PM, Fonarow GC, Hamilton MA, Harper RM (2011) Brain axonal and myelin evaluation in heart failure. J Neurol Sci 307(1–2):106–113
Kumar R, Macey PM, Woo MA, Harper RM (2010) Rostral brain axonal injury in congenital central hypoventilation syndrome. J Neurosci Res 88(10):2146–2154
Beck AT, Epstein N, Brown G, Steer RA (1988) An inventory for measuring clinical anxiety: psychometric properties. J Consult Clin Psychol 56(6):893–897
Kroenke K, Spitzer RL, Williams JB (2001) The PHQ-9: validity of a brief depression severity measure. J Gen Intern Med 16(9):606–613
Nasreddine ZS, Phillips NA, Bedirian V, Charbonneau S, Whitehead V, Collin I, Cummings JL, Chertkow H (2005) The Montreal cognitive assessment, MoCA: a brief screening tool for mild cognitive impairment. J Am Geriatr Soc 53(4):695–699
Pike NA, Poulsen MK, Woo MA (2017) Validity of the Montreal cognitive assessment screener in adolescents and young adults with and without congenital heart disease. Nurs Res 66(3):222–230
Sheslow D, Adams W (2003) In: 2nd ed. (ed) Wide range assessment of memory and learning administration and technical manual. Wide Range Inc, Wilmington
Zhang H, Yushkevich PA, Alexander DC, Gee JC (2006) Deformable registration of diffusion tensor MR images with explicit orientation optimization. Med Image Anal 10(5):764–785
Le Bihan D, Mangin JF, Poupon C, Clark CA, Pappata S, Molko N, Chabriat H (2001) Diffusion tensor imaging: Concepts and applications. J Magn Reson Imaging 13(4):534–546. https://doi.org/10.1002/jmri.1076
Ashburner J, Friston KJ (2005) Unified segmentation. NeuroImage 26(3):839–851
von Rhein M, Scheer I, Loenneker T, Huber R, Knirsch W, Latal B (2011) Structural brain lesions in adolescents with congenital heart disease. J Pediatr 158(6):984–989
Lebihan D, Moonen CTW, Vanzijl PCM, Pekar J, Despres D (1991) Measuring random microscopic motion of water in tissues with MR imaging—a cat brain study. J Comput Assist Tomogr 15(1):19–25
Wheeler-Kingshott CA, Cercignani M (2009) About “axial” and “radial” diffusivities. Magn Reson Med 61(5):1255–1260
Acosta-Cabronero J, Williams GB, Pengas G, Nestor PJ (2010) Absolute diffusivities define the landscape of white matter degeneration in Alzheimer’s disease. Brain 133(Pt 2):529–539
Saini J, Bagepally BS, Bhatt MD, Chandran V, Bharath RD, Prasad C, Yadav R, Pal PK (2012) Diffusion tensor imaging: tract based spatial statistics study in essential tremor. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 18(5):477–482
Gooijers J, Swinnen SP (2014) Interactions between brain structure and behavior: the corpus callosum and bimanual coordination. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 43:1–19
Aralasmak A, Ulmer JL, Kocak M, Salvan CV, Hillis AE, Yousem DM (2006) Association, commissural, and projection pathways and their functional deficit reported in literature. J Comput Assist Tomogr 30(5):695–715
Pike NA, Woo MA, Poulsen MK, Evangelista W, Faire D, Halnon NJ, Lewis AB, Kumar R (2016) Predictors of memory deficits in adolescents and young adults with congenital heart disease compared to healthy controls. Front Pediatr 4:117
Cassidy AR, White MT, DeMaso DR, Newburger JW, Bellinger DC (2015) Executive function in children and adolescents with critical cyanotic congenital heart disease. J Int Neuropsychol Soc 21(1):34–49
Liamlahi R, von Rhein M, Buhrer S, Valsangiacomo Buechel ER, Knirsch W, Landolt MA, Latal B (2014) Motor dysfunction and behavioural problems frequently coexist with congenital heart disease in school-age children. Acta Paediatr 103(7):752–758
Vann SD, Nelson AJD (2015) The mammillary bodies and memory: more than a hippocampal relay. Prog Brain Res 219:163–185
Clarke S, Assal G, Bogousslavsky J, Regli F, Townsend DW, Leenders KL, Blecic S (1994) Pure amnesia after unilateral left polar thalamic infarct—topographic and sequential neuropsychological and metabolic (PET) correlations. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 57(1):27–34
Aminoff EM, Kveraga K, Bar M (2013) The role of the parahippocampal cortex in cognition. Trends Cogn Sci 17(8):379–390
Ploner CJ, Gaymard BM, Rivaud-Pechoux S, Baulac M, Clemenceau S, Samson S, Pierrot-Deseilligny C (2000) Lesions affecting the parahippocampal cortex yield spatial memory deficits in humans. Cereb Cortex 10(12):1211–1216
Hedden T, Gabrieli JD (2010) Shared and selective neural correlates of inhibition, facilitation, and shifting processes during executive control. NeuroImage 51(1):421–431
Desmond JE, Fiez JA (1998) Neuroimaging studies of the cerebellum: language, learning and memory. Trends Cogn Sci 2(9):355–362
Drevets WC, Price JL, Furey ML (2008) Brain structural and functional abnormalities in mood disorders: implications for neurocircuitry models of depression. Brain Struct Funct 213(1–2):93–118
Phillips ML, Drevets WC, Rauch SL, Lane R (2003) Neurobiology of emotion perception II: implications for major psychiatric disorders. Biol Psychiatry 54(5):515–528
Shoemaker JK, Goswami R (2015) Forebrain neurocircuitry associated with human reflex cardiovascular control. Front Physiol 6:240
Harper RM, Bandler R, Spriggs D, Alger JR (2000) Lateralized and widespread brain activation during transient blood pressure elevation revealed by magnetic resonance imaging. J Comp Neurol 417(2):195–204
Harper RM, Gozal D, Bandler R, Spriggs D, Lee J, Alger J (1998) Regional brain activation in humans during respiratory and blood pressure challenges. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 25(6):483–486
Sethi V, Tabbutt S, Dimitropoulos A, Harris KC, Chau V, Poskitt K, Campbell A, Azakie A, Xu D, Barkovich AJ, Miller SP, McQuillen PS (2013) Single-ventricle anatomy predicts delayed microstructural brain development. Pediatr Res 73(5):661–667
Mahle WT, Tavani F, Zimmerman RA, Nicolson SC, Galli KK, Gaynor JW, Clancy RR, Montenegro LM, Spray TL, Chiavacci RM, Wernovsky G, Kurth CD (2002) An MRI study of neurological injury before and after congenital heart surgery. Circulation 106(12 Suppl 1):I109–I114
Mebius MJ, Kooi EMW, Bilardo CM, Bos AF (2017) Brain injury and neurodevelopmental outcome in congenital heart disease: a systematic review. Pediatrics 140(1):e20164055
DeMaso DR, Calderon J, Taylor GA, Holland JE, Stopp C, White MT, Bellinger DC, Rivkin MJ, Wypij D, Newburger JW (2017) Psychiatric disorders in adolescents with single ventricle congenital heart disease. Pediatrics 139(3). https://doi.org/10.1542/peds.2016-2241
Miller SP, McQuillen PS, Hamrick S, Xu D, Glidden DV, Charlton N, Karl T, Azakie A, Ferriero DM, Barkovich AJ, Vigneron DB (2007) Abnormal brain development in newborns with congenital heart disease. N Engl J Med 357(19):1928–1938
Acknowledgements
Authors would like to thank Patty Chung, and Paola Moreno for assistance with data collection.
Funding
This study was funded by the National Institutes of Health R01NR016463.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional research committee.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Singh, S., Roy, B., Pike, N. et al. Altered brain diffusion tensor imaging indices in adolescents with the Fontan palliation. Neuroradiology 61, 811–824 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-019-02208-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-019-02208-x