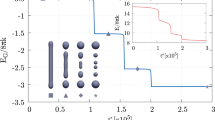
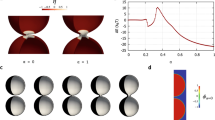
Abstract
In the current article, the dynamic evolution of two-phase vesicles is presented as an extension to a previous stationary model and based on an equilibrium of local forces. In the simplified model, ignoring the effects of membrane inertia, a dynamic equilibrium between the membrane bending potential and local fluid friction is considered in each phase. The equilibrium equations at the domain borders are completed by extended introduction of membrane section reactions. We show that in some cases, the results of stationary and evolutionary models are in agreement with each other and also with experimental observations, while in others the two models differ markedly. The value of our approach is that we can account for unresponsive points of uncertainty using our equations with the local velocity of the lipid membranes and calculating the intermediate states (shapes) in the consequent evolutionary, or response, path.




Experimental vesicle is redrawn from (García-Sáez et al. 2007)

Fusion-budding process is redrawn from experiment by Riske et al. (2006)

Experimental vesicle is redrawn from Dimova et al. (2006)


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- V:
-
Volume
- v:
-
Reduced volume
- v :
-
Membrane local velocity vector
- v :
-
Membrane normal velocity (scalar)
References
Baumgart T, Das S, Webb W, Jenkins J (2005) Membrane elasticity in giant vesicles with fluid phase coexistence. Biophys J 89:1067–1080
Bonito A, Nochetto RH, Pauletti MS (2010) Parametric FEM for geometric biomembranes. J Comput Phys 229:3171–3188
Campelo F, Hernandez-Machado A (2006) Dynamic model and stationary shapes of fluid vesicles. Eur Phys J E 20:37–45
Campelo F, Hernández-Machado A (2007) Model for curvature-driven pearling instability in membranes. Phys Rev Lett 99:088101
Cox G, Lowengrub J (2015) The effect of spontaneous curvature on a two-phase vesicle. Nonlinearity 28:773
Dimova R, Aranda S, Bezlyepkina N, Nikolov V, Riske KA, Lipowsky R (2006) A practical guide to giant vesicles. Probing the membrane nano regime via optical microscopy. J Phys Condens Matter 18:S1151
García-Sáez AJ, Chiantia S, Schwille P (2007) Effect of line tension on the lateral organization of lipid membranes. J Biol Chem 282:33537–33544
Givli S, Giang H, Bhattacharya K (2012) Stability of multicomponent biological membranes. SIAM J Appl Math 72:489–511
Haluska CK, Riske KA, Marchi-Artzner V, Lehn J-M, Lipowsky R, Dimova R (2006) Time scales of membrane fusion revealed by direct imaging of vesicle fusion with high temporal resolution. Proc Natl Acad Sci 103:15841–15846
Haußer F, Li S, Lowengrub J, Marth W, Rätz A, Voigt A (2013) Thermodynamically consistent models for two-component vesicles. IJBB 2:19–48
Hess ST, Gudheti MV, Mlodzianoski M, Baumgart T (2007) Shape analysis of giant vesicles with fluid phase coexistence by laser scanning microscopy to determine curvature, bending elasticity, and line tension Methods in membrane lipids. Springer, Berlin, pp 367–387
Ikonen E (2001) Roles of lipid rafts in membrane transport. Curr Opin Cell Biol 13:470–477
Jenkins J (1977) Static equilibrium configurations of a model red blood cell. J Math Biol 4:149–169
Jülicher F, Lipowsky R (1996) Shape transformations of vesicles with intramembrane domains. Phys Rev E 53:2670
Knorr RL, Dimova R, Lipowsky R (2012) Curvature of double-membrane organelles generated by changes in membrane size and composition. PloS One 7:e32753
Kuwert E, Schatzle R (2002) Gradient flow for the Willmore functional. Commun Anal Geom 10:307–339
Link F (2013) Gradient Flow for the Willmore functional in Riemannian manifolds of bounded geometry. arXiv preprint arXiv:13086055
Lipowsky R (1993) Domain-induced budding of fluid membranes. Biophys J 64:1133
Perko L (2013) Differential equations and dynamical systems, vol 7. Springer Science & Business Media, Berlin
Rahimi M, Arroyo M (2012) Shape dynamics, lipid hydrodynamics, and the complex viscoelasticity of bilayer membranes. Phys Rev E 86:011932
Riske K, Bezlyepkina N, Lipowsky R, Dimova R (2006) Electrofusion of model lipid membranes viewed with high temporal resolution. Biophys Rev Lett 1:387–400
Simons K, Ikonen E (1997) Functional rafts in cell membranes. Nature 387:569–572
Simons K, Vaz WL (2004) Model systems, lipid rafts, and cell membranes 1. Annu Rev Biophys Biomol Struct 33:269–295
Sohn JS, Tseng Y-H, Li S, Voigt A, Lowengrub JS (2010) Dynamics of multicomponent vesicles in a viscous fluid. J Comput Phys 229:119–144
Streets J (2012) The gradient flow of the L 2 curvature functional with small initial energy. J Geom Anal 22:691–725
Vequi-Suplicy CC, Riske KA, Knorr RL, Dimova R (2010) Vesicles with charged domains. Biochim et Biophys Acta (BBA) Biomembr 1798:1338–1347
Wang X, Du Q (2008) Modelling and simulations of multi-component lipid membranes and open membranes via diffuse interface approaches. J Math Biol 56:347–371
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sahebifard, M., Shahidi, A. & Ziaei-Rad, S. Two-phase vesicles: a study on evolutionary and stationary models. Eur Biophys J 46, 343–350 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00249-016-1177-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00249-016-1177-3