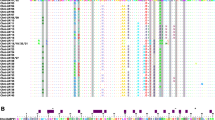
Abstract
In order to investigate the mechanisms creating and maintaining variability at the major histocompatibility (MH) class II alpha (DAA) locus we examined patterns of polymorphism in two isolated Atlantic salmon populations which share a common post-glacial origin. As expected from their common origin, but contrary to the observation at the MH class I locus, these populations shared the majority of DAA alleles: out of 17 sequences observed, 11 were common to both populations. Recombination seems to play a more important role in the origin of new alleles at the class II alpha locus than at the class I locus. A greater than expected proportion of sites inferred to be positively selected (potentially peptide binding residues, PBRs) were found to be involved in recombination events, suggesting a mechanism for increasing MH variability through an interaction between recombination and natural selection. Thus it appears that although selection and recombination are important mechanisms for the evolution of both class II alpha and class I loci in the Atlantic salmon, the pattern of variability differs markedly between these classes of MH loci.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anisimova M, Nielsen R, Yang Z (2003) Effect of recombination on the accuracy of the likelihood method for detecting positive selection at amino acid sites. Genetics 164:1229–1236
Apanius V, Penn D, Slev PR, Ruff LR, Potts WK (1997) The nature of selection on the major histocompatibility complex. Crit Rev Immunol 17:179–224
Belich MP, Madrigal JA, Hildebrand WH, Zemmour J, Williams RC, Luz R, Petzl-Erler ML, Parham P (1992) Unusual HLA-B alleles in two tribes of Brazilian Indians. Nature 357:326–329
Bernatchez L, Landry C (2003) MHC studies in non-model vertebrates:what have we learned about natural selection in 15 years? J Evol Biol 16:363–377
Bonneaud C, Sorci G, Morin V, Westerdahl H, Zoorob R, Wittzell H (2004) Diversity of MHC class I and IIB genes in house sparrows (Passer domesticus). Immunogenetics 55:855–865
Boyson JE, Shufflebotham C, Cadavid LF, Urvater JA, Knapp LA, Hughes AL, Watkins DI (1996) The MHC class I genes of the rhesus monkey. Different evolutionary histories of MHC class I and class II genes in primates. J Immunol 156:4656–4665
Brown JH, Jardetzky T, Saper MA, Samaraoui B, Bjorkman PJ, Wiley DC (1993) Three dimensional structure of the human class II histocompatibility molecules. Nature 364:33–39
Castellino F, Zhong G, Germain RN (1997) Antigen presentation by MHC class II molecules: invariant chain function, protein trafficking, and the molecular basis of diverse determinant capture. Hum Immunol 54:159–169
Edwards SV, Hedrick PW (1998) Evolution and ecology of MHC molecules: from genomics to sexual selection. Trends Ecol Evol 13:305–311
Felsenstein J (1989) PHYLIP-Phylogeny Inference Package (Version 32). Cladistics 5:164–166
Go YY, Satta Y, Kawamoto G, Rakotoarisoa A, Randrianjafy N, Koyama H, Hirai H (2003) Frequent segmental sequence exchanges and rapid gene duplication characterize the MHC class I genes in lemurs. Immunogenetics 55:450–461
Grassly NC, Holmes EC (1997) A likelihood method for the detection of selection and recombination using sequence data. Mol Biol Evol 14:239–247
Grimholt U, Hordvik I, Fosse VM, Olsaker I, Endresen C, Lie O (1993) Molecular cloning of major histocompatibilty complex class I cDNA from Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar). Immunogenetics 37:469–473
Grimholt U, Getahun A, Hermsen T, Stet RJ (2000) The major histocompatibility class II alpha chain in salmonid fishes. Dev Comp Immunol 24:751–763
Grimholt U, Drablös F, Jörgensen SM, Höyheim B, Stet RJM (2002) The major histocompatibility class I locus in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.): polymorphism, linkage analysis and protein modelling. Immunogenetics 54:570–581
Gromme M, Neefjes J (2002) Antigen degradation or presentation by MHC class I molecules via classical and non-classical pathways. Mol Immunol 39:181–202
Hambuch TM, Lacey EA (2002) Enhanced selection for mhc diversity in social tuco-tucos. Evolution 56:841–845
Hedrick PW (1999) Highly variable loci and their interpretations in evolution and conservation. Evolution 53:313–318
Hedrick PW (2002) Pathogen resistance and genetic variation at MHC loci. Evolution 56:1902–1908
Hewitt GM (1999) Post-glacial re-colonization of European biota. Biol J Linn Soc 68:87–112
Hoelzel AR, Stephens JC, O’Brien SJ (1999) Molecular genetic diversity and evolution at the MHC DQB locus in four species of pinnipeds. Mol Biol Evol 16:611–618
Housset D, Malissen B (2003) What do TCR-pMHC crystal structures teach us about MHC restriction and alloreactivity? Trends Immunol 24:429–437
Hudson RR, Kaplan NL (1985) Statistical properties of the number of recombination events in the history of a sample of DNA sequences. Genetics 111:147–164
Hughes AL, Nei M (1988) Pattern of nucleotide substitution at major histocompatibility complex class I loci reveals overdominant selection. Nature 335:167–170
Hughes AL, Nei M (1989) Nucleotide substitution at major histocompatibility complex class II loci: evidence for overdominant selection. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 86l:958–962
Hughes AL, Hughes MK, Howell CY, Nei M (1994) Natural selection at the class II major histocompatibility complex loci of mammals. Phil Trans R Soc Lond B 345:359–367
Huseby ES, Crawford F, White J, Kappler J, Marrack P (2003) Negative selection imparts peptide specificity to the mature T cell repertoire. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 20:11565–11570
Jordan WC, Bruford MW (1998) New perspectives on mate choice and the MHC. Heredity 81:127–133
Kaufman J, Salomonsen J, Flajnik M (1994) Evolutionary conservation of MHC class I and class II molecules -different yet the same. Semin Immunol 6:411–424
Kaufman J, Milne S, Gobel TWF, Walker BA, Jacob JP, Auffray C, Zoorob R, Beck S (1999) The chicken B locus is a minimal essential major histocompatibility complex. Nature 401:923–925
Kim TJ, Parker KM, Hedrick PW (1999) Major histocompatibility complex differentiation in Sacramento River Chinook salmon. Genetics 151:1115–1122
Klein J (1986) Natural history of the major histocompatibility complex. Wiley, New York
Klein J, O’Huigin C (1994) MHC polymorphism and parasites. Phil Trans R Soc Lond B 346:351–358
Kruiswijk CP (2002) Evolution of major histocompatibilitygenes in cyprinid fish. Molecular analyses and phylogenies. Dissertation, Wageningen University. ISBN 90-5808-735-2
Kumar S, Tamura K, Jakobsen IB, Nei M (2001) MEGA2: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis software. Bioinformatics 17:1244
Martinsohn JT, Sousa AB, Guethlein LA, Howard JC (1999) The gene conversion hypothesis of MHC evolution: a review. Immunogenetics 50:168–200
McVean G, Awadalla P, Fearnhead P (2002) A coalescent-based method for detecting and estimating recombination from gene sequences. Genetics 160:1231–1241
Nonaka M, Namikawa C, Kato Y, Sasaki M, Salter-Cid L, Flajnik MF (1997) Major histocompatibility complex gene mapping in the amphibian Xenopus implies a primordial organisation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94:5789–5791
Parham P, Ohta T (1996) Population biology of antigen presentation by MHC class I molecules. Science 272:67–74
Penn DJ, Damjanovich K, Potts WK (2002) MHC heterozygosity confers a selective advantage against multiple-strain infections. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:11260–11264
Posada D, Crandall KA (1998) MODELTEST: testing the model of DNA substitution. Bioinformatics 14:817–818
Reche PA, Reinherz EL (2003) Sequence variability analysis of human class I and class II MHC molecules: functional and structural correlates of amino acid polymorphisms. J Mol Biol 331:623–641
Rozas J, Rozas R (1999) DnaSP v3: an integrated program for molecular population genetics and molecular evolution analysis. Bioinformatics 15:174–175
Schierup MH, Hein J (2000) Consequences of recombination on traditional phylogenetic analysis. Genetics 156:879–891
Seddon JM, Ellegren H (2002) MHC class II genes in European wolves: a comparison with dogs. Immunogenetics 54:490–500
Shannon CE (1949) The mathematical theory of communication. University of Illinois Press, Urbana
Shum BP, Guethlein L, Flodin LR, Adkison MD, Hedrick RP, Nehring RB, Stet RJM, Secombes C, Parham P (2001) Modes of Salmonid MHC class I and II evolution differ from the primate paradigm. J Immunol 166:3297–3308
Stern L, Brown J, Jardetzky T, Gorga J, Urban R, Strominger J (1994) Crystal structure of the human class II MHC protein HLA-DR1 complexed with an influenza virus peptide. Nature 368:215–221
Stet RJM, de Vries B, Mudde K, Hermsen T, van Heerwaarden J, Shum BP, Grimholt U (2002) Unique haplotypes of co-segregating major histocompatibility. Immunogenetics 54:320–331
Stet RJM, Kruiswijk CP, Dixon B (2003) Major histocompatibility lineages and immune gene function in fish: the road not taken. Crit Rev Immunol 23:441–471
Stewart JJ, Lee CY, Ibrahim S, Watts P, Shlomick M, Weigert S, Litwin S (1997) A Shannon entropy analysis of immunoglobin and T cell receptor. Mol Immunol 34:1067–1082
Takahata N (1990) A simple genealogical structure of strongly balanced allelic lines and transspecies evolution of diversity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 87:2419–2423
Takahata N, Satta Y (1998) Selection, convergence, and intragenic recombination in HLA diversity. Genetica 102:320–331
Watkins DI, McAdam SN, Liu X, Strang CR, Milford EL, Levine CG, Garbert TL, Dogon AL, Lord CI, Ghim SH, Troup GM, Hughes AL, Letvin NL (1992) New recombinant HLA-B alleles in a tribe of South American Amerindians indicate rapid evolution of MHC class I loci. Nature 357:329–333
Yang Z (1997) PAML: a program package for phylogenetic analysis by maximum likelihood. CABIOS 13:555–556
Yang Z, Bielawski JP (2000) Statistical methods for detecting molecular adaptation. Trends Ecol Evol 15:496–503
Yang Z, Nielsen R, Goldman N, Pedersen AMK (2000) Codon-substitution models for heterogeneous selection pressure at amino acid sites. Genetics 155:431–449
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to Helmut Schaschl for technical guidance and Elvira De Eyto and Phil McGinnity for providing the samples on which this study is based. Funding was provided by a contract from the European Commission (SALIMPACT: QLRT-2000-01185)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Consuegra, S., Megens, H.J., Leon, K. et al. Patterns of variability at the major histocompatibility class II alpha locus in Atlantic salmon contrast with those at the class I locus. Immunogenetics 57, 16–24 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00251-004-0765-z
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00251-004-0765-z