Abstract
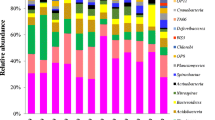
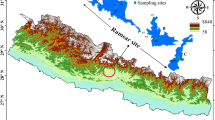
In this study, bacterial community structure in a horizontal subsurface flow constructed wetland (HSF-CW) planted with Phragmites australis was investigated using the 16S rRNA cloning–sequencing technique. Two layer depths were considered: the rhizosphere zone (RH) and the deep-layer zone (DL) in different sampling periods. Bacteria-specific primers 008F and 1492R were used to amplify the 16S rRNA genes and construct six clone libraries. A total of 1,284 individual sequences were used to assess the HSF-CW diversity. Phylogenetic analysis of RH and DL clone libraries shows that 41.57 and 42.17 % of the 16S rRNA sequences are affiliated with the Proteobacteria in the RH and the DL, respectively. The remaining major phylogenetic groups are Bacteroidetes, Planctomycetes, and Chloroflexi with 11.78, 9.36, and 7.6 %, respectively, in the RH and 11.38, 6.48, and 7.65 % in the DL, respectively. Minor divisions such as Verrucomicrobia, TM7, Nitrospira, and Gemmatimonadetes represented <6 % of the total sequences, while 14.2 % were unidentified Bacteria. Among the Proteobacteria, the Alphaproteobacteria subclass is represented in both locations, while the Deltaproteobacteria and Gammaproteobacteria subclasses were predominant in the RH and the DL, respectively. Results suggest that Archaea and Bacteria in the HSF-CW are the essential actors in the nitrogen cycle and that the established microbial community is efficient in nitrogen removal from wastewater.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
An DS, Im WT, Yang HC, Lee ST (2006) Shinella granuli gen. nov., sp. nov., and proposal of the reclassification of Zoogloea ramigera ATCC 19623 as Shinella zoogloeoides sp. nov. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 56:443–448
Artiguenave F, Wincker P, Brottier P, Dupart F, Scarpelli C, Verdier J, Vico V, Weissenbach J, Saurin W (2000) Genomic exploration of the hemiascomycetous yeast: 2. Data generation and processing. FEBS Lett 487:13–16
Bagge E, Persson M, Johansson KE (2010) Diversity of spore-forming Bacteria in cattle manure, slaughterhouse waste and samples from biogas plants. J Appl Microbiol 109:1549–1565
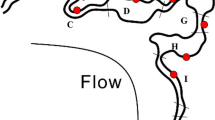
Bouali M, Zrafi NI, Bakhrouf A, Le Paslier D, Chaussonnerie S, Ammar E, Sghir A (2012) The structure and spatio-temporal distribution of the Archaea in a horizontal subsurface flow constructed wetland. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 435–436:465–471
Brummer IH, Felske AD, Wagner-Dobler I (2004) Diversity and seasonal changes of uncultured Planctomycetales in river biofilms. Appl Environ Microbiol 70:5094–5101
Calheiros SC, Teixeira A, Pires C, Franco AR, Duque AF, CrispimL FC, Moura SC, Castro PML (2010) Bacterial community dynamics in horizontal flow constructed wetlands with different plants for high salinity industrial wastewater polishing. Water Res 44:5032–5038
Caltheiros SC, Duque AF, Moura A, Henriques IS, Correia A, Rangel A, Castro PML (2009) Changes in the bacterial community structure in two-stage constructed wetlands with different plants for industrial wastewater treatment. Bioresource Technol 100:3228–3235
Chao A (1987) Estimating the population size for capture–recapture data with unequal catchability. Biometrics 43:783–791
Chen C, Ren N, Wang A, Liu L, Lee D (2010) Functional consortium for denitrifying sulfide removal process. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 86:353–358
Chouari R, Le Paslier D, Daegelen P, Ginestet P, Weissenbach J, Sghir A (2005) Novel predominant archaeal and bacterial groups revealed by molecular analysis of an anaerobic sludge digester. Environ microbiol 7:1104–1115
De Santis TZ, Hugenholtz P, Larsen N, Rojas M, Brodie EL, Keller K, Huber T, Dalevi D, Hu P, Andersen GL (2006) Greengenes, a chimera-checked 16S rRNA gene database and workbench compatible with ARB. Appl Environ Microbiol 72:5069–5072
Fernandez N, Sierra-Alvarez R, Field JA, Amils R, Sanz JL (2008) Microbial community dynamics in a chemolithotrophic denitrification reactor inoculated with methanogenic granular sludge. Chemosphere 70:462–474
Good IJ (1953) The population frequencies of species and the estimation of population parameters. Biometrika 40:237–264
Herrmann M, Saunders AM, Schramm A (2008) Archaea dominate the ammonia-oxidizing community in the rhizosphere of the freshwater macrophyte Littorella uniflora. Appl Environ Microbiol 74:3279–3283
Hicks RE, Amann RI, Stahl DA (1992) Dual staining of natural bacterioplankton with 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole and fluorescent oligonucleotide probes targeting kingdom level 16S rRNA sequences. Appl Environ Microbiol 58:2158–2163
Hughes JB, Hellmann JJ, Ricketts TH, Bohannan BM (2001) Counting the uncountable: statistical approaches to estimating microbial diversity. Appl Environ Microbiol 67:4399–4406
Humbert S, Tarnawski S, Fromin N, Mallet MP, Aragno M, Zopfi J (2010) Molecular detection of anammox Bacteria in terrestrial ecosystems: distribution and diversity. ISME J 4:450–454
Juretschko S, Loy A, Lehner A, Wagner M (2002) The microbial community composition of a nitrifying–denitrifying activated sludge from an industrial sewage treatment plant analyzed by the full-cycle rRNA approach. Syst Appl Microbiol 25:84–99
Kielak A, Pijl AS, van Veen JA, Kowalchuk GA (2009) Phylogenetic diversity of Acidobacteria in a former agricultural soil. ISME J 3:378–382
Knowles PR, Griffin P, Davies PA (2010) Complementary methods to investigate the development of clogging within a horizontal sub-surface flow tertiary treatment wetland. Water Res 44:320–330
Krasnitsa E, Friedlera E, Sabbahb I, Beliavski M, Tarrea S, Greena M (2009) Spatial distribution of major microbial groups in a well established constructed wetland treating municipal wastewater. Ecol Eng 35:1085–1089
Kulakov LA, McAlister MB, Ogden KL, Larkin MJ, O’Hanlon JF (2002) Analysis of bacteria contaminating ultrapure water in industrial systems. Appl Environ Microbiol 68:1548–1555
Kwon KK, Lee HS, Yang SH, Kim SJ (2005) Kordiimonas gwangyangensis gen. nov., sp. nov., a marine bacterium isolated from marine sediments that forms a distinct phylogenetic lineage (Kordiimonadales ord. nov.) in the ‘Alphaproteobacteria’. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 55:2033–2037
Lalucat J, Bennasar A, Bosch R, García-Valdês E, Palleroni JN (2006) Biology of Pseudomonas stutzeri. Microbiol Mol Biol R 70:510–547
Langergraber G (2007) Simulation of the treatment performance of outdoor subsurface flow constructed wetlands in temperate climates. Sci Total Environ 380:210–219
Li D, Yang M, Li Z, Qi R, He J, Liu H (2008) Change of bacterial communities in sediments along Songhua River in Northeastern China after a nitrobenzene pollution event. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 65:494–503
Magurran AE (1996) Ecological diversity and its measurement. Chapman and Hall, London, pp 274–286
Maszenan AM, Seviour RJ, Patel BKC (1998) The hunt for the G-bacteria in activated sludge biomass. Wat Sci Tech 37:65–69
Nellen-Anthamatten D, Rossi P, Preisig O, Kullik I, Babst M, Fischer HM, Hennecke H (1998) Bradyrhizobium japonicum, FixK2, a crucial distributor in the FixLJ-Dependent regulatory cascade for control of genes inducible by low oxygen levels. J. Bacteriol 180:5251–5255
Nogales B, Moore ER, Llobet-Brossa E, Rossello-Mora R, Amann R, Timmis KN (2001) Combined use of 16S ribosomal DNA and 16S rRNA to study the bacterial community of polychlorinated biphenyl-polluted soil. Appl Environ Microbiol 67:1874–1884
Quaiser A, Ochsenreiter T, Lanz C, Schuster SC, Treusch AH, Eck J, Schleper C (2003) Acidobacteria form a coherent but highly diverse group within the bacterial domain: evidence from environmental genomics. Mol Microbiol 50:563–575
Ragusa SR, McNevin D, Qasem S, Mitchell C (2004) Indicators of biofilm development and activity in constructed wetlands microcosms. Water Res 38:2865–2873
Richardson JL, Vepraskas MJ (2000) Wetland soils: genesis, hydrology, landscapes and classification. CRC, Boca Raton
Reichenbach H (1970) Nannocystis exedens gen. nov., spec. nov., a new myxobacterium of the family Sorangiaceae. Archiv für Mikrobiologie 70:119–138
Salmassi TM, Venkateswaren K, Satomi M, Newman DK, Hering JG (2002) Oxidation of arsenite by agrobacterium albertimagni, AOL15, sp. nov., Isolated from hot creek, California. Geomicrobiology J. 19:53–66
Schloss PD, Handelsman J (2005) Introducing DOTUR, a computer program for defining operational taxonomic units and estimating species richness. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:1501–1506
Schramm A, de Beer D, Wagner M, Amann R (1998) Identification and activity in situ of Nitrosospira and Nitrospira spp. as dominant populations in a nitrifying fluidized bed reactor. Appl and Environ Microbiol 64:3480–3485
Stapleton C, Anthony S, Crowther C, Gladstone M, Kay D, Proctor C, Wyer MD (2005) Assessment of point and diffuse sources of faecal indicators and nutrients in the Windermere and Crake catchments, Phase I scoping and desk study. CREH, IGES, Aberystwyth
Stottmeister U, Wiesner A, Kuschk P, Kappelmeyer U, Kastner M, Bederski O, Muller RA, Moormann H (2003) Effects of plants and microorganisms in constructed wetlands for wastewater treatment. Biotechnol Advances 22:93–117
Truu M, Juhanson J, Truu J (2009) Microbial biomass, activity and community composition in constructed wetlands. Sci Total Environ 407:3958–3971
Wang Y, Inamori R, Kong H, Xu K, Inamori Y, Kondo T, Zhang J (2008) Influence of plant species and wastewater strength on constructed wetland methane emissions and associated microbial populations. Ecol eng 32:22–29
Yamada T, Sekiguchi Y, Hanada S, Imachi H, Ohashi A, Harada H, Kamagata Y (2006) Anaerolinea thermolimosa sp. nov., Levilinea saccharolytica gen. nov., sp. nov. and Leptolinea tardivitalis gen. nov., sp. nov., novel filamentous anaerobes, and description of the new classes Anaerolineae classis nov. and Caldilineae classis nov. in the bacterial phylum Chloroflexi. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 56:1331–1340
Yi H, Chun J (2004) Nocardioides ganghwensis sp. nov., isolated from tidal flat sediment. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 54:1295–1299
Yoon JH, Lee CH, Oh TK (2005) Aeromicrobium alkaliterrae sp. nov., isolated from an alkaline soil, and emended description of the genus Aeromicrobium. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 55:2171–2175
Zhang CB, Wang J, Liu WL, Zhu SX, Ge HL, Chang SX, Chang J, Ge Y (2010) Effects of plant diversity on microbial biomass and community metabolic profiles in a full-scale constructed wetland. Ecol Eng 36:62–68
Zheng D, Alm EW, Stahl DA, Raskin L (1996) Characterization of universal small subunit rRNA hybridization probes for quantitative molecular microbial ecology studies. Appl Environ Microbiol 62:4504–4513
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bouali, M., Zrafi, I., Bakhrouf, A. et al. Bacterial structure and spatiotemporal distribution in a horizontal subsurface flow constructed wetland. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 98, 3191–3203 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-013-5341-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-013-5341-8