Abstract
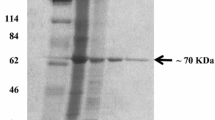
A highly active amide hydrolase (DamH) was purified from Delftia sp. T3-6 using ammonium sulfate precipitation, diethylaminoethyl anion exchange, hydrophobic interaction chromatography, and Sephadex G-200 gel filtration. The molecular mass of the purified enzyme was estimated to be 32 kDa by sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS)–polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. The sequence of the N-terminal 15 amino acid residues was determined to be Gly-Thr-Ser-Pro-Gln-Ser-Asp-Phe-Leu-Arg-Ala-Leu-Phe-Gln-Ser. Based on the N-terminal sequence and results of peptide mass fingerprints, the gene (damH) was cloned by PCR amplification and expressed in Escherichia coli BL21(DE3). DamH was a bifunctional hydrolase showing activity to amide and ester bonds. The specific activities of recombinant DamH were 5,036 U/mg for 2′-methyl-6′-ethyl-2- chloroacetanilide (CMEPA) (amide hydrolase function) and 612 U/mg for 4-nitrophenyl acetate (esterase function). The optimum substrate of DamH was CMEPA, with K m and k cat values of 0.197 mM and 2,804.32 s−1, respectively. DamH could also hydrolyze esters such as 4-nitrophenyl acetate, glycerol tributyrate, and caprolactone. The optimal pH and temperature for recombinant DamH were 6.5 and 35 °C, respectively; the enzyme was activated by Mn2+ and inhibited by Cu2+, Zn2+, Ni2+, and Fe2+. DamH was inhibited strongly by phenylmethylsulfonyl and SDS and weakly by ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid and dimethyl sulfoxide.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akutsu-Shigeno Y, Adachi Y, Yamada C, Toyoshima K, Nomura N, Uchiyama H, Nakajima-Kambe T (2006) Isolation of a bacterium that degrades urethane compounds and characterization of its urethane hydrolase. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 70(4):422–429
Arpigny J, Jaeger K (1999) Bacterial lipolytic enzymes: classification and properties. Biochem J 343:177–183
Bano S, Qader SAU, Aman A, Syed MN, Azhar A (2011) Purification and characterization of novel α-amylase from Bacillus subtilis KIBGE HAS. AAPS PharmSciTech 12(1):255–261
Bornscheuer UT (2002) Microbial carboxyl esterases: classification, properties and application in biocatalysis. FEMS Microbiol Rev 26(1):73–81
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72(1):248–254
Capel PD, Ma L, Schroyer BR, Larson SJ, Gilchrist TA (1995) Analysis and detection of the new corn herbicide acetochlor in river water and rain. Environ Sci Technol 29(6):1702–1705
Cheng Q, Thomas SM, Kostichka K, Valentine JR, Nagarajan V (2000) Genetic analysis of a gene cluster for cyclohexanol oxidation in Acinetobacter sp. strain SE19 by in vitro transposition. J Bacteriol 182(17):4744–4751
Coleman S, Linderman R, Hodgson E, Rose RL (2000) Comparative metabolism of chloroacetamide herbicides and selected metabolites in human and rat liver microsomes. Environ Health Perspect 108(12):1151–1157
Crump D, Werry K, Veldhoen N, Van Aggelen G, Helbing CC (2002) Exposure to the herbicide acetochlor alters thyroid hormone-dependent gene expression and metamorphosis in Xenopus Laevis. Environ Health Perspect 110(12):1199–1205
Dagnac T, Jeannot R, Mouvet C, Baran N (2002) Determination of oxanilic and sulfonic acid metabolites of acetochlor in soils by liquid chromatography–electrospray ionisation mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A 957(1):69–77
Dictor M-C, Baran N, Gautier A, Mouvet C (2008) Acetochlor mineralization and fate of its two major metabolites in two soils under laboratory conditions. Chemosphere 71(4):663–670
Dowd JE, Riggs DS (1965) A comparison of estimates of Michaelis–Menten kinetic constants from various linear transformations. J Biol Chem 240(2):863–869
El-Dib MA, Abdel-Rahman MO, Aly OA (1975) 4-Aminoantipyrine as a chromogenic agent for aromatic amine determination in natural water. Water Res 9(5):513–516
Grube A, Donaldson D, Kiely T, Wu L (2011) Pesticides industry sales and usage: 2006 and 2007 market estimates. In: Office of Chemical Safety and Pollution Prevention. US EPA, Washington
Hua N (2011) Amide herbicides formulations and their progress of R&D. Mod Agrochem 10(1):8–15
Ihara F, Kageyama Y, Hirata M, Nihira T, Yamada Y (1991) Purification, characterization, and molecular cloning of lactonizing lipase from Pseudomonas species. J Biol Chem 266(27):18135–18140
Jablonkai I (2000) Microbial and photolytic degradation of the herbicide acetochlor. Int J Environ Anal Chem 78(1):1–8
Janknecht R, de Martynoff G, Lou J, Hipskind RA, Nordheim A, Stunnenberg HG (1991) Rapid and efficient purification of native histidine-tagged protein expressed by recombinant vaccinia virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 88(20):8972–8976
Kaiser P, Raina C, Parshad R, Johri S, Verma V, Andrabi KI, Qazi GN (2006) A novel esterase from Bacillus subtilis (RRL 1789): purification and characterization of the enzyme. Protein Expr Purif 45(2):262–268
Khersonsky O, Roodveldt C, Tawfik DS (2006) Enzyme promiscuity: evolutionary and mechanistic aspects. Curr Opin Chem Biol 10(5):498–508
Kolkenbrock S, Parschat K, Beermann B, Hinz H-J, Fetzner S (2006) N-Acetylanthranilate amidase from Arthrobacter nitroguajacolicus Rü61a, an α/β-hydrolase-fold protein active towards aryl-acylamides and-esters, and properties of its cysteine-deficient variant. J Bacteriol 188(24):8430–8440
Kotresha D, Vidyasagar G (2008) Isolation and characterisation of phenol-degrading Pseudomonas aeruginosa MTCC 4996. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 24(4):541–547
Kourist R, Bartsch S, Fransson L, Hult K, Bornscheuer UT (2008) Understanding promiscuous amidase activity of an esterase from Bacillus subtilis. ChemBioChem 9(1):67–69
Laemmli UK (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227(5259):680–685
Liu Y, Whittier RF (1995) Thermal asymmetric interlaced PCR: automatable amplification and sequencing of insert end fragments from P1 and YAC clones for chromosome walking. Genomics 25(3):674–681
Liu Y, Zhang Y, Liu J, Huang D (2006) The role of reactive oxygen species in the herbicide acetochlor-induced DNA damage on Bufo raddei tadpole liver. Aquat Toxicol 78(1):21–26
Liu Z, Yang H, Huang Z, Zhou P, Liu S-J (2002) Degradation of aniline by newly isolated, extremely aniline-tolerant Delftia sp. AN3. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 58(5):679–682
Mayaux JF, Cerebelaud E, Soubrier F, Faucher D, Pétré D (1990) Purification, cloning, and primary structure of an enantiomer-selective amidase from Brevibacterium sp. strain R312: structural evidence for genetic coupling with nitrile hydratase. J Bacteriol 172(12):6764–6773
Mirza IA, Yachnin BJ, Wang S, Grosse S, Bergeron H, Imura A, Iwaki H, Hasegawa Y, Lau PCK, Berghuis AM (2009) Crystal structures of cyclohexanone monooxygenase reveal complex domain movements and a sliding cofactor. J Am Chem Soc 131(25):8848–8854
Nielsen TK, Hildmann C, Dickmanns A, Schwienhorst A, Ficner R (2005) Crystal structure of a bacterial class 2 histone deacetylase homologue. J Mol Biol 354(1):107–120
Norwitz G, Keliher PN (1980) Effect of acidity and alkalinity on the distillation of phenol: interferences of aromatic amines and formaldehyde with the 4-aminoantipyrine spectro-photometric method for phenol. Anal Chim Acta 119(1):99–111
Ohtaki A, Murata K, Sato Y, Noguchi K, Miyatake H, Dohmae N, Yamada K, Yohda M, Odaka M (2010) Structure and characterization of amidase from Rhodococcus sp. N-771: insight into the molecular mechanism of substrate recognition. BBA-Proteins Proteomics 1804(1):184–192
Patricelli MP, Lovato MA, Cravatt BF (1999) Chemical and mutagenic investigations of fatty acid amide hydrolase: evidence for a family of serine hydrolases with distinct catalytic properties. Biochemistry 38(31):9804–9812
Pohlenz H-D, Boidol W, Schüttke I, Streber WR (1992) Purification and properties of an Arthrobacter oxydans P52 carbamate hydrolase specific for the herbicide phenmedipham and nucleotide sequence of the corresponding gene. J Bacteriol 174(20):6600–6607
Rashamuse K, Magomani V, Ronneburg T, Brady D (2009) A novel family VIII carboxylesterase derived from a leachate metagenome library exhibits promiscuous β-lactamase activity on nitrocefin. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 83(3):491–500
Saha S, Dutta D, Karmakar R, Ray DP (2012) Structure–toxicity relationship of chloroacetanilide herbicides: relative impact on soil microorganisms. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 34(2):307–314
Sambrook J, Russell D (2001) Molecular cloning, a laboratory manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, Cold Spring Harbor
Schmidt M, Henke E, Heinze B, Kourist R, Hidalgo A, Bornscheuer UT (2007) A versatile esterase from Bacillus subtilis: cloning, expression, characterization, and its application in biocatalysis. Biotechnol J 2(2):249–253
Shen W, Chen H, Jia K, Ni J, Yan X, Li S (2012) Cloning and characterization of a novel amidase from Paracoccus sp. M-1, showing aryl acylamidase and acyl transferase activities. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 94(4):1007–1018
Shin S, Lee T-H, Ha N-C, Koo HM, Kim S-Y, Lee H-S, Kim YS, Oh B-H (2002) Structure of malonamidase E2 reveals a novel Ser-cisSer-Lys catalytic triad in a new serine hydrolase fold that is prevalent in nature. EMBO J 21(11):2509–2516
Syrén P-O, Hult K (2011) Amidases have a hydrogen bond that facilitates nitrogen inversion, but esterases have not. Chemcatchem 3(5):853–860
Terauchi R, Kahl G (2000) Rapid isolation of promoter sequences by TAIL-PCR: the 5′-flanking regions of Pal and Pgi genes from yams (Dioscorea). Mol Gen Genet 263(3):554–560
Van Beilen JB, Mourlane F, Seeger MA, Kovac J, Li Z, Smits TH, Fritsche U, Witholt B (2003) Cloning of Baeyer–Villiger monooxygenases from Comamonas, Xanthobacter and Rhodococcus using polymerase chain reaction with highly degenerate primers. Environ Microbiol 5(3):174–182
Wang J-L, Xu J-M, Wu Q, Lv D-S, Lin X-F (2009) Promiscuous enzyme-catalyzed regioselective Michael addition of purine derivatives to α, β-unsaturated carbonyl compounds in organic solvent. Tetrahedron 65(12):2531–2536
Weatherburn M (1967) Phenol-hypochlorite reaction for determination of ammonia. Anal Chem 39(8):971–974
Wei Y-L, Kurihara T, Suzuki T, Esaki N (2003) A novel esterase from a psychrotrophic bacterium, Acinetobacter sp. strain no. 6, that belongs to the amidase signature family. J Mol Catal B Enzym 23(2):357–365
Xiao N, Jing B, Ge F, Liu X (2006) The fate of herbicide acetochlor and its toxicity to Eisenia fetida under laboratory conditions. Chemosphere 62(8):1366–1373
Xu J, Qiu X, Dai J, Cao H, Yang M, Zhang J, Xu M (2006) Isolation and characterization of a Pseudomonas oleovorans degrading the chloroacetamide herbicide acetochlor. Biodegradation 17(3):219–225
Xu J, Yang M, Dai J, Cao H, Pan C, Qiu X, Xu M (2008) Degradation of acetochlor by four microbial communities. Bioresour Technol 99(16):7797–7802
Yasmin S, D'Souza D (2010) Effects of pesticides on the growth and reproduction of earthworm: a review. Appl Environ Soil Sci 2010(2010):1–9
Ye C, Wang X, Zheng H (2002) Biodegradation of acetanilide herbicides acetochlor and butachlor in soil. J Environ Sci China 14(4):524–529
Zafeiridou G, Geronikaki A, Papaefthimiou C, Tryfonos M, Kosmidis EK, Theophilidis G (2006) Assessing the effects of the three herbicides acetochlor, 2, 4, 5-trichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2, 4, 5-T) and 2, 4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid on the compound action potential of the sciatic nerve of the frog (Rana ridibunda). Chemosphere 65(6):1040–1048
Zhang J, Sun J-Q, Yuan Q-Y, Li C, Yan X, Hong Q, Li S-P (2011) Characterization of the propanil biodegradation pathway in Sphingomonas sp. Y57 and cloning of the propanil hydrolase gene prpH. J Hazard Mater 196:412–419
Zhang J, Yin J-G, Hang B-J, Cai S, He J, Zhou S-G, Li S-P (2012) Cloning of a novel arylamidase gene from Paracoccus sp. strain FLN-7 that hydrolyzes amide pesticides. Appl Environ Microbiol 78(14):4848–4855
Zhou Q-X, Zhang Q-R, Liang J-D (2006) Toxic effects of acetochlor and methamidophos on earthworm Eisenia fetida in phaiozem, northeast China. J Environ Sci-China 18(4):741–745
Acknowledgments
Grants from the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province, China (No. BK2012029), the Natural Science Foundation of China (31270095), and the National Science and Technology Support Program (2012BAD14B02) supported this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, F., Hou, Y., Zhou, J. et al. Purification of an amide hydrolase DamH from Delftia sp. T3-6 and its gene cloning, expression, and biochemical characterization. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 98, 7491–7499 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-014-5710-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-014-5710-y