Abstract
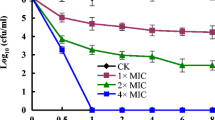
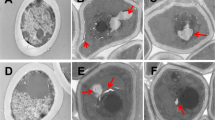
New anti-Candida albicans drugs are needed due to the emergence of resistant cases in recent years. Perillaldehyde (PAE) is a natural monoterpenoid compound derived from Perilla frutescens. The minimum inhibitory concentration of PAE against C. albicans was 0.4 μL/mL. We aimed to elucidate the antifungal mode of action of PAE against C. albicans. The antifungal activity of PAE against C. albicans was found to correlate with an elevation in intracellular Ca2+ and accumulation of ROS. Several downstream apoptosis events such as the disruption of mitochondrial membrane potential, phosphatidylserine externalization, cytochrome c release, and metacaspase activation were observed in PAE-treated cells. DNA damage and nuclear fragmentation assays also revealed apoptosis of C. albicans cells. In summary, by means of fluorescent microscopy, flow cytometer analysis, and Western blot, our data uncovered that PAE exerts its antifungal activity through Ca2+ and oxidative stress-mediated apoptosis mechanisms. This study deciphered the mode of action of PAE, which will be useful in the design of improved antifungal therapies.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amin S, Mousavi A, Robson GD (2004) Oxidative and amphotericin B-mediated cell death in the opportunistic pathogen Aspergillus fumigatus is associated with an apoptotic-like phenotype. Microbiology-Sgm 150(6):1937–1945
Atanasov AG, Waltenberger B, Pferschy-Wenzig EM, Linder T, Wawrosch C, Uhrin P, Temml V, Wang LM, Schwaiger S, Heiss EH, Rollinger JM, Schuster D, Breuss JM, Bochkov V, Mihovilovic MD, Kopp B, Bauer R, Dirsch VM, Stuppner H (2015) Discovery and resupply of pharmacologically active plant-derived natural products: a review. Biotechnol Adv 33(8):1582–1614
Barroso G, Taylor S, Morshedi M, Manzur F, Gavino F, Oehninger S (2006) Mitochondrial membrane potential integrity and plasma membrane translocation of phosphatidylserine as early apoptotic markers: a comparison of two different sperm subpopulations. Fertil Steril 85(1):149–154
Benaroudj N, Lee DH, Goldberg AL (2001) Trehalose accumulation during cellular stress protects cells and cellular proteins from damage by oxygen radicals. J Biol Chem 276(26):24261–24267
Buttner S, Eisenberg T, Carmona-Gutierrez D, Ruli D, Knauer H, Ruckenstuhl C, Sigrist C, Wissing S, Kollroser M, Frohlich KU, Sigrist S, Madeo F (2007) Endonuclease G regulates budding yeast life and death. Mol Cell 25(2):233–246
Cao YY, Huang S, Dai BD, Zhu ZY, Lu H, Dong LL, Cao YB, Wang Y, Gao PH, Chai YF, Jiang YY (2009) Candida albicans cells lacking CaMCA1-encoded metacaspase show resistance to oxidative stress-induced death and change in energy metabolism. Fungal Genet Biol 46(2):183–189
Chen WJ, Yu C, Yang Z, He JL, Yin J, Liu HZ, Liu HT, Wang YX (2012) Tubeimoside-1 induces G2/M phase arrest and apoptosis in SKOV-3 cells through increase of intracellular Ca2+ and caspase-dependent signaling pathways. Int J Oncol 40(2):535–543
Cheng JJ, Park TS, Chio LC, Fischl AS, Ye XS (2003) Induction of apoptosis by sphingoid long-chain bases in Aspergillus nidulans. Mol Cell Biol 23(1):163–177
Cheng XL, Zhang WQ, Ji YL, Meng J, Guo H, Liu J, Wu XC, Xu HY (2013) Revealing silver cytotoxicity using Au nanorods/Ag shell nanostructures: disrupting cell membrane and causing apoptosis through oxidative damage. RSC Adv 3(7):2296–2305
Cho J, Lee DG (2011) The antimicrobial peptide arenicin-1 promotes generation of reactive oxygen species and induction of apoptosis. Biochim Biophys Acta 1810(12):1246–1251
Collins JA, Schandl CA, Young KK, Vesely J, Willingham MC (1997) Major DNA fragmentation is a late event in apoptosis. J Histochem Cytochem 45(7):923–934
Daniel B, DeCoster MA (2004) Quantification of sPLA(2)-induced early and late apoptosis changes in neuronal cell cultures using combined TUNEL and DAPI staining. Brain Res Protocol 13(3):144–150
Dobrucki J, Darzynkiewicz Z (2001) Chromatin condensation and sensitivity of DNA in situ to denaturation during cell cycle and apoptosis—a confocal microscopy study. Micron 32(7):645–652
Frey TG, Mannella CA (2000) The internal structure of mitochondria. Trends Biochem Sci 25(7):319–324
Gavrieli Y, Sherman Y, Ben-Sasson SA (1992) Identification of programmed cell death in situ via specific labeling of nuclear DNA fragmentation. J Biol 119(3):493–501
Gogvadze V, Orrenius S (2006) Mitochondrial regulation of apoptotic cell death. Chem Biol Interact 163(1–2):4–14
Hwang JH, Hwang IS, Liu QH, Woo ER, Lee DG (2012) (+)-Medioresinol leads to intracellular ROS accumulation and mitochondria-mediated apoptotic cell death in Candida albicans. Biochimie 94(8):1784–1793
Kobayashi D, Kondo K, Uehara N, Otokozawa S, Tsuji N, Yagihashi A, Watanabe N (2002) Endogenous reactive oxygen species is an important mediator of miconazole antifungal effect. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 46(10):3113–3117
Kruman I, Guo Q, Mattson MP (1998) Calcium and reactive oxygen species mediate staurosporine-induced mitochondrial dysfunction and apoptosis in PC12 cells. J Neurosci Res 51(3):293–308
Lee J, Hwang JS, Hwang IS, Cho J, Lee E, Kim Y, Lee DG (2012) Coprisin-induced antifungal effects in Candida albicans correlate with apoptotic mechanisms. Free Radic Biol Med 52(11–12):2302–2311
Lu Y, Su C, Liu HP (2014) Candida albicans hyphal initiation and elongation. Trends Microbiol 22(12):707–714
Machida K, Tanaka T, Fujita KI, Taniguchi M (1998) Farnesol-induced generation of reactive oxygen species via indirect inhibition of the mitochondrial electron transport chain in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Bacteriol 180(17):4460–4465
Madeo F, Frohlich E, Frohlich KU (1997) A yeast mutant showing diagnostic markers of early and late apoptosis. J Cell Biol 139(3):729–734
Madeo F, Herker E, Maldener C, Wissing S, Lachelt S, Herlan M, Fehr M, Lauber K, Sigrist SJ, Wesselborg S, Frohlich KU (2002) A caspase-related protease regulates apoptosis in yeast. Mol Cell 9(4):911–917
Mallick S, Dey S, Mandal S, Dutta A, Mukherjee D, Biswas G, Chatterjee S, Mallick S, Lai TK, Acharya K, Pal C (2015) A novel triterpene from Astraeus hygrometricus induces reactive oxygen species leading to death in Leishmania donovani. Future Microbiol 10(5):763–789
Maurya IK, Thota CK, Sharma J, Tupe SG, Chaudhary P, Singh MK, Thakur IS, Deshpande M, Prasad R, Chauhan VS (2013) Mechanism of action of novel synthetic dodecapeptides against Candida albicans. Biochim Biophys Acta 1830(11):5193–5203
Munoz AJ, Wanichthanarak K, Meza E, Petranovic D (2012) Systems biology of yeast cell death. FEMS Yeast Res 12(2):249–265
Pinto E, Hrimpeng K, Lopes G, Vaz S, Goncalves MJ, Cavaleiro C, Salgueiro L (2013) Antifungal activity of Ferulago capillaris essential oil against Candida, Cryptococcus, Aspergillus and dermatophyte species. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 32(10):1311–1320
Pushpanathan M, Gunasekaran P, Rajendhran J (2013) Mechanisms of the antifungal action of marine metagenome-derived peptide, MMGP1, against Candida albicans. PLoS ONE 8(7)
Sen Gupta S, Ton VK, Beaudry V, Rulli S, Cunningham K, Rao R (2003) Antifungal activity of amiodarone is mediated by disruption of calcium homeostasis. J Biol Chem 278(31):28831–28839
Sharon A, Finkelstein A, Shlezinger N, Hatam I (2009) Fungal apoptosis: function, genes and gene function. FEMS Microbiol Rev 33(5):833–854
Tian J, Ban XQ, Zeng H, He JS, Chen YX, Wang YW (2012) The mechanism of antifungal action of essential oil from dill (Anethum graveolens L.) on Aspergillus flavus. PLoS ONE 7(1)
Tian J, Zeng XB, Zhang S, Wang YZ, Zhang P, Lu AJ, Peng X (2014) Regional variation in components and antioxidant and antifungal activities of Perilla frutescens essential oils in China. Ind Crop and Prod 59:69–79
Tian J, Wang YZ, Zeng H, Li ZY, Zhang P, Tessema A, Peng X (2015a) Efficacy and possible mechanisms of perillaldehyde in control of Aspergillus niger causing grape decay. Int J Food Microbiol 202(2):27–34
Tian J, Zeng XB, Lu AJ, Zhu AH, Peng X, Wang YW (2015b) Perillaldehyde, a potential preservative agent in foods: assessment of antifungal activity against microbial spoilage of cherry tomatoes. Lwt-Food Sci Technol 60(1):63–70
Tian J, Wang YZ, Lu ZQ, Sun CH, Zhang M, Zhu AH, Peng X (2016) Perillaldehyde, a promising antifungal agent used in food preservation, triggers apoptosis through a metacaspase-dependent pathway in Aspergillus flavus. J Agric Food Chem 64(39):7404–7413
Wang C, Youle RJ (2009) The role of mitochondria in apoptosis. Annu Rev Genet 43:95–118
Wu XZ, Chang WQ, Cheng AX, Sun LM, Lou HX (2010) Plagiochin E, an antifungal active macrocyclic bis(bibenzyl), induced apoptosis in Candida albicans through a metacaspase-dependent apoptotic pathway. Biochim Biophys Acta 1800(4):439–447
Yun DG, Lee DG (2016) Silibinin triggers yeast apoptosis related to mitochondrial Ca2+ influx in Candida albicans. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 80:1–9
Acknowledgements
This study was funded by National Natural Science Foundation of China (31671944, 31301585), Qing Lan Project of Jiangsu Province, National Undergraduate Training Programs for Innovation and Entrepreneurship (201610320027), Xinjiang Production & Construction Crops, Key Laboratory of Protection and Utilization of Biological Resources in Tarim Basin (BRZD1502), China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2016M600678), the Industry-University-Academy Prospective Joint Research Project of Jiangsu Province (BY2016028-01), and the PAPD of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Hui Tian and Su Qu contributed equally to this work
An erratum to this article is available at http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00253-017-8217-5.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tian, H., Qu, S., Wang, Y. et al. Calcium and oxidative stress mediate perillaldehyde-induced apoptosis in Candida albicans . Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 101, 3335–3345 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-017-8146-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-017-8146-3