Abstract
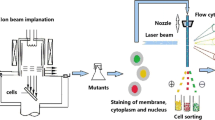
Avermectins, produced by Streptomyces avermitilis, are important antiparasitic agents. The use of traditional microbial breeding methods for this organism has been limited by the low-throughput shake flask-based screening process. The unique growth cycle of actinomycetes makes the establishment of a reliable high-throughput screening (HTS) process difficult. To enhance the efficiency of screening strains with high yields of avermectin, a HTS process aided by fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS) was established. Four different spore solutions were investigated for maintaining a relatively high viability of spores. Propidium iodide (PI) and fluorescein diacetate (FDA) were used to discriminate between dead and live spores using the FACS system. Spores stained with 7-μg/mL PI and 15-μg/mL FDA at 4 °C in the dark for 30 min resulted in optimum sorting. Spores were treated by atmospheric and room temperature plasma (ARTP). Single live spores were sorted and sprayed into 96-well microtiter plates containing 50 μL of solid agar culture medium. Solid-liquid combinatorial microculture was used for high-throughput avermectin culture. A high-titer avermectin producer (G9) was obtained from 5760 mutants after mutagenesis and HTS. Compared with the original strain, the titer was improved by 18.9% on flask culture and 20.6% on fermenter, respectively. The HTS process established in this study could easily be transferred to other similar target products produced by actinomycetes.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Blum A, Benfield AH, Stiller J, Kazan K, Batley J, Gardiner DM (2016) High-throughput FACS-based mutant screen identifies a gain-of-function allele of the Fusarium graminearum adenylyl cyclase causing deoxynivalenol over-production. Fungal genetics and biology : FG & B 90:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fgb.2016.02.005
Bougaran G, Rouxel C, Dubois N, Kaas R, Grouas S, Lukomska E, Le JR, Cadoret JP (2012) Enhancement of neutral lipid productivity in the microalga Isochrysis affinis Galbana (T-Iso) by a mutation-selection procedure. Biotechnol Bioeng 109(11):2737–2745. https://doi.org/10.1002/bit.24560
Bradley J, Gill J, Bertelli F, Letafat S, Corbau R, Hayter P, Harrison P, Tee A, Keighley W, Perros M, Ciaramella G, Sewing A, Williams C (2004) Development and automation of a 384-well cell fusion assay to identify inhibitors of CCR5/CD4-mediated HIV virus entry. J Biomol Screen 9(6):516–524. https://doi.org/10.1177/1087057104264577
Brandish PE, Chiu CS, Schneeweis J, Brandon NJ, Leech CL, Kornienko O, Scolnick EM, Strulovici B, Zheng W (2006) A cell-based ultra-high-throughput screening assay for identifying inhibitors of D-amino acid oxidase. J Biomol Screen 11(5):481–487. https://doi.org/10.1177/1087057106288181
Chen Z, Wen J, Song Y, Wen Y, Li JL (2007) Enhancement and selective production of avermectin B by recombinants of Streptomyces avermitilis via intraspecific protoplast fusion. Chin Sci Bull 52(5):616–622. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-007-0119-y
Cousin A, Heel K, Cowling WA, Nelson MN (2009) An efficient high-throughput flow cytometric method for estimating DNA ploidy level in plants. Cytometry Part A: the Journal of the International Society for Analytical Cytology 75(12):1015–1019. https://doi.org/10.1002/cyto.a.20816
Doan TY, Philip OJ (2012) Enhanced intracellular lipid in Nannochloropsis sp. via random mutagenesis and flow cytometric cell sorting. Algal Res 1(1):17–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.algal.2012.03.001
Eun YJ, Utada AS, Copeland MF, Takeuchi S, Weibel DB (2011) Encapsulating bacteria in agarose microparticles using microfluidics for high-throughput cell analysis and isolation. ACS Chem Biol 6(3):260–266. https://doi.org/10.1021/cb100336p
Galbraith DW, Harkins KR, Maddox JM, Ayres NM, Sharma DP, Firoozabady E (1983) Rapid flow cytometric analysis of the cell cycle in intact plant tissues. Science 220(4601):1049–1051. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.220.4601.1049
Héctor MG, Adelina V, Karen FP, Laura CD (2012) Quick estimation of intraspecific variation of fatty acid composition in Dunaliella salina using flow cytometry and Nile Red. J Appl Phycol 24(5):1237–1243. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-011-9768-y
Ikeda H (1982) The avermectins: a new family of antiparasitic agents. J S Afr Vet Assoc 53:87–90
Ikeda H, Nonomiya T, Ōmura S (2001) Organization of biosynthetic gene cluster for avermectin in Streptomyces avermitilis: analysis of enzymatic domains in four polyketide synthases. Journal of Industrial Microbiology &Biotechnology 27:170–176
Ikeda H, Ishikawa J, Hanamoto A, Shinose M, Kikuchi H, Shiba T, Sakaki Y, Hattori M, Omura S (2003) Complete genome sequence and comparative analysis of the industrial microorganism Streptomyces avermitilis. Nat Biotechnol 21(5):526–531. https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt820
Ikeda H, Ōmura S (1997) Avermectin biosynthesis. Chem Rev 97(7):2591–2610. https://doi.org/10.1021/cr960023p
Lee JH, Lee SH, Yim SS, Kang KH, Lee SY, Park SJ, Jeong KJ (2013) Quantified high-throughput screening of Escherichia coli producing poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) based on FACS. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 170(7):1767–1779. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-013-0311-2
Li M, Chen Z, Zhang X, Song Y, Wen Y, Li JL (2010) Enhancement of avermectin and ivermectin production by overexpression of the maltose ATP-binding cassette transporter in Streptomyces avermitilis. Bioresour Technol 101(23):9228–9235. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2010.06.132
Lim DKY, Schuhmann H, Sharma K, Schenk PM (2014) Isolation of high-lipid Tetraselmis suecica strains following repeated UV-C mutagenesis, FACS, and high-throughput growth selection. BioEnergy Research 8(2):750–759. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12155-014-9553-2
Liu Y, Xue ZL, Chen SP, Wang Z, Zhang Y, Gong WL, Zheng ZM (2016) A high-throughput screening strategy for accurate quantification of menaquinone based on fluorescence-activated cell sorting. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 43(6):751–760. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-016-1757-3
Lu Y, Wang LY, Ma K, Li G, Zhang C, Zhao HX, Lai QH, Li HP, Xing XH (2011) Characteristics of hydrogen production of an Enterobacter aerogenes mutant generated by a new atmospheric and room temperature plasma (ARTP). Biochem Eng J 55(1):17–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bej.2011.02.020
Luo ZS, Zeng WZ, GC D, Liu S, Fang F, Zhou JW, Chen J (2017) A high-throughput screening procedure for enhancing pyruvate production in Candida glabrata by random mutagenesis. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 40(5):693–701. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-017-1734-x
Mattanovich D (2006) Applications of cell sorting in biotechnology. Microb Cell Factories 5(1):12. https://doi.org/10.1186/1475-2859-5-12
Montero MF, Aristizábal M, Reina GG (2011) Isolation of high lipid-content strains of the marine microalgae Tetraselmis suecica for biodiesel production by flow cytometry and single-cell sorting. J Appl Phycol 23(6):1053–1057. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-010-9623-6
Mustafi N, Grünberger A, Kohlheyer D, Bott M, Frunzke J (2012) The development and application of a single-cell biosensor for the detection of l-methionine and branched-chain amino acids. Metab Eng 14(4):449–457. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymben.2012.02.002
Qiu JF, Zhuo Y, Zhu DQ, Zhou XF, Zhang LX, Bai LQ, Deng ZX (2011) Overexpression of the ABC transporter AvtAB increases avermectin production in Streptomyces avermitilis. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 92(2):337–345. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-011-3439-4
Shi L, Chen XS, Tang WY, Li ZY, Liu J, Gao F, Sang JL (2014) Combination of FACS and homologous recombination for the generation of stable and high-expression engineered cell lines. PLoS One 9(3):e91712. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0091712
Siddique S, Syed Q, Adnan A, Qureshi FA (2014a) Production and screening of high yield avermectin B1b mutant of Streptomyces avermitilis 41445 through mutagenesis. Jundishapur journal of microbiology 7(2):e8626. https://doi.org/10.5812/jjm.8626
Siddique S, Nelofer R, Syed Q, Adnan A, Qureshi FA (2014b) Optimization for the enhanced production of avermectin B1b from Streptomyces avermitilis DSM 41445 using artificial neural network. Journal of the Korean Society for Applied Biological Chemistry 57(5):677–683. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13765-014-4194-x
Takeda H, Yamakuchi H, Ihara N, Hara K, Watanabe T, Sugimoto Y, Oshiro T, Kishine H, Kano Y, K K (1998) Construction of a bovine yeast artificial chromosome (YAC) library. Anim Genet 29:216–219, 3, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2052.1998.00325.x
Thuan NH, Pandey RP, Sohng JK (2014) Recent advances in biochemistry and biotechnological synthesis of avermectins and their derivatives. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 98(18):7747–7759. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-014-5926-x
Wang HY, Zhang J, Zhang YJ, Zhang B, Liu CX, He HR, Wang XJ, Xiang WS (2014) Combined application of plasma mutagenesis and gene engineering leads to 5-oxomilbemycins A3/A4 as main components from Streptomyces bingchenggensis. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 98(23):9703–9712. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-014-5970-6
Wang LY, Huang ZL, Li G, Zhao HX, Xing XH, Sun WT, Li HP, Gou ZX, Bao CY (2010) Novel mutation breeding method for Streptomyces avermitilis using an atmospheric pressure glow discharge plasma. J Appl Microbiol 108(3):851–858. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2672.2009.04483.x
Wolstenholme AJ, Rogers AT (2005) Glutamate-gated chloride channels and the mode of action of the avermectin/milbemycin anthelmintics. Parasitology 131(Suppl):S85–S95. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0031182005008218
Wunder F, Stasch JP, Hutter J, Alonso AC, Huser J, Lohrmann E (2005) A cell-based cGMP assay useful for ultra-high-throughput screening and identification of modulators of the nitric oxide/cGMP pathway. Anal Biochem 339(1):104–112. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ab.2004.12.025
Yang G, Rich JR, Gilbert M, Wakarchuk WW, Feng Y, Withers SG (2010) Fluorescence activated cell sorting as a general ultra-high-throughput screening method for directed evolution of glycosyltransferases. J Am Chem Soc 132(30):10570–10577. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja104167y
Zeng WZ, GC D, Chen J, Li JH, Zhou JW (2015) A high-throughput screening procedure for enhancing α-ketoglutaric acid production in Yarrowia lipolytica by random mutagenesis. Process Biochem 50(10):1516–1522. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2015.06.011
Zhang X, Zhang C, Zhou QQ, Zhang XF, Wang LY, Chang HB, Li HP, Oda Y, Xing XH (2015) Quantitative evaluation of DNA damage and mutation rate by atmospheric and room-temperature plasma (ARTP) and conventional mutagenesis. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 99(13):5639–5646. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-015-6678-y
Zhang X, Zhang XF, Li HP, Wang LY, Zhang C, Xing XH, Bao CY (2014) Atmospheric and room temperature plasma (ARTP) as a new powerful mutagenesis tool. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 98(12):5387–5396. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-014-5755-y
Zhuo Y, Zhang T, Wang Q, Cruz MP, Zhang B, Liu M, Barona G, F., Zhang L (2014) Synthetic biology of avermectin for production improvement and structure diversification. Biotechnol J 9(3):316–325 doi:https://doi.org/10.1002/biot.201200383
Funding
This work was supported by the Major State Basic Research Development Program of China (973 Program, 2013CB733602), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (21390204, 21406087), the Key Research and Development Program of Jiangsu Province (BE2016689), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (JUSRP51701A), the Six Talent Peaks Project in Jiangsu Province (2015-JY-005), the Distinguished Professor Project of Jiangsu Province, and the 111 Project (111-2-06).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 76 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cao, X., Luo, Z., Zeng, W. et al. Enhanced avermectin production by Streptomyces avermitilis ATCC 31267 using high-throughput screening aided by fluorescence-activated cell sorting. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 102, 703–712 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-017-8658-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-017-8658-x