Abstract
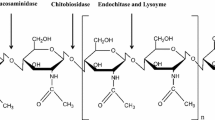
A range of chitinase genes from microorganisms have been cloned and the potential uses of these genetically manipulated organisms are being investigated by various researchers. Fungi and yeast are better producers of chitinase than bacteria. Since fungi grow at a slower rate, there have been efforts to clone the fungal chitinase genes into fast-growing bacteria. This review gives a brief survey of recent progress in the regulation and cloning of microbial chitinase genes. Emphasis is placed on the post-translational modification and localization of the recombinant protein in the host. Various amino acid domains are present in this protein. The mode of catalytic activity of the recombinant protein in comparison to the wild-type protein is discussed in the available literature. The different mechanisms involved in the regulation of chitinase genes from various microorganisms is discussed by the researchers. The scope of future research and conclusions yet to be obtained in this particular area are also outlined in this review.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 13 July 1998 / Received revision: 28 October 1998 / Accepted: 30 October 1998
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Felse, P., Panda, T. Regulation and cloning of microbial chitinase genes. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 51, 141–151 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002530051374
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002530051374